本篇文章为大家展示了如何在Java中使用Property类,内容简明扼要并且容易理解,绝对能使你眼前一亮,通过这篇文章的详细介绍希望你能有所收获。
概念理解
Properties 继承于 Hashtable。表示一个持久的属性集,属性列表以key-value的形式存在,key和value都是字符串。Properties类被许多Java类使用。例如,在获取环境遍历时它就作为System.getProperties()方法的返回值。我们在很多需要避免硬编码的应用场景下需要使用Properties文件来加载程序需要配置的信息,比如JDBC、MyBatis框架等。Properties类则是Properties文件和程序的中间桥梁,不论是从properties文件读取信息还是写入信息到properties文件都要经由Properties类。
写入
Properties类调用setProperty方法将键值对保存到内存中,此时可以通过getProperty方法读取,propertyNames方法进行遍历,但是并没有将键值对持久化到属性文件中,故需要调用store方法持久化键值对到属性文件中。
我们写一个类测试
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.OutputStream;
import java.util.Date;
import java.util.Properties;
public class TestProperties {
public void writeProperties() {
Properties properties = new Properties();
OutputStream output = null;
try {
output = new FileOutputStream("config.properties");
properties.setProperty("url", "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/");
properties.setProperty("username", "root");
properties.setProperty("password", "root");
properties.setProperty("databases", "music_player");
properties.store(output, "Steven1997 modify" + new Date().toString());
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
if(output!=null) {
try {
output.close();
}catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
TestProperties t = new TestProperties();
t.writeProperties();
}
}执行后,工程下面会出现一个config.properties文件,属性文件内容如下:
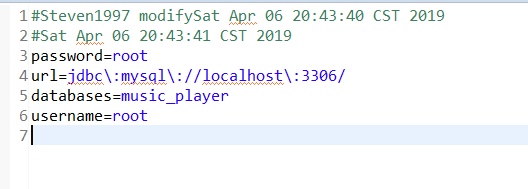
读取
使用getProperty获取config.properties文件配置文件的各项属性。
package property;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.util.Properties;
public class LoadProperties {
public void loadProperties() {
Properties properties = new Properties();
InputStream inputStream = null;
try {
inputStream = new FileInputStream("config.properties");
properties.load(inputStream);
System.out.println("url:" + properties.getProperty("url"));
System.out.println("username:" + properties.getProperty("username"));
System.out.println("password:" + properties.getProperty("password"));
System.out.println("database:" + properties.getProperty("database"));
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
if(inputStream !=null) {
try {
inputStream.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
LoadProperties l = new LoadProperties();
l.loadProperties();
}
}运行后的结果
url:jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/
username:root
password:root
database:music_player
遍历
遍历属性文件中的键值对
package property;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.util.Enumeration;
import java.util.Map.Entry;
import java.util.Properties;
import java.util.Set;
public class PropertiesTest {
public void printAll() {
Properties prop = new Properties();
InputStream input = null;
try {
String file = "config.properties";
input = getClass().getClassLoader().getResourceAsStream(file);
if(input == null) {
System.out.println("无法加载文件" + file);
return ;
}
prop.load(input);
// 方法一
Set<Object> keys = prop.keySet();
for(Object key:keys) {
System.out.println("key:" + key.toString() + "|" + "value:" + prop.get(key));
}
//方法二:
Set<Entry<Object, Object>> entrys = prop.entrySet();//返回的属性键值对实体
for(Entry<Object, Object> entry:entrys){
System.out.println("key:"+entry.getKey()+",value:"+entry.getValue());
}
//方法三:
Enumeration<?> e = prop.propertyNames();
while (e.hasMoreElements()) {
String key = (String) e.nextElement();
String value = prop.getProperty(key);
System.out.println("Key:" + key + ",Value:" + value);
}
}catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
if(input != null) {
try {
input.close();
}catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
PropertiesTest p = new PropertiesTest();
p.printAll();
}
}运行结果如下:
key:url|value:jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/
key:password|value:root
key:database|value:music_player
key:username|value:root
key:url,value:jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/
key:password,value:root
key:database,value:music_player
key:username,value:root
Key:password,Value:root
Key:url,Value:jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/
Key:database,Value:music_player
Key:username,Value:root
Java的基本数据类型分为:1、整数类型,用来表示整数的数据类型。2、浮点类型,用来表示小数的数据类型。3、字符类型,字符类型的关键字是“char”。4、布尔类型,是表示逻辑值的基本数据类型。
上述内容就是如何在Java中使用Property类,你们学到知识或技能了吗?如果还想学到更多技能或者丰富自己的知识储备,欢迎关注亿速云行业资讯频道。
亿速云「云服务器」,即开即用、新一代英特尔至强铂金CPU、三副本存储NVMe SSD云盘,价格低至29元/月。点击查看>>
免责声明:本站发布的内容(图片、视频和文字)以原创、转载和分享为主,文章观点不代表本网站立场,如果涉及侵权请联系站长邮箱:is@yisu.com进行举报,并提供相关证据,一经查实,将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容。