这篇文章将为大家详细讲解有关Spring Boot中如何实现静态资源处理,文章内容质量较高,因此小编分享给大家做个参考,希望大家阅读完这篇文章后对相关知识有一定的了解。
默认资源映射
我们在启动应用的时候,可以在控制台中看到如下信息:
2016-01-08 09:29:30.362 INFO 24932 --- [ main] o.s.w.s.handler.SimpleUrlHandlerMapping : Mapped URL path [/webjars/**] onto handler of type [class org.springframework.web.servlet.resource.ResourceHttpRequestHandler] 2016-01-08 09:29:30.362 INFO 24932 --- [ main] o.s.w.s.handler.SimpleUrlHandlerMapping : Mapped URL path [/**] onto handler of type [class org.springframework.web.servlet.resource.ResourceHttpRequestHandler] 2016-01-08 09:29:30.437 INFO 24932 --- [ main] o.s.w.s.handler.SimpleUrlHandlerMapping : Mapped URL path [/**/favicon.ico] onto handler of type [class org.springframework.web.servlet.resource.ResourceHttpRequestHandler]
其中默认配置的 /** 映射到 /static (或/public、/resources、/META-INF/resources)
其中默认配置的 /webjars/** 映射到 classpath:/META-INF/resources/webjars/
PS:上面的 static、public、resources 等目录都在 classpath: 下面(如 src/main/resources/static)。
如果我按如下结构存放相同名称的图片,那么Spring Boot 读取图片的优先级是怎样的呢?
如下图:
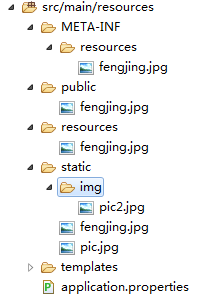
当我们访问地址 http://localhost:8080/fengjing.jpg 的时候,显示哪张图片?这里博主可以直接告诉大家,优先级顺序为:META/resources > resources > static > public
如果我们想访问pic2.jpg,请求地址 http://localhost:8080/img/pic2.jpg
自定义资源映射
上面我们介绍了Spring Boot 的默认资源映射,一般够用了,那我们如何自定义目录?
这些资源都是打包在jar包中的,然后实际应用中,我们还有很多资源是在管理系统中动态维护的,并不可能在程序包中,对于这种随意指定目录的资源,如何访问?
自定义目录
以增加 /myres/* 映射到 classpath:/myres/* 为例的代码处理为:
实现类继承 WebMvcConfigurerAdapter 并重写方法 addResourceHandlers (对于 WebMvcConfigurerAdapter 上篇介绍拦截器的文章中已经有提到)
package org.springboot.sample.config;
import org.springboot.sample.interceptor.MyInterceptor1;
import org.springboot.sample.interceptor.MyInterceptor2;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.config.annotation.InterceptorRegistry;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.config.annotation.ResourceHandlerRegistry;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.config.annotation.WebMvcConfigurerAdapter;
@Configuration
public class MyWebAppConfigurer
extends WebMvcConfigurerAdapter {
@Override
public void addResourceHandlers(ResourceHandlerRegistry registry) {
registry.addResourceHandler("/myres/**").addResourceLocations("classpath:/myres/");
super.addResourceHandlers(registry);
}
}访问myres 文件夹中的fengjing.jpg 图片的地址为 http://localhost:8080/myres/fengjing.jpg
这样使用代码的方式自定义目录映射,并不影响Spring Boot的默认映射,可以同时使用。
如果我们将/myres/* 修改为 /* 与默认的相同时,则会覆盖系统的配置,可以多次使用 addResourceLocations 添加目录,优先级先添加的高于后添加的。
// 访问myres根目录下的fengjing.jpg 的URL为 http://localhost:8080/fengjing.jpg (/** 会覆盖系统默认的配置)
// registry.addResourceHandler("/**").addResourceLocations("classpath:/myres/").addResourceLocations("classpath:/static/");其中 addResourceLocations 的参数是动参,可以这样写 addResourceLocations(“classpath:/img1/”, “classpath:/img2/”, “classpath:/img3/”);
使用外部目录
如果我们要指定一个绝对路径的文件夹(如 H:/myimgs/ ),则只需要使用 addResourceLocations 指定即可。
// 可以直接使用addResourceLocations 指定磁盘绝对路径,同样可以配置多个位置,注意路径写法需要加上file:
registry.addResourceHandler("/myimgs/**").addResourceLocations("file:H:/myimgs/");通过配置文件配置
上面是使用代码来定义静态资源的映射,其实Spring Boot也为我们提供了可以直接在 application.properties(或.yml)中配置的方法。
配置方法如下:
# 默认值为 /** spring.mvc.static-path-pattern= # 默认值为 classpath:/META-INF/resources/,classpath:/resources/,classpath:/static/,classpath:/public/ spring.resources.static-locations=这里设置要指向的路径,多个使用英文逗号隔开,
使用 spring.mvc.static-path-pattern 可以重新定义pattern,如修改为 /myres/** ,则访问static 等目录下的fengjing.jpg文件应该为 http://localhost:8080/myres/fengjing.jpg ,修改之前为 http://localhost:8080/fengjing.jpg
使用 spring.resources.static-locations 可以重新定义 pattern 所指向的路径,支持 classpath: 和 file: (上面已经做过说明)
注意 spring.mvc.static-path-pattern 只可以定义一个,目前不支持多个逗号分割的方式。
页面中使用
上面几个例子中也已经说明了怎么访问静态资源,其实在页面中使用不管是jsp还是freemarker,并没有什么特殊之处,也我们平时开发web项目一样即可。
下面是我的index.jsp:
<body>
<img alt="读取默认配置中的图片" src="${pageContext.request.contextPath }/pic.jpg">
<br/>
<img alt="读取自定义配置myres中的图片" src="${pageContext.request.contextPath }/myres/fengjing.jpg">
</body>使用webjars
先说一下什么是webjars?我们在Web开发中,前端页面中用了越来越多的JS或CSS,如jQuery等等,平时我们是将这些Web资源拷贝到Java的目录下,这种通过人工方式拷贝可能会产生版本误差,拷贝版本错误,前端页面就无法正确展示。
WebJars 就是为了解决这种问题衍生的,将这些Web前端资源打包成Java的Jar包,然后借助Maven这些依赖库的管理,保证这些Web资源版本唯一性。
WebJars 就是将js, css 等资源文件放到 classpath:/META-INF/resources/webjars/ 中,然后打包成jar 发布到maven仓库中。
简单应用
以jQuery为例,文件存放结构为:
META-INF/resources/webjars/jquery/2.1.4/jquery.js
META-INF/resources/webjars/jquery/2.1.4/jquery.min.js
META-INF/resources/webjars/jquery/2.1.4/jquery.min.map
META-INF/resources/webjars/jquery/2.1.4/webjars-requirejs.js
Spring Boot 默认将 /webjars/** 映射到 classpath:/META-INF/resources/webjars/ ,结合我们上面讲到的访问资源的规则,便可以得知我们在JSP页面中引入jquery.js的方法为:
<script type="text/javascript" src="${pageContext.request.contextPath }/webjars/jquery/2.1.4/jquery.js"></script>想实现这样,我们只需要在pom.xml 文件中添加jquery的webjars 依赖即可,如下:
<dependency> <groupId>org.webjars</groupId> <artifactId>jquery</artifactId> <version>2.1.4</version> </dependency>
版本号统一管理
但是我们实际开发中,可能会遇到升级版本号的情况,如果我们有100多个页面,几乎每个页面上都有按上面引入jquery.js 那么我们要把版本号更换为3.0.0,一个一个替换显然不是最好的办法。
如何来解决?按如下方法处理即可。
首先在pom.xml 中添加依赖:
<dependency> <groupId>org.webjars</groupId> <artifactId>webjars-locator</artifactId> </dependency>
然后增加一个WebJarsController:
package org.springboot.sample.controller;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import org.springframework.core.io.ClassPathResource;
import org.springframework.http.HttpStatus;
import org.springframework.http.ResponseEntity;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PathVariable;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseBody;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.HandlerMapping;
import org.webjars.WebJarAssetLocator;
/**
* 处理WebJars,自动读取版本号
*
* @author 单红宇(365384722)
* @myblog http://blog.csdn.net/catoop/
* @create 2016年1月8日
*/
@Controller
public class WebJarsController {
private final WebJarAssetLocator assetLocator = new WebJarAssetLocator();
@ResponseBody
@RequestMapping("/webjarslocator/{webjar}/**")
public ResponseEntity<Object> locateWebjarAsset(@PathVariable String webjar, HttpServletRequest request) {
try {
String mvcPrefix = "/webjarslocator/" + webjar + "/"; // This prefix must match the mapping path!
String mvcPath = (String) request.getAttribute(HandlerMapping.PATH_WITHIN_HANDLER_MAPPING_ATTRIBUTE);
String fullPath = assetLocator.getFullPath(webjar, mvcPath.substring(mvcPrefix.length()));
return new ResponseEntity<>(new ClassPathResource(fullPath), HttpStatus.OK);
} catch (Exception e) {
return new ResponseEntity<>(HttpStatus.NOT_FOUND);
}
}
}最后在页面中使用的方式:
<script type="text/javascript" src="${pageContext.request.contextPath }/webjarslocator/jquery/jquery.js"></script>静态资源版本管理
Spring 默认提供了静态资源版本映射的支持。
当我们的资源内容发生改变时,由于浏览器缓存,用户本地的资源还是旧资源,为了防止这种情况发生导致的问题。我们可能会选择在资源文件后面加上参数“版本号”或其他方式。
使用版本号参数,如:
<script type="text/javascript" src="${pageContext.request.contextPath }/js/common.js?v=1.0.1"></script>使用这种方式,当我们文件修改后,手工修改版本号来达到URL文件不被浏览器缓存的目的。同样也存在很多文件都需要修改的问题。或者有的人会增加时间戳的方式,这样我认为是最不可取的,每次浏览器都要请求为服务器增加了不必要的压力。
然而Spring在解决这种问题方面,提供了2种解决方式。
* 资源名称md5方式 *
1. 修改 application.properties 配置文件(或.yml)
spring.resources.chain.strategy.content.enabled=true spring.resources.chain.strategy.content.paths=/**
所有 /** 请求的静态资源都会被处理。
1.创建 ResourceUrlProviderController 文件
package org.springboot.sample.config;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ControllerAdvice;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ModelAttribute;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.resource.ResourceUrlProvider;
/**
* 处理静态资源URL
*
* @author 单红宇(365384722)
* @myblog http://blog.csdn.net/catoop/
* @create 2016年1月8日
*/
@ControllerAdvice
public class ResourceUrlProviderController {
@Autowired
private ResourceUrlProvider resourceUrlProvider;
@ModelAttribute("urls")
public ResourceUrlProvider urls() {
return this.resourceUrlProvider;
}
}1.在页面中使用的写法
<script type="text/javascript" src="${pageContext.request.contextPath }${urls.getForLookupPath('/js/common.js') }"></script>当我们访问页面后,HTML中实际生成的代码为:
<script type="text/javascript" src="/myspringboot/js/common-c6b7da8fffc9be141b48c073e39c7340.js"></script>
其中 /myspringboot 为我这个项目的 contextPath
* 资源版本号方式 *
该方式本人觉得并无多大意义,也不做详细说明,这是对所有资源的统一版本控制,不像上面一个md5是针对文件的。
除了在 application.properties(或.yml)中的配置有所区别,页面使用和md5的一样。
spring.resources.chain.strategy.fixed.enabled=true spring.resources.chain.strategy.fixed.paths=/js/**,/v1.0.0/** spring.resources.chain.strategy.fixed.version=v1.0.0
这样配置后,以上面 common.js 为例,实际页面中生成的HTML代码为:
<script type="text/javascript" src="/myspringboot/v1.0.0/js/common.js"></script>
* md5与版本号方式的处理原理 *
页面中首先会调用urls.getForLookupPath方法,返回一个/v1.0.0/js/common.js或/css/common-c6b7da8fffc9be141b48c073e39c7340.js
然后浏览器发起请求。
当请求的地址为md5方式时,会尝试url中的文件名中是否包含-,如果包含会去掉后面这部分,然后去映射的目录(如/static/)查找/js/common.js文件,如果能找到就返回。
当请求的地址为版本号方式时,会在url中判断是否存在/v1.0.0 ,如果存在,则先从URL中把 /v1.0.0 去掉,然后再去映射目录查找对应文件,找到就返回。
总结
有这么多方式来管理我们的资源文件,然而在实际应用中虽然也都有可能用到(存在就有存在的道理嘛),但是凭借个人经验来说。
1. 我们使用第三方的库时,建议使用webjars的方式,通过动态版本号(webjars-locator 的方式)来使用(因为第三方库在项目开发中变动频率很小,即便是变动也是版本号的修改)。
2. 我们使用自己存放在静态资源映射目录中的资源的时候,建议使用md5 资源文件名的方式来使用(项目开发中一些css、js文件会经常修改)。
3. 项目素材文件建议放到 classpath:/static (或其他)目录中,打包在项目中,通过CMS维护的一些图片和资源,我们使用配置引用到具体的磁盘绝对路径来使用。
4. 注意使用md5文件名方式的时候,Spring 是有缓存机制的,也就是说,在服务不重启的情况下,你去变动修改这些资源文件,其文件名的md5值并不会改变,只有重启服务再次访问才会生效。如果需要每次都获取实际文件的md5值,需要重写相关类来实现,我们不建议这样做,因为一直去计算文件md5值是需要性能代价的。
关于Spring Boot中如何实现静态资源处理就分享到这里了,希望以上内容可以对大家有一定的帮助,可以学到更多知识。如果觉得文章不错,可以把它分享出去让更多的人看到。
免责声明:本站发布的内容(图片、视频和文字)以原创、转载和分享为主,文章观点不代表本网站立场,如果涉及侵权请联系站长邮箱:is@yisu.com进行举报,并提供相关证据,一经查实,将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容。