这篇文章主要介绍了Spring Cloud Feign的示例分析,具有一定借鉴价值,感兴趣的朋友可以参考下,希望大家阅读完这篇文章之后大有收获,下面让小编带着大家一起了解一下。
Feign包含了Ribbon和Hystrix,这个在实战中才慢慢体会到它的意义,所谓的包含并不是Feign的jar包包含有Ribbon和Hystrix的jar包这种物理上的包含,而是Feign的功能包含了其他两者的功能这种逻辑上的包含。简言之:Feign能干Ribbon和Hystrix的事情,但是要用Ribbon和Hystrix自带的注解必须要引入相应的jar包才可以。
案例一:
Eureka注册中心:https://github.com/yejingtao/forblog/tree/master/demo-eureka-register
服务提供方:https://github.com/yejingtao/forblog/tree/master/demo-feign-freeservice
服务调用方:https://github.com/yejingtao/forblog/tree/master/demo-feign-freeconsumer
服务提供方就是个简单的EurekaClient端+web应用,提供以下方法
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/feign-service")
public class HelloServiceContorller {
private Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(this.getClass());
private void sleep(String methodName) {
int sleepMinTime = new Random().nextInt(3000);
logger.info("helloService "+methodName+" sleepMinTime: "+sleepMinTime);
try {
Thread.sleep(sleepMinTime);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
@RequestMapping(value="/serviceGet",method=RequestMethod.GET)
public String helloService(@RequestParam String name) {
sleep("get");
return "HelloServiceImpl name :"+name;
}
@RequestMapping(value="/serviceHead", method=RequestMethod.HEAD)
public String helloService(@RequestHeader String name,
@RequestHeader String password) {
sleep("header");
return "helloServiceHead name :"+name +" password:"+password;
}
@RequestMapping(value="/servicePost", method=RequestMethod.POST)
public String helloService(@RequestBody UserDemo userDemo) {
sleep("post");
return userDemo.toString();
}
}需要注意的以下注解不可以省略。
@RequestParam:Annotation which indicates that amethod parameter should be bound to a web request parameter
@RequestBody:Annotation indicating a methodparameter should be bound to the body of the web request.
@RequestHeader:Annotation which indicates that amethod parameter should be bound to a web request header.
如果缺少了以上注解,服务运行起来以后虽然不会报错,但是获取不到入参。
服务调用方项目:
<dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId> <artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-feign</artifactId> </dependency>
这里只依赖了Feign,没有依赖Ribbon和Hystrix。
application.yml:
server: port: 9051 spring: application: name: demo-feign-freeconsumer eureka: client: serviceUrl: defaultZone: http://peer1:1111/eureka/,http://peer2:1112/eureka/ feign: hystrix: enabled: true #Ribbon 超时时间设置 #ribbon: # ConnectTimeout: 500 # ReadTimeout: 3000
hystrix这个配置坑了我好久我用的Spring Cloud是Dalston版本SR1,比网上其他材料的版本要新,因为在新版本中Feign对Hystrix的支持默认是关闭的,所以要通过配置手动打开feign.hystrix.enabled=true,这样服务降级等功能才有效果。
Application启动程序
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableEurekaClient
@EnableFeignClients
public class DemoFeignApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(DemoFeignApplication.class, args);
}
}注意这里还有个坑,我这里用的是@SpringBootApplication+@EnableEurekaClient,而不是用的@SpringCloudApplication,因为后者包含了@EnableCircuitBreaker,而@EnableCircuitBreaker又是属于Hystrix包里的内容,我的pom里并没有引入Hystrix。所以这一点Spring Cloud做的还是有不足的地方,直接用@SpringCloudApplication编译不会报错,但是启动不了。当然这里的主角还是@EnableFeignClients这个注解。
核心客户端代码
@FeignClient(name="demo-feign-freeservice",fallback=DemoFeignFallback.class)
public interface DemoFeignService{
@RequestMapping(value="/feign-service/serviceGet",method=RequestMethod.GET)
String helloService(@RequestParam("name") String name);
@RequestMapping(value="/feign-service/serviceHead", method=RequestMethod.HEAD)
String helloService(@RequestHeader("name") String name,
@RequestHeader("password") String password);
@RequestMapping(value="/feign-service/servicePost", method=RequestMethod.POST)
String helloService(@RequestBody UserDemo userDemo);
}@FeignClient注解定义了该接口是一个Feign客户端,name指定了注册到Eureka上的服务名,fallback是服务降级后的接口实现类。
@RequestMapping里指定了请求的相对url和http请求方式,与服务端一一对应。入参里的@RequestParam、
@RequestBody、@RequestHeader注解比起服务端多了value属性,这里不能省略,需要显式的告知Feign客户端参数要如何对应。
降级服务代码:
@Component
public class DemoFeignFallback implements DemoFeignService{
@Override
public String helloService(String name) {
return "get error";
}
@Override
public String helloService(String name,String password) {
return "head error";
}
@Override
public String helloService(UserDemo userDemo) {
return "post error";
}
}发现这里的入参里我故意去掉了@RequestParam、@RequestBody、@RequestHeader注解,因为这几个注解本质上的意义就在于Feign在做微服务调用的时候对http传递参数用的,但服务降级根本不会做http请求了,所以此处可以省略。
Controller代码:
@RestController
public class DemoFeignController {
@Autowired
private DemoFeignService demoFeignService;
@RequestMapping(value="/test", method=RequestMethod.GET)
public String demoServiceTest() {
StringBuffer sb = new StringBuffer();
sb.append(demoFeignService.helloService("yuanyuan"));
sb.append("\n");
sb.append(demoFeignService.helloService("yjt","xixihaha"));
sb.append("\n");
sb.append(demoFeignService.helloService(new UserDemo("yejingtao","123456")));
return sb.toString();
}
}我们来看效果:

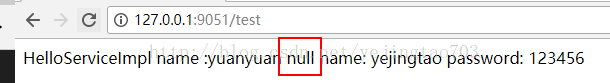
我们服务都没超时,3个方法全部正常,但是head请求没有拿到返回值,这个是因为head方式http请求的特性决定的,head不返回response的body体,一般用来做连通性测试来用。
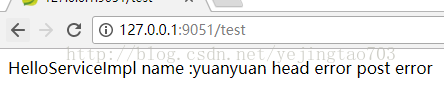
再看一组:
运气不好head和post请求方法处理时间超过了2000ms,服务降级,实现被fallback处理类取代。

在案例一中我们总有种感觉,服务提供方和服务调用方存在重复的代码,是否可以进行优化?请看案例二。
案例二:
Eureka注册中心:https://github.com/yejingtao/forblog/tree/master/demo-eureka-register
接口API:https://github.com/yejingtao/forblog/tree/master/demo-feign-serviceapi
服务提供方:https://github.com/yejingtao/forblog/tree/master/demo-feign-serviceimpl
服务调用方:https://github.com/yejingtao/forblog/tree/master/demo-feign-apiconsumer
案例二最大的变动是将服务能力单独写到一个API的project中,调用方和提供方pom都依赖这个API。
API:
public interface HelloService {
@RequestMapping(value="/feign-service/serviceGet",method=RequestMethod.GET)
String helloService(@RequestParam("name") String name);
@RequestMapping(value="/feign-service/serviceHead", method=RequestMethod.HEAD)
String helloService(@RequestHeader("name") String name,
@RequestHeader("password") String password);
@RequestMapping(value="/feign-service/servicePost", method=RequestMethod.POST)
String helloService(@RequestBody UserDemo userDemo);
}服务提供方:
@RestController
public class HelloServiceContorller implements HelloService{
private Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(this.getClass());
private void sleep(String methodName) {
int sleepMinTime = new Random().nextInt(3000);
logger.info("helloService "+methodName+" sleepMinTime: "+sleepMinTime);
try {
Thread.sleep(sleepMinTime);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
@Override
public String helloService(@RequestParam("name") String name) {
sleep("get");
return "HelloServiceImpl name :"+name;
}
@Override
public String helloService(@RequestHeader("name") String name,
@RequestHeader("password") String password) {
sleep("header");
return "helloServiceHead name :"+name +" password:"+password;
}
@Override
public String helloService(@RequestBody UserDemo userDemo) {
sleep("post");
return userDemo.toString();
}
}服务调用方:
@FeignClient(name="demo-feign-serviceimpl", fallback=FeignServiceFallback.class)
public interface FeignService extends HelloService{
}其它代码基本不变,效果也一样。
两种风格各有优缺点:freestyle的更自由,服务端新增方法不会影响客户端代码,缺点是服务能力不同步服务能力的变动会引起异常;API格式服务端客户端服务能力同步,但是接口的变动需要修改两边的代码,需要构建的时候就要考虑清楚。
感谢你能够认真阅读完这篇文章,希望小编分享的“Spring Cloud Feign的示例分析”这篇文章对大家有帮助,同时也希望大家多多支持亿速云,关注亿速云行业资讯频道,更多相关知识等着你来学习!
免责声明:本站发布的内容(图片、视频和文字)以原创、转载和分享为主,文章观点不代表本网站立场,如果涉及侵权请联系站长邮箱:is@yisu.com进行举报,并提供相关证据,一经查实,将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容。