这篇文章将为大家详细讲解有关Java中io流解析的示例分析,小编觉得挺实用的,因此分享给大家做个参考,希望大家阅读完这篇文章后可以有所收获。
IO流
Java中IO流分为两种,字节流和字符流,顾名思义字节流就是按照字节来读取和写入的,字符刘是按照字符来存取的;常用的文件读取用的就是字符流,在网络通信里面用的就是字节流
下面这张图是Java中IO流的总体框架:
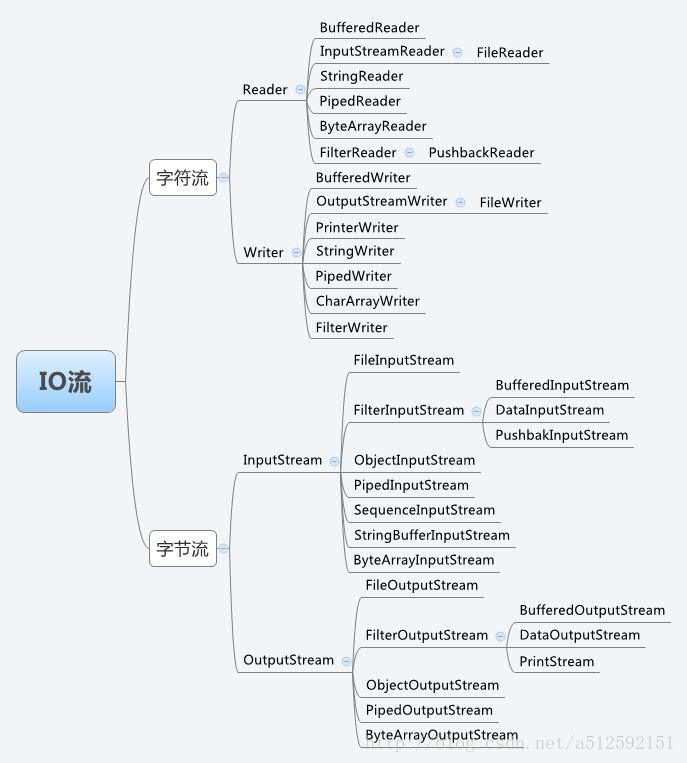
字节流
Java中字节流一般都是以stream结尾的,输入的字节流叫InputStream,输出字节流叫OutputStream;InputStream和OutputStream是表示自己输入/输出的所有类的超类,是抽象类(abstract)
常用的字节流有:
1.FileInputStream/FileOutputStream 2.BufferedInputStream/BufferedOutputStream 3.SequenceInputStream(序列流) 4.ObjectInputStream/ObjectOutputStream(对象的输入输出流) 5.PrintStream(打印流)
字符流
Java中输入字符流是以Reader结尾的,输出字符流是以Writer结尾的,比如我们常见的FileReader和FileWriter就是个字符流,Reader和Witer是输入/输出字符流的超类,也是抽象类
常用的字符流有:
1.FileReader/FileWriter 2.BufferedReader/BufferedWriter 3.InputStremReader/OutputStreamWriter(转换流)
转换流
转换流就是将字节流转换为字符流的类,有两种:
·InputStreamReader ·OutputStreamWriter
InputStreamReader是个字符流(Reader),需要包装一个字节流(InputStream);
OutputStreamWriter是个字符流(Writer),需要包装一个字节流(OutputStream)
包装(decorate)
包装的作用的就是在原始的对象的基础上增加新的功能,比如BufferedReader包装一个Reader,实际就是对Reader功能的增强;原始的Reader只能按照一个字符一个字符的读取,经过包装之后形成的BufferedReader就具有了新的功能:直接读取一行(readLine)的功能,直观上说这就是所谓的Decorate.
在设计模式上这就是典型的装饰模式,其特点是:
1.装饰对象和真实对象有相同的接口。这样客户端对象就能以和真实对象相同的方式和装饰对象交互 2.装饰对象可以在转发这些请求以前或以后增加一些附加功能。这样就确保了在运行时,不用修改给定对象的结构就可以在外部增加附加的功能
对应到我们上来就是,BufferedReader和Reader都是个Reader,通过包装之后BufferedReader功能增强,但是依然可以当做Reader来用(OO的父类引用可以指向子类)
例子
字节流的例子
将mp3文件切割成多份数,然后重新组合起来
package cn.xdian.test;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.SequenceInputStream;
import java.util.Enumeration;
import java.util.Vector;
public class Demo2 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
cutFile();
//切割MP3文件
mergeFlile();
//合并MP3文件
}
//合并MP3
public static void mergeFlile() throws IOException{
File dir = new File("/home/gavinzhou/music_test");
//找到文件夹下所有的MP3文件
Vector<FileInputStream> vector = new Vector<FileInputStream>();
File[] files = dir.listFiles();
for (File file : files){
if(file.getName().endsWith(".mp3")){
vector.add(new FileInputStream(file));
}
}
//通过Vector获取迭代器
Enumeration<FileInputStream> e = vector.elements();
//创建序列流
SequenceInputStream inputStream = new SequenceInputStream(e);
//输出流
FileOutputStream fileOutputStream = new FileOutputStream("/home/gavinzhou/conbine.mp3");
//读取分割的MP3文件
byte[] buf = new byte[1024];
int length = 0 ;
while((length = inputStream.read(buf))!=-1){
fileOutputStream.write(buf,0,length);
}
//关闭流
fileOutputStream.close();
inputStream.close();
}
//切割MP3
public static void cutFile() throws IOException{
File file = new File("/home/gavinzhou/test.mp3");
File dir = new File("/home/gavinzhou/music_test");
//输入字节流
FileInputStream fileInputStream = new FileInputStream(file);
//读取文件
byte[] buf = new byte[1024*1024];
int length = 0;
for (int i = 0 ; (length = fileInputStream.read(buf))!=-1 ; i++){
FileOutputStream fileOutputStream = new FileOutputStream(new File(dir,"part"+i+".mp3"));
fileOutputStream.write(buf,0,length);
fileOutputStream.close();
}
//关闭流
fileInputStream.close();
}
}字符流的例子
拷贝文件A变为文件B
package cn.xidian.test;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.BufferedWriter;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileReader;
import java.io.FileWriter;
import java.io.IOException;
public class Demo1 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
File sourceFile = new File("/home/gavinzhou/a.txt");
File desFile = new File("/home/gavinzhou/b.txt");
//创建输入流
BufferedReader input = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(sourceFile));
//创建输出流
BufferedWriter output = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter(desFile));
//读取源文件,写入到新的文件
String line = null;
while((line = input.readLine()) != null){
output.write(line);
output.newLine();
}
//关闭输入输出流
input.close();
output.close();
}
}打印流的例子
package cn.xidian.test;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.PrintStream;
/*
打印流可以打印任意类型的数据,打印数据之前都会先把数据转换成字符串再进行打印
*/
class Animal{
String name;
String color;
public Animal(String name,String color){
this.name = name;
this.color = color;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "名字:"+this.name+ " 颜色:"+ this.color;
}
}
public class Demo6 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
/*
File file = new File("/home/gavinzhou/a.txt");
//创建打印流
PrintStream printStream = new PrintStream(file);
//打印任何信息到文件中
printStream.println(97);
printStream.println(3.14);
printStream.println('a');
printStream.println(true);
Animal a = new Animal("老鼠", "黑色");
printStream.println(a);
//更改标准的输入输出
System.setOut(printStream); //标准输出是到屏幕上
System.out.println("test.......");
*/
//收集异常的日志信息。
File logFile = new File("/home/gavinzhou/test.log");
PrintStream logPrintStream = new PrintStream( new FileOutputStream(logFile,true) );
try{
int c = 4/0;
//引起异常
System.out.println("c="+c);
int[] arr = null;
System.out.println(arr.length);
}
catch(Exception e){
e.printStackTrace(logPrintStream);
//输出到文件而不是屏幕上
}
}
}关于“Java中io流解析的示例分析”这篇文章就分享到这里了,希望以上内容可以对大家有一定的帮助,使各位可以学到更多知识,如果觉得文章不错,请把它分享出去让更多的人看到。
免责声明:本站发布的内容(图片、视频和文字)以原创、转载和分享为主,文章观点不代表本网站立场,如果涉及侵权请联系站长邮箱:is@yisu.com进行举报,并提供相关证据,一经查实,将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容。