这篇文章将为大家详细讲解有关如何在Android中利用view实现一个手势密码功能,文章内容质量较高,因此小编分享给大家做个参考,希望大家阅读完这篇文章后对相关知识有一定的了解。
用法:
<com.leo.library.view.GestureContentView android:id="@+id/id_gesture_pwd" android:layout_gravity="center_horizontal" android:layout_marginTop="10dp" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" app:column="3" app:row="3" app:padding="50dp" app:normalDrawable="@drawable/gesture_node_normal" app:selectedDrawable="@drawable/gesture_node_pressed" app:erroDrawable="@drawable/gesture_node_wrong" app:normalStrokeColor="#000" app:erroStrokeColor="#ff0000" app:strokeWidth="4dp" />
app打头的是自定义的一些属性,
attrs.xml:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <resources> <declare-styleable name="IndicatorView"> <!--默认状态的drawable--> <attr name="normalDrawable" format="reference" /> <!--被选中状态的drawable--> <attr name="selectedDrawable" format="reference" /> <!--错误状态的drawabe--> <attr name="erroDrawable" format="reference" /> <!--列数--> <attr name="column" format="integer" /> <!--行数--> <attr name="row" format="integer" /> <!--padding值,padding值越大点越小--> <attr name="padding" format="dimension" /> <!--默认连接线颜色--> <attr name="normalStrokeColor" format="color" /> <!--错误连接线颜色--> <attr name="erroStrokeColor" format="color" /> <!--连接线size--> <attr name="strokeWidth" format="dimension" /> </declare-styleable> </resources>
MainActivity.java:
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity implements IGesturePwdCallBack {
private GestureContentView mGestureView;
private IndicatorView indicatorView;
private TextView tvIndicator;
private int count=0;
private String pwd;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
mGestureView= (GestureContentView) findViewById(R.id.id_gesture_pwd);
indicatorView= (IndicatorView) findViewById(R.id.id_indicator_view);
tvIndicator= (TextView) findViewById(R.id.id_indicator);
mGestureView.setGesturePwdCallBack(this);
}
@Override
public void callBack(List<Integer> pwds) {
StringBuffer sbPwd=new StringBuffer();
for (Integer pwd:pwds) {
sbPwd.append(pwd);
}
tvIndicator.setText(sbPwd.toString());
if(pwds!=null&&pwds.size()>0){
indicatorView.setPwds(pwds);
}
if(count++==0){
pwd=sbPwd.toString();
Toast.makeText(this,"请再次绘制手势密码",Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
mGestureView.changePwdState(PointState.POINT_STATE_NORMAL,0);
} else{
count=0;
if(pwd.equals(sbPwd.toString())){
Toast.makeText(this,"密码设置成功",Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
}else{
Toast.makeText(this,"两次密码不一致,请重新绘制",Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
indicatorView.startAnimation(AnimationUtils.loadAnimation(this,R.anim.anim_shake));
count=0;
mGestureView.changePwdState(PointState.POINT_STATE_ERRO,0);
new Handler().postDelayed(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
mGestureView.changePwdState(PointState.POINT_STATE_NORMAL,0);
}
},1000);
}
}
}
}看不懂也没关系啊,我们先明确下我们要完成的目标,然后一步一步实现:
先实现下我们的指示器view,因为实现了指示器view也就相当于实现了一半的手势密码view了:
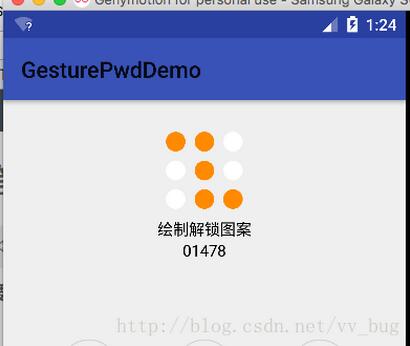
实现思路:
1、我们需要知道指示器有多少行、多少列、默认显示什么、选中后显示什么?
2、然后根据传入的密码把对应的点显示成选中状态,没有选中的点为默认状态。
好了,知道我们的思路,首先自定义一个view叫IndicatorView继承view,然后重写三个构造方法:
public class IndicatorView extends View {
public IndicatorView(Context context) {
this(context, null);
}
public IndicatorView(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {
this(context, attrs, 0);
}
public IndicatorView(Context context, AttributeSet attrs, int defStyleAttr) {
super(context, attrs, defStyleAttr);
}
}定义自定义属性(在res/values下创建attrs.xml文件):
1、我们需要传入的默认显示图片:
<!--默认状态的drawable--> <attr name="normalDrawable" format="reference" />
2、我们需要拿到传入的选中时图片:
<!--被选中状态的drawable--> <attr name="selectedDrawable" format="reference" />
其它的一些属性:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <resources> <declare-styleable name="IndicatorView"> <!--默认状态的drawable--> <attr name="normalDrawable" format="reference" /> <!--被选中状态的drawable--> <attr name="selectedDrawable" format="reference" /> <!--列数--> <attr name="column" format="integer" /> <!--行数--> <attr name="row" format="integer" /> </declare-styleable> </resources>
定义完属性后,此时我们xml中就可以引用自定义view了:
<com.leo.library.view.IndicatorView android:id="@+id/id_indicator_view" android:layout_marginTop="20dp" android:layout_width="85dp" android:layout_height="85dp" android:layout_alignParentTop="true" android:layout_centerHorizontal="true" app:column="3" app:normalDrawable="@drawable/shape_white_indicator" app:padding="8dp" app:row="3" app:selectedDrawable="@drawable/shape_orange_indicator" />
注意:
中间的drawable文件可以在github项目中找到,链接我会在文章最后给出。
有了自定义属性,然后我们在带三个参数的构造方法中获取我们在布局文件传入的自定义属性:
private static final int NUMBER_ROW = 3; private static final int NUMBER_COLUMN = 3; private int DEFAULT_PADDING = dp2px(10); private final int DEFAULT_SIZE = dp2px(40); private Bitmap mNormalBitmap; private Bitmap mSelectedBitmap; private int mRow = NUMBER_ROW; private int mColumn = NUMBER_COLUMN;
public IndicatorView(Context context, AttributeSet attrs, int defStyleAttr) {
super(context, attrs, defStyleAttr);
final TypedArray a = context.obtainStyledAttributes(
attrs, R.styleable.IndicatorView, defStyleAttr, 0);
mNormalBitmap = drawableToBitmap(a.getDrawable(R.styleable.IndicatorView_normalDrawable));
mSelectedBitmap = drawableToBitmap(a.getDrawable(R.styleable.IndicatorView_selectedDrawable));
if (a.hasValue(R.styleable.IndicatorView_row)) {
mRow = a.getInt(R.styleable.IndicatorView_row, NUMBER_ROW);
}
if (a.hasValue(R.styleable.IndicatorView_column)) {
mColumn = a.getInt(R.styleable.IndicatorView_row, NUMBER_COLUMN);
}
if (a.hasValue(R.styleable.IndicatorView_padding)) {
DEFAULT_PADDING = a.getDimensionPixelSize(R.styleable.IndicatorView_padding, DEFAULT_PADDING);
}
}好了,现在我们已经拿到了我们想要的东西了,接下来我们需要知道我的view要多大,相比小伙伴都知道接下来要干什么了吧?对~! 我们需要重写下onMeasure方法,然后指定我们view的大小:
@Override
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
}那么我们该以一个什么样的规则指定我们的view的大小呢?
1、当用户自己指定了view的大小的话,我们就用用户传入的size,然后根据传入的宽、高计算出我们的点的大小。
<com.leo.library.view.IndicatorView android:id="@+id/id_indicator_view" android:layout_marginTop="20dp" android:layout_width="85dp" android:layout_height="85dp"
2、如果用户没有指定view的大小,宽高都设置为wrap_content的话,我们需要根据用户传入的选中图片跟没选中图片的大小计算view的大小:
android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content"
好了,既然知道咋测量我们的view后,我们接下来就实现出来:
@Override
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
int widthMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(widthMeasureSpec);
int heightMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(heightMeasureSpec);
float width = MeasureSpec.getSize(widthMeasureSpec);
float height = MeasureSpec.getSize(heightMeasureSpec);
float result=Math.min(width,height);
height = getHeightValue(result, heightMode);
width = getWidthValue(result, widthMode);
} private float getHeightValue(float height, int heightMode) {
//当size为确定的大小的话
//每个点的高度等于(控件的高度-(行数+1)*padding值)/行数
if (heightMode == MeasureSpec.EXACTLY) {
mCellHeight = (height - (mRow + 1) * DEFAULT_PADDING) / mRow;
} else {
//高度不确定的话,我们就取选中的图片跟未选中图片中的高度的最小值
mCellHeight = Math.min(mNormalBitmap.getHeight(), mSelectedBitmap.getHeight());
//此时控件的高度=点的高度*行数+(行数+1)*默认padding值
height = mCellHeight * mRow + (mRow + 1) * DEFAULT_PADDING;
}
return height;
}宽度计算方式也是一样的话,只是行数换成了列数:
private float getWidthValue(float width, int widthMode) {
if (widthMode == MeasureSpec.EXACTLY) {
mCellWidth = (width - (mColumn + 1) * DEFAULT_PADDING) / mColumn;
} else {
mCellWidth = Math.min(mNormalBitmap.getWidth(), mSelectedBitmap.getWidth());
width = mCellWidth * mColumn + (mColumn + 1) * DEFAULT_PADDING;
}
return width;
}好了,现在是知道了点的高度跟宽度,然后控件的宽高自然也就知道了,但是如果我们传入的选中的图片跟未选择的图片大小不一样咋办呢?没关系,接下来我们重新修改下图片的size:
@Override
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
.....
height = getHeightValue(result, heightMode);
width = getWidthValue(result, widthMode);
setMeasuredDimension((int) width, (int) height);
//重新修改图片的size
resizeBitmap(mCellWidth, mCellHeight);
} private void resizeBitmap(float width, float height) {
if (width > 0 && height > 0) {
if (mNormalBitmap.getWidth() != width || mNormalBitmap.getHeight() !=height) {
if (mNormalBitmap.getWidth() > 0 && mNormalBitmap.getHeight() > 0) {
mNormalBitmap = Bitmap.createScaledBitmap(mNormalBitmap, (int) width, (int) height, false);
}
}
if (mSelectedBitmap.getWidth()!=width || mSelectedBitmap.getHeight() !=height) {
if (mSelectedBitmap.getWidth() > 0 && mSelectedBitmap.getHeight() > 0) {
mSelectedBitmap = Bitmap.createScaledBitmap(mSelectedBitmap, (int) width, (int) height, false);
}
}
}
}好了,图片也拿到了,控件的宽高跟点的宽高都知道,所以接下来我们该进入我们的核心代码了(重写onDraw方法,画出我们的点):
@Override
protected void onDraw(Canvas canvas) {
super.onDraw(canvas);
//遍历行数
for (int i = 0; i < mRow; i++) {
//遍历列数
for (int j = 0; j < mColumn; j++) {
float left = (j + 1) * DEFAULT_PADDING + j * mCellWidth;
float top = (i + 1) * DEFAULT_PADDING + i * mCellHeight;
//每个点代表的密码值=点对应的行数值*列数+对应的列数
//比如3*3的表格,然后第二排的第一个=1*3+0=3
int num=i * mColumn + j;
//此点是不是在传入的密码集合中?
if (pwds!=null&&pwds.contains(num)) {
//这个点在传入的密码集合中的话就画一个选中的bitmap
canvas.drawBitmap(mSelectedBitmap, left, top, null);
} else {
canvas.drawBitmap(mNormalBitmap, left, top, null);
}
}
}
}嗯嗯!!然后我们暴露一个方法,让外界传入需要现实的密码集合:
public void setPwds(List<Integer> pwds) {
if(pwds!=null)this.pwds=pwds;
if (Looper.myLooper() == Looper.getMainLooper()) {
invalidate();
} else {
postInvalidate();
}
}关于如何在Android中利用view实现一个手势密码功能就分享到这里了,希望以上内容可以对大家有一定的帮助,可以学到更多知识。如果觉得文章不错,可以把它分享出去让更多的人看到。
免责声明:本站发布的内容(图片、视频和文字)以原创、转载和分享为主,文章观点不代表本网站立场,如果涉及侵权请联系站长邮箱:is@yisu.com进行举报,并提供相关证据,一经查实,将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容。