1,ansible剧本
playbook 翻译过来就是“剧本”, 那 playbook 组成如下
play: 定义的是主机的角色
task: 定义的是具体执行的任务
playbook: 由一个或多个 play 组成,一个 play 可以包含多个 task 任务
简单理解为: 使用不同的模块完成一件事情
2,ansible剧本的优势
1,功能比ansible命令更强大
2,能控制先后执行顺序和依赖关系
3,语法更加直观
3,ansible使用yaml语法
1)以缩进代表不同层级之间的关系
2)对缩进有严格要求
3)-横杠,横杠后面有空格代表列表
4):冒号,冒号后有空格,表示赋值
4,ansible剧本小实例模板
ansible nfs -m group -a "name=www gid=666 state=present"
ansible nfs -m user -a "name=www uid=666 group=666 shell=/sbin/nologin create_home=no"
ansible nfs -m yum -a "name=nfs-utils"
ansible nfs -m file -a "path=/data state=directory"
ansible nfs -m copy -a "src=exports dest=/etc/exports backup=yes"
ansible nfs -m service -a "name=rpcbind state=started enabled=yes"
ansible nfs -m service -a "name=nfs state=started enabled=yes"
ansible nfs -m shell -a "showmount -e" 小试牛刀:
小试牛刀:
- hosts: nfs 主机组
tasks: 任务
- name: create group 取名字任意,要方便记
group: 引用的模块
name: www 参数1
gid: 666 参数2
state: present 参数3
- name: create user
user:
name: www
uid: 666
group: www
shell: /sbin/nologin
create_home: no
- name: install nfs soft
yum:
name: nfs-utils
- name: mkdir directory
file:
path: /data
state: directory
- name: copy file
copy:
src: /root/exports
dest: /etc/exports
backup: yes
- name: start rpcbind
service:
name: rpcbind
state: started
enbaled: yes
- name: start nfs
service:
name: nfs
state: started
enbaled: yes
- name: show mount
shell: showmount -e5,ansible执行方式
1)ansible-playbook --syntax-check xxx.yaml 语法检查
2)ansible-playbook -C xxx.yaml 模拟执行
3)ansible-playbook xxx.yaml 执行剧本
6,anisble剧本高级特性-loop
使用场景:在写ansible剧本中我们经常会写到重复性命令,比如创建多个用户,多个组,多个目录,安装多个软件
一个个写就太麻烦了,也体现不出ansible剧本的优越性。所以我们就要用到它的一些高级特性
- hosts: nfs
tasks:
- name: create directory
file:
path: "{{ item }}"
state: present
loop:
- /data
- /dat2
- name: add group
group:
name: "{{ item.name }}"
gid: "{{ item.gid }}"
state: present
loop:
- { name: group1, gid: 1111 }
- { name: group2, gid: 2222 }
-name: add user
user:
name: "{{ item.name }}"
uid: "{{ item.uid }}"
group: "{{ item.group }}"
shell: /sbin/nologin
create_home: no
loop:
- { name: user1, uid: 7777 group: group1 }
- { name: user2, uid: 8888 group: group2 } 六,ansible剧本高级特性-变量
使用情景:
1.自定义某个名称,在任务中会多次引用
2.从主机收集的系统信息中提取某个变量并引用,例如网卡信息
- hosts: nfs
var:
path: /opt/data
tasks:
- name: create directory
file:
path:"{{ path }}"
state: present
也可以写在/etc/ansible/hosts 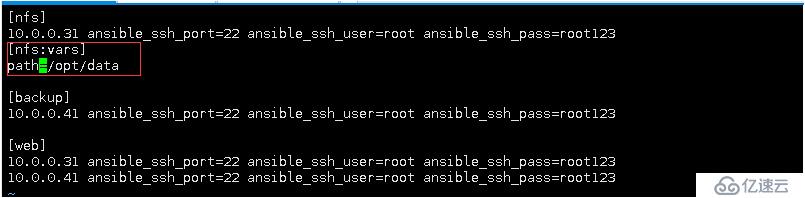
- hsots: nfs
tasks:
- name: show ip
shell: "echo {{ ansible_facts.eth2.ipv4.address }} > /root/ip_eth2.txt"
shell: "echo {{ ansible_facts.eth0.ipv4.address }} > /root/ip_eth0.txt"(ansible内置变量提取ip地址的变量)
六,ansible剧本高级特性-注册变量
使用情景:将配置文件的状态注册成一个变量,方便其他任务引用
例:
- hosts: nfs
tasks:
- name: show ip
shell: "echo {{ ansible_facts.eth2.ipv4.address }}"
register: eth2 (register是固定用法,表示注册一个叫eth2的变量)
- name: echo eth2
debug:
msg: "{{ eth2.stdout }} " (固定用法,加.stdout表示显示带stdout的行因为这行刚好有ip)六,ansible剧本高级特性-触发机制
使用场景:通常剧本里定义的配置文件一旦修改后,我们都要重启服务,但是ansible定义的service模块只能state: started
所以要有一个触发机制,当配置文件修改,服务自动重启
- hosts: nfs
tasks:
- name: copy export
copy:
src: /root/exports
dest: /etc/exports
backup: yes
notify: restart_nfs_server
handlers:
- name: restart_nfs_server
service:
name: "{{ item }}"
state: restarted
loop:
- rpcbind
- nfs六,ansible剧本高级特性-标签tags
应用场景:给剧本里执行的每个模块打上tags,在你执行的时候你可以灵活指定执行哪个模块或者对于报错的模块单独执行,而不需要再从头执行一遍
- hosts: 172.16.1.41
tasks:
- name: 01-add group
group: name=www gid=666
tags: 01-add-group
- name: 02-add user
user: name=www create_home=no shell=/sbin/nologin group=www uid=666
tags: 02-add-user
- name: 03-install rsync
yum: name=rsync state=installed
tags: 03-install-rsync
- name: 04-copy rsync conf
copy: src=/server/scripts/rsyncd.conf dest=/etc/
tags: 04-copy-conf
- name: 05-create passwd conf
copy: content='rsync_backup:oldboy' dest=/etc/rsync.passwd mode=600
tags: 05-create-passwd
- name: 06-create backup dir
file: path=/backup state=directory owner=www group=www
tags: 06-create-backup
- name: 07-create backup dir
file: path=/data state=directory owner=www group=www
tags: 07-create-data
- name: 08-start rsyncd service
service: name=rsyncd state=started
tags: 08-start-rsyncd
- name: 09-enabled rsyncd service
systemd: name=rsyncd enabled=yes
tags: 09-enable 1)指定运行某个tags:
ansible-playbook -t 05-create-passwd tags2.yml
2)指定运行多个tags:
ansible-playbook -t 05-create-passwd,06-create-backup tags2.yml
3)指定不运行某个tags:
ansible-playbook --skip-tags=05-create-passwd tags2.yml
4)指定不运行多个tags:
ansible-playbook --skip-tags=05-create-passwd,06-create-backup tags2.yml
免责声明:本站发布的内容(图片、视频和文字)以原创、转载和分享为主,文章观点不代表本网站立场,如果涉及侵权请联系站长邮箱:is@yisu.com进行举报,并提供相关证据,一经查实,将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容。