这篇文章主要讲解了“分析PostgreSQL中的数据结构HTAB”,文中的讲解内容简单清晰,易于学习与理解,下面请大家跟着小编的思路慢慢深入,一起来研究和学习“分析PostgreSQL中的数据结构HTAB”吧!
/*
* Top control structure for a hashtable --- in a shared table, each backend
* has its own copy (OK since no fields change at runtime)
* 哈希表的顶层控制结构.
* 在这个共享哈希表中,每一个后台进程都有自己的拷贝
* (之所以没有问题是因为fork出来后,在运行期没有字段会变化)
*/
struct HTAB
{
//指向共享的控制信息
HASHHDR *hctl; /* => shared control information */
//段目录
HASHSEGMENT *dir; /* directory of segment starts */
//哈希函数
HashValueFunc hash; /* hash function */
//哈希键比较函数
HashCompareFunc match; /* key comparison function */
//哈希键拷贝函数
HashCopyFunc keycopy; /* key copying function */
//内存分配器
HashAllocFunc alloc; /* memory allocator */
//内存上下文
MemoryContext hcxt; /* memory context if default allocator used */
//表名(用于错误信息)
char *tabname; /* table name (for error messages) */
//如在共享内存中,则为T
bool isshared; /* true if table is in shared memory */
//如为T,则固定大小不能扩展
bool isfixed; /* if true, don't enlarge */
/* freezing a shared table isn't allowed, so we can keep state here */
//不允许冻结共享表,因此这里会保存相关状态
bool frozen; /* true = no more inserts allowed */
/* We keep local copies of these fixed values to reduce contention */
//保存这些固定值的本地拷贝,以减少冲突
//哈希键长度(以字节为单位)
Size keysize; /* hash key length in bytes */
//段大小,必须为2的幂
long ssize; /* segment size --- must be power of 2 */
//段偏移,ssize的对数
int sshift; /* segment shift = log2(ssize) */
};
/*
* Header structure for a hash table --- contains all changeable info
* 哈希表的头部结构 -- 存储所有可变信息
*
* In a shared-memory hash table, the HASHHDR is in shared memory, while
* each backend has a local HTAB struct. For a non-shared table, there isn't
* any functional difference between HASHHDR and HTAB, but we separate them
* anyway to share code between shared and non-shared tables.
* 在共享内存哈希表中,HASHHDR位于共享内存中,每一个后台进程都有一个本地HTAB结构.
* 对于非共享哈希表,HASHHDR和HTAB没有任何功能性的不同,
* 但无论如何,我们还是把它们区分为共享和非共享表.
*/
struct HASHHDR
{
/*
* The freelist can become a point of contention in high-concurrency hash
* tables, so we use an array of freelists, each with its own mutex and
* nentries count, instead of just a single one. Although the freelists
* normally operate independently, we will scavenge entries from freelists
* other than a hashcode's default freelist when necessary.
* 在高并发的哈希表中,空闲链表会成为竞争热点,因此我们使用空闲链表数组,
* 数组中的每一个元素都有自己的mutex和条目统计,而不是使用一个.
*
* If the hash table is not partitioned, only freeList[0] is used and its
* spinlock is not used at all; callers' locking is assumed sufficient.
* 如果哈希表没有分区,那么只有freelist[0]元素是有用的,自旋锁没有任何用处;
* 调用者锁定被认为已足够OK.
*/
/* Number of freelists to be used for a partitioned hash table. */
//#define NUM_FREELISTS 32
FreeListData freeList[NUM_FREELISTS];
/* These fields can change, but not in a partitioned table */
//这些域字段可以改变,但不适用于分区表
/* Also, dsize can't change in a shared table, even if unpartitioned */
//同时,就算是非分区表,共享表的dsize也不能改变
//目录大小
long dsize; /* directory size */
//已分配的段大小(<= dsize)
long nsegs; /* number of allocated segments (<= dsize) */
//正在使用的最大桶ID
uint32 max_bucket; /* ID of maximum bucket in use */
//进入整个哈希表的模掩码
uint32 high_mask; /* mask to modulo into entire table */
//进入低位哈希表的模掩码
uint32 low_mask; /* mask to modulo into lower half of table */
/* These fields are fixed at hashtable creation */
//下面这些字段在哈希表创建时已固定
//哈希键大小(以字节为单位)
Size keysize; /* hash key length in bytes */
//所有用户元素大小(以字节为单位)
Size entrysize; /* total user element size in bytes */
//分区个数(2的幂),或者为0
long num_partitions; /* # partitions (must be power of 2), or 0 */
//目标的填充因子
long ffactor; /* target fill factor */
//如目录是固定大小,则该值为dsize的上限值
long max_dsize; /* 'dsize' limit if directory is fixed size */
//段大小,必须是2的幂
long ssize; /* segment size --- must be power of 2 */
//段偏移,ssize的对数
int sshift; /* segment shift = log2(ssize) */
//一次性分配的条目个数
int nelem_alloc; /* number of entries to allocate at once */
#ifdef HASH_STATISTICS
/*
* Count statistics here. NB: stats code doesn't bother with mutex, so
* counts could be corrupted a bit in a partitioned table.
* 统计信息.
* 注意:统计相关的代码不会影响mutex,因此对于分区表,统计可能有一点点问题
*/
long accesses;
long collisions;
#endif
};
/*
* Per-freelist data.
* 空闲链表数据.
*
* In a partitioned hash table, each freelist is associated with a specific
* set of hashcodes, as determined by the FREELIST_IDX() macro below.
* nentries tracks the number of live hashtable entries having those hashcodes
* (NOT the number of entries in the freelist, as you might expect).
* 在一个分区哈希表中,每一个空闲链表与特定的hashcodes集合相关,通过下面的FREELIST_IDX()宏进行定义.
* nentries跟踪有这些hashcodes的仍存活的hashtable条目个数.
* (注意不要搞错,不是空闲的条目个数)
*
* The coverage of a freelist might be more or less than one partition, so it
* needs its own lock rather than relying on caller locking. Relying on that
* wouldn't work even if the coverage was the same, because of the occasional
* need to "borrow" entries from another freelist; see get_hash_entry().
* 空闲链表的覆盖范围可能比一个分区多或少,因此需要自己的锁而不能仅仅依赖调用者的锁.
* 依赖调用者锁在覆盖面一样的情况下也不会起效,因为偶尔需要从另一个自由列表“借用”条目,详细参见get_hash_entry()
*
* Using an array of FreeListData instead of separate arrays of mutexes,
* nentries and freeLists helps to reduce sharing of cache lines between
* different mutexes.
* 使用FreeListData数组而不是一个独立的mutexes,nentries和freelists数组有助于减少不同mutexes之间的缓存线共享.
*/
typedef struct
{
//该空闲链表的自旋锁
slock_t mutex; /* spinlock for this freelist */
//相关桶中的条目个数
long nentries; /* number of entries in associated buckets */
//空闲元素链
HASHELEMENT *freeList; /* chain of free elements */
} FreeListData;
/*
* HASHELEMENT is the private part of a hashtable entry. The caller's data
* follows the HASHELEMENT structure (on a MAXALIGN'd boundary). The hash key
* is expected to be at the start of the caller's hash entry data structure.
* HASHELEMENT是哈希表条目的私有部分.
* 调用者的数据按照HASHELEMENT结构组织(位于MAXALIGN的边界).
* 哈希键应位于调用者hash条目数据结构的开始位置.
*/
typedef struct HASHELEMENT
{
//链接到相同桶中的下一个条目
struct HASHELEMENT *link; /* link to next entry in same bucket */
//该条目的哈希函数结果
uint32 hashvalue; /* hash function result for this entry */
} HASHELEMENT;
/* Hash table header struct is an opaque type known only within dynahash.c */
//哈希表头部结构,非透明类型,用于dynahash.c
typedef struct HASHHDR HASHHDR;
/* Hash table control struct is an opaque type known only within dynahash.c */
//哈希表控制结构,非透明类型,用于dynahash.c
typedef struct HTAB HTAB;
/* Parameter data structure for hash_create */
//hash_create使用的参数数据结构
/* Only those fields indicated by hash_flags need be set */
//根据hash_flags标记设置相应的字段
typedef struct HASHCTL
{
//分区个数(必须是2的幂)
long num_partitions; /* # partitions (must be power of 2) */
//段大小
long ssize; /* segment size */
//初始化目录大小
long dsize; /* (initial) directory size */
//dsize上限
long max_dsize; /* limit to dsize if dir size is limited */
//填充因子
long ffactor; /* fill factor */
//哈希键大小(字节为单位)
Size keysize; /* hash key length in bytes */
//参见上述数据结构注释
Size entrysize; /* total user element size in bytes */
//
HashValueFunc hash; /* hash function */
HashCompareFunc match; /* key comparison function */
HashCopyFunc keycopy; /* key copying function */
HashAllocFunc alloc; /* memory allocator */
MemoryContext hcxt; /* memory context to use for allocations */
//共享内存中的哈希头部结构地址
HASHHDR *hctl; /* location of header in shared mem */
} HASHCTL;
/* A hash bucket is a linked list of HASHELEMENTs */
//哈希桶是HASHELEMENTs链表
typedef HASHELEMENT *HASHBUCKET;
/* A hash segment is an array of bucket headers */
//hash segment是桶数组
typedef HASHBUCKET *HASHSEGMENT;
/*
* Hash functions must have this signature.
* Hash函数必须有它自己的标识
*/
typedef uint32 (*HashValueFunc) (const void *key, Size keysize);
/*
* Key comparison functions must have this signature. Comparison functions
* return zero for match, nonzero for no match. (The comparison function
* definition is designed to allow memcmp() and strncmp() to be used directly
* as key comparison functions.)
* 哈希键对比函数必须有自己的标识.
* 如匹配则对比函数返回0,不匹配返回非0.
* (对比函数定义被设计为允许在对比键值时可直接使用memcmp()和strncmp())
*/
typedef int (*HashCompareFunc) (const void *key1, const void *key2,
Size keysize);
/*
* Key copying functions must have this signature. The return value is not
* used. (The definition is set up to allow memcpy() and strlcpy() to be
* used directly.)
* 键拷贝函数必须有自己的标识.
* 返回值无用.
*/
typedef void *(*HashCopyFunc) (void *dest, const void *src, Size keysize);
/*
* Space allocation function for a hashtable --- designed to match malloc().
* Note: there is no free function API; can't destroy a hashtable unless you
* use the default allocator.
* 哈希表的恐惧分配函数 -- 被设计为与malloc()函数匹配.
* 注意:这里没有释放函数API;不能销毁哈希表,除非使用默认的分配器.
*/
typedef void *(*HashAllocFunc) (Size request);其结构如下图所示: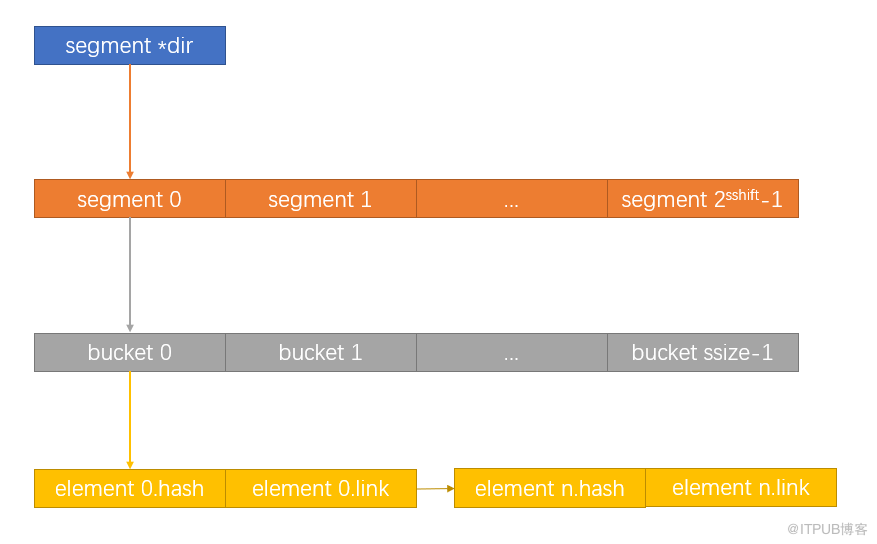
测试脚本
\pset footer off \pset tuples_only on \o /tmp/drop.sql SELECT 'drop table if exists tbl' || id || ' ;' as "--" FROM generate_series(1, 20000) AS id; \i /tmp/drop.sql \pset footer off \pset tuples_only on \o /tmp/create.sql SELECT 'CREATE TABLE tbl' || id || ' (id int);' as "--" FROM generate_series(1, 10000) AS id; begin; \o /tmp/ret.txt \i /tmp/create.sql
跟踪分析
...
HASHSEGMENT *dir --> HASHELEMENT ***dir;
dir --> HASHELEMENT ***
(gdb) p *hctl
$1 = {freeList = {{mutex = 0 '\000', nentries = 312, freeList = 0x7fd906ab84c0}, {mutex = 0 '\000',
nentries = 298, freeList = 0x7fd907097c40}, {mutex = 0 '\000', nentries = 292,
freeList = 0x7fd906ac2520}, {mutex = 0 '\000', nentries = 321, freeList = 0x7fd906ac8120}, {
mutex = 0 '\000', nentries = 341, freeList = 0x7fd907229980}, {mutex = 0 '\000', nentries = 334,
freeList = 0x7fd906ad3f08}, {mutex = 0 '\000', nentries = 316, freeList = 0x7fd906ad6fb8}, {
mutex = 0 '\000', nentries = 299, freeList = 0x7fd906ade550}, {mutex = 0 '\000', nentries = 328,
freeList = 0x7fd906ae1600}, {mutex = 0 '\000', nentries = 328, freeList = 0x7fd906ae62e8}, {
mutex = 0 '\000', nentries = 308, freeList = 0x7fd906aeb660}, {mutex = 0 '\000', nentries = 327,
freeList = 0x7fd90706f338}, {mutex = 0 '\000', nentries = 346, freeList = 0x7fd906af6bc0}, {
mutex = 0 '\000', nentries = 323, freeList = 0x7fd907237bc0}, {mutex = 0 '\000', nentries = 304,
freeList = 0x7fd9071ddb40}, {mutex = 0 '\000', nentries = 311, freeList = 0x7fd906b06238}, {
mutex = 0 '\000', nentries = 292, freeList = 0x7fd90707b620}, {mutex = 0 '\000', nentries = 303,
freeList = 0x7fd90723dd20}, {mutex = 0 '\000', nentries = 302, freeList = 0x7fd906b137e0}, {
mutex = 0 '\000', nentries = 307, freeList = 0x7fd9070873c8}, {mutex = 0 '\000', nentries = 314,
freeList = 0x7fd90723bb68}, {mutex = 0 '\000', nentries = 279, freeList = 0x7fd906b22678}, {
mutex = 0 '\000', nentries = 297, freeList = 0x7fd907073e08}, {mutex = 0 '\000', nentries = 309,
freeList = 0x7fd90721f888}, {mutex = 0 '\000', nentries = 317, freeList = 0x7fd906b33880}, {
mutex = 0 '\000', nentries = 283, freeList = 0x7fd907086168}, {mutex = 0 '\000', nentries = 331,
freeList = 0x7fd906b3d838}, {mutex = 0 '\000', nentries = 330, freeList = 0x7fd906b41f38}, {
mutex = 0 '\000', nentries = 313, freeList = 0x7fd906b46440}, {mutex = 0 '\000', nentries = 304,
freeList = 0x7fd906b4b5c0}, {mutex = 0 '\000', nentries = 310, freeList = 0x7fd90720ed80}, {
mutex = 0 '\000', nentries = 323, freeList = 0x7fd906b575a0}}, dsize = 256, nsegs = 16,
max_bucket = 4095, high_mask = 8191, low_mask = 4095, keysize = 16, entrysize = 152, num_partitions = 16,
ffactor = 1, max_dsize = 256, ssize = 256, sshift = 8, nelem_alloc = 48}
(gdb) p *hashp
$2 = {hctl = 0x7fd906aae980, dir = 0x7fd906aaecd8, hash = 0xa79ac6 <tag_hash>, match = 0x47cb70 <memcmp@plt>,
keycopy = 0x47d0a0 <memcpy@plt>, alloc = 0x8c3419 <ShmemAllocNoError>, hcxt = 0x0,
tabname = 0x160f1d0 "LOCK hash", isshared = true, isfixed = false, frozen = false, keysize = 16,
ssize = 256, sshift = 8}
(gdb) p *hashp->dir
$3 = (HASHSEGMENT) 0x7fd906aaf500
(gdb) p hashp->dir
$4 = (HASHSEGMENT *) 0x7fd906aaecd8
(gdb) p **hashp->dir
$5 = (HASHBUCKET) 0x7fd907212dd0
(gdb) p ***hashp->dir
$6 = {link = 0x7fd9071a7b90, hashvalue = 1748602880}
(gdb) n
949 if (action == HASH_ENTER || action == HASH_ENTER_NULL)
(gdb)
956 if (!IS_PARTITIONED(hctl) && !hashp->frozen &&
(gdb)
965 bucket = calc_bucket(hctl, hashvalue); --> hash桶
(gdb)
967 segment_num = bucket >> hashp->sshift; --> 桶号右移8位得到段号
(gdb)
968 segment_ndx = MOD(bucket, hashp->ssize); --> 桶号取模得到段内偏移
(gdb)
970 segp = hashp->dir[segment_num]; --> 获取段(HASHELEMENT **)
(gdb)
972 if (segp == NULL)
(gdb) p bucket
$7 = 2072
(gdb) p segment_num
$8 = 8
(gdb) p segment_ndx
$9 = 24
(gdb) p segp -->
$10 = (HASHSEGMENT) 0x7fd906ab3500
(gdb)
(gdb) n
975 prevBucketPtr = &segp[segment_ndx]; --> HASHELEMENT **
(gdb)
976 currBucket = *prevBucketPtr; --> HASHELEMENT *
(gdb)
981 match = hashp->match; /* save one fetch in inner loop */
(gdb) p prevBucketPtr
$12 = (HASHBUCKET *) 0x7fd906ab35c0
(gdb) p currBucket
$13 = (HASHBUCKET) 0x7fd90714da68
(gdb)感谢各位的阅读,以上就是“分析PostgreSQL中的数据结构HTAB”的内容了,经过本文的学习后,相信大家对分析PostgreSQL中的数据结构HTAB这一问题有了更深刻的体会,具体使用情况还需要大家实践验证。这里是亿速云,小编将为大家推送更多相关知识点的文章,欢迎关注!
免责声明:本站发布的内容(图片、视频和文字)以原创、转载和分享为主,文章观点不代表本网站立场,如果涉及侵权请联系站长邮箱:is@yisu.com进行举报,并提供相关证据,一经查实,将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容。