SAP has the following objectives behind the introduction of the New General Ledger:
The following table gives the business requirements at the backend which prompts the finance department of the comapny to go for NEW GL implementation.
| S.N | Business Requirements | New GL Functionality |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Reporting as per different GAAP | Concept of multile ledgers- leading and non leading ledgers |
| 2 | Unified Mangement & legal reporting | Profit Centre integrated with the New ledger |
| 3 | Requirement of segmental reporting(in line with US GAAP) | Segment can be defined as an enterprise element |
| 4 | Financial statement below company code level | Document spilt functionality |
| 5 | Reporting as per cost of sales accounting | Functional area included |
Each one of these functionality is unique and elaborate and has the features ingrained to meet the different requirements emerging for the external reporting purpose.
A leading ledger is defined and additional ledgers are defined for parallel accounting or management reporting by assigning different characteristic values and fiscal-year definitions
Additional ledgers can be defined - Leading Ledger & Non-leading ledgers are created and maintained, with only one accounting entry.
The new general ledger uses the special-purpose ledger techniques to save total values.
All Company Codes are assigned to a Leading ledger for each client, which contains the group-valuation view. Additional ledgers can be defined for each company code.
Additional ledgers can be used for parallel accounting or management reporting by assigning different characteristic values and fiscal-year definitions.
For general-ledger account postings that have a specified cost center, the system always reconciles the profit center and general-ledger account simultaneously, since the data is stored in the same table.
Two views of the new General Ledger:
Ø Regular entry view &
Ø General-Ledger view
Elimination of following activities
Document splitting means the document is split according to the proportions of the account assignments in the expense or revenue lines of the original document. Examples: Cash discounts and realized exchange rate differences are split according to the source document.
Example: Creation of balance sheets at the segment or
profit-center level or balance sheets based on company-specific or
industry-specific entities
Three new tables in the new general ledger handle totals, store general-ledger and specific line items, and calculate valuations for year-end closings in parallel ledgers
Two new tables (FAGLFLEXA & FAGLFLEXP) store the ledger-specific line items (Actual & Planned) & contain additional information for use in the entry view. The tables help in updating different characteristics and document splitting information, different period shifts, and different currencies in specific ledgers for individual documents. Helps in preparing reports for specific dimensions at item level.
The third table (BSEG_ADD) contains documents that are posted in connection with valuations for year-end closing in selected parallel ledgers. However, these documents are inapplicable if one do not use parallel accounting or use the accounting approach to portray parallel accounting.
In addition to the three tables, own table can be defined using FAGLFLEXT as template
The new totals table contains additional standard fields for storing totals. This standard table can activate support for many scenarios by customizing the software. It supports Segment Reporting, Profit-Center updating, Cost-of-Sales accounting, Cost-center updating, Preparation for consolidation and Business-area updating
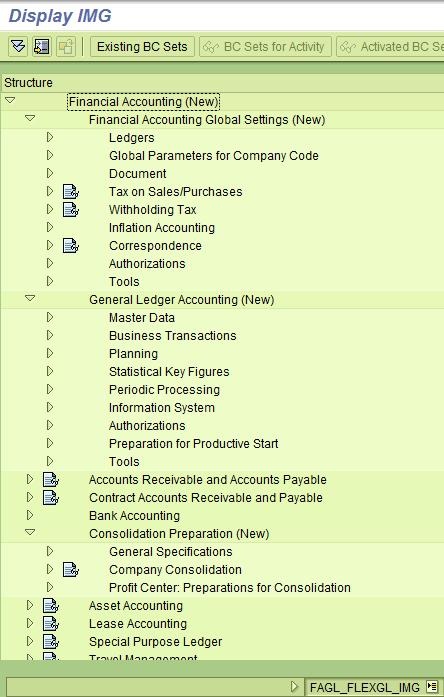
Customization of the NewGL is reusing the nodes of the original GL,
but now has additional branches. e.g. Ledgers. The shell transaction is
FAGL_FLEXGL_IMG.
亿速云「云服务器」,即开即用、新一代英特尔至强铂金CPU、三副本存储NVMe SSD云盘,价格低至29元/月。点击查看>>
免责声明:本站发布的内容(图片、视频和文字)以原创、转载和分享为主,文章观点不代表本网站立场,如果涉及侵权请联系站长邮箱:is@yisu.com进行举报,并提供相关证据,一经查实,将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容。
原文链接:http://blog.itpub.net/81815/viewspace-1034292/