JAVA中怎么利用二叉树对递归进行遍历?相信很多没有经验的人对此束手无策,为此本文总结了问题出现的原因和解决方法,通过这篇文章希望你能解决这个问题。
一.基本概念
二叉树有5种基本形态:
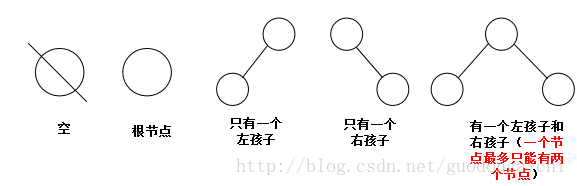
注:二叉树有序树,就是说一个节点的左右节点是有大小之分的,我们通常设定为左孩子一定大于右孩子,下面的实现都是基于这个规则的。二叉树分为三种:满二叉树,完全二叉树,不完全二叉树
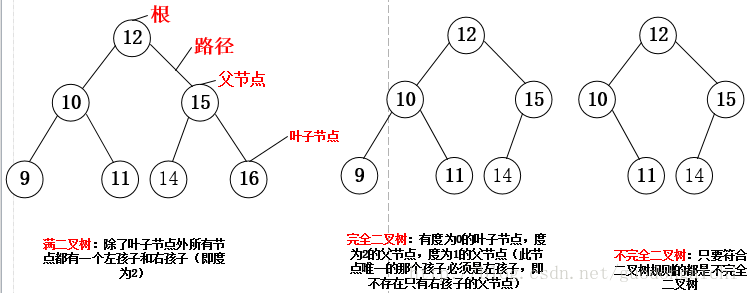
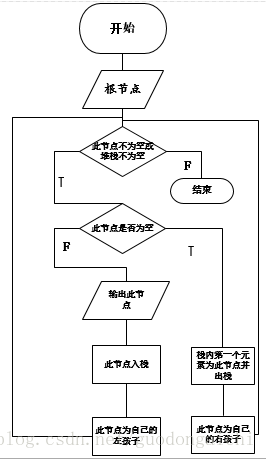
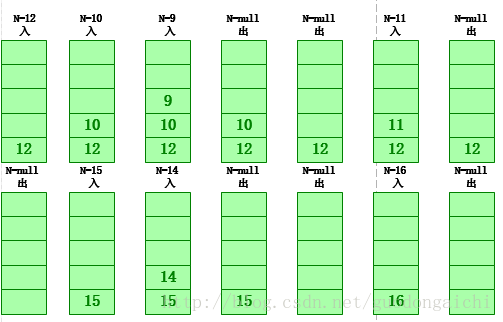
二叉树的四种遍历:层次,先序,中序,后序首先是非递归实现上图的满二叉树:1.先序:根左右,用栈来实现,下面是它的流程图和入栈出栈的状态图(n是每个节点的值) 输出:12,10,9,11,15,14,16
2.中序:左根右,用栈来实现,中序的堆栈状态和先序一样,只是输出的位置不同,先序在入栈前输出,中序在出栈后输出 输出:9,10,11,12,14,15,16
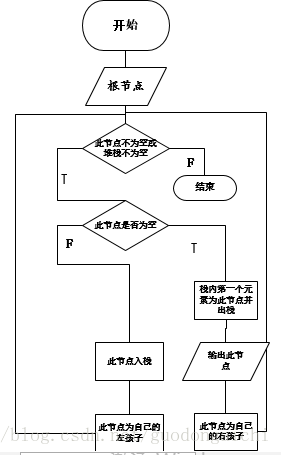
3.后序:左右根,采用了两个栈 输出:9,11,10,14,16,15,12
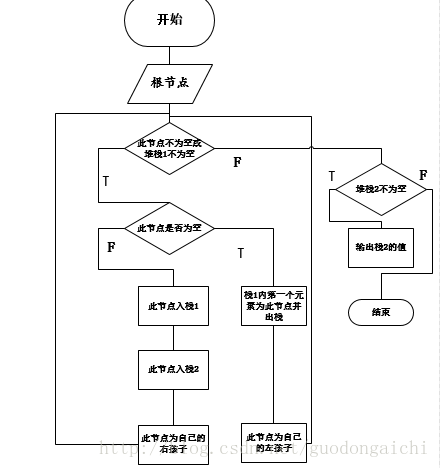
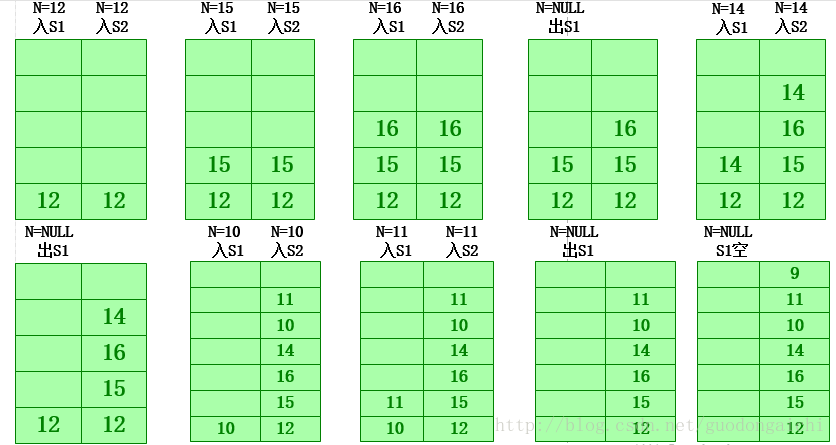
下面是实现的代码:
//创建一个节点类
class Node {
public int key;//节点的值
public String Data;//节点存储的内容
public Node leftNode;//左孩子
public Node rightNode;//右孩子
//节点类的构造方法
public Node(int key,String Data){
this.key=key;
this.Data=Data;
this.leftNode=null;
this.rightNode=null;
}
//得到数据
public int getKey(){
return key;
}
}
public class BinaryTree {
public Node root;
public int h=0;
//插入数据
public void insert(int key,String Data){
//实例化一个节点
Node newNode=new Node(key, Data);
//判断此二叉树是否有根节点
if(root==null){
root=newNode;
}
else
{
Node current=root;
Node parent;
while(true){
parent=current;
//判断大小,决定新节点是放在左边还是右边
if(key<current.key){
current=current.leftNode;//往左子树方向找
if(current==null){
parent.leftNode=newNode;//找到叶子节点
return;
}//叶子节点的If end;
}//左子树的If end;
else{
current=current.rightNode;
if(current==null){
parent.rightNode=newNode;
return;
}//叶子
}//右子树
}
}
}//insert end;
//打印
public void printlTree(Node node){
System.out.print("*");
System.out.print(node.getKey());
}
//深度
public int Height(Node node){
if(node==null){
return 0;
}
else{
int i=Height(node.leftNode);
int j=Height(node.rightNode);
return (i>j)?(i+1):(j+1);
}
}
//节点个数
public int NodeNum(Node node){
if(node==null){
return 0;
}
return NodeNum(node.leftNode)+NodeNum(node.rightNode)+1;
}
//第K层节点的个数
public int getLeafNodeNum(Node node,int i){
if(node==null){
return 0;
}
else{
if(i==0){
return 1;
}
else{
int numLeft=getLeafNodeNum(node.leftNode,i-1);
int numRight=getLeafNodeNum(node.rightNode,i-1);
return (numLeft+numRight);
}
}
}
//分层遍历
public void LevelOrder(Node node){
Queue<Node> queue=new LinkedList<Node>();
if(node==null){
return;
}
queue.add(node);
while(!queue.isEmpty()){
Node temp=queue.poll();
System.out.print("*");
System.out.print(temp.getKey());
if(temp.leftNode!=null){
queue.add(temp.leftNode);
}
if(temp.rightNode!=null){
queue.add(temp.rightNode);
}
}
}
//递归前序遍历
public void preOrder(Node node){
if(node!=null){
printlTree(node);
preOrder(node.leftNode);
preOrder(node.rightNode);
}
}
//非递归前序遍历
public void NpreOrder(Node node){
Stack<Node> sk=new Stack<Node>();
Node n=node;
while(!sk.isEmpty()||n!=null){
if(n!=null){
System.out.print("<<<");
System.out.print(n.getKey());
sk.push(n);
n=n.leftNode;
}
else{
n=sk.pop();;
n=n.rightNode;
}
}
}
//中序遍历
public void inOrder(Node node){
if(node!=null){
preOrder(node.leftNode);
printlTree(node);
preOrder(node.rightNode);
}
}
//非递归的中序遍历
public void NinOrder(Node node){
Stack<Node> s=new Stack<Node>();
Node n=node;
while(n!=null||!s.isEmpty()){
if(n!=null){
s.push(n);
n=n.leftNode;
}
else{
n=s.pop();
System.out.println(n.getKey());
n=n.rightNode;
}
}
}
//后序遍历
public void postOrder(Node node){
if(node!=null){
preOrder(node.leftNode);
preOrder(node.rightNode);
printlTree(node);
}
}
//非递归后序遍历
public void NpostOrder(Node node){
Stack<Node> s1=new Stack<Node>();//第一次入栈
Stack<Node> s2=new Stack<Node>();//第二次入栈
Node n=node;
while(!s1.isEmpty()||n!=null){
if(n!=null){
s1.push(n);
s2.push(n);
n=n.rightNode;
}
else{
n=s1.pop();
n=n.leftNode;
}
}
while(!s2.isEmpty()){
System.out.println("((("+s2.pop().getKey());
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
BinaryTree bt=new BinaryTree();
bt.insert(12, "A");
bt.insert(10, "B");
bt.insert(15, "C");
bt.insert(9, "D");
bt.insert(11, "E");
bt.insert(14, "F");
bt.insert(16, "G");
System.out.println("这个二叉树的深度:"+bt.Height(bt.root));
System.out.println("这个二叉树的节点个数:"+bt.NodeNum(bt.root));
System.out.println("前序遍历:");
bt.preOrder(bt.root);
System.out.println();
System.out.println("非递归前序遍历:");
bt.NpreOrder(bt.root);
System.out.println();
System.out.println("中序遍历:");
bt.inOrder(bt.root);
System.out.println();
System.out.println("非递归中序遍历:");
bt.NinOrder(bt.root);
System.out.println();
System.out.println("后序遍历:");
bt.postOrder(bt.root);
System.out.println();
System.out.println("非递归后序遍历:");
bt.NpostOrder(bt.root);
System.out.println();
System.out.println("分层遍历:");
bt.LevelOrder(bt.root);
System.out.println();
System.out.println("第二层有"+bt.getLeafNodeNum(bt.root, 2));
}
}看完上述内容,你们掌握JAVA中怎么利用二叉树对递归进行遍历的方法了吗?如果还想学到更多技能或想了解更多相关内容,欢迎关注亿速云行业资讯频道,感谢各位的阅读!
亿速云「云服务器」,即开即用、新一代英特尔至强铂金CPU、三副本存储NVMe SSD云盘,价格低至29元/月。点击查看>>
免责声明:本站发布的内容(图片、视频和文字)以原创、转载和分享为主,文章观点不代表本网站立场,如果涉及侵权请联系站长邮箱:is@yisu.com进行举报,并提供相关证据,一经查实,将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容。