这篇文章主要为大家分享Linux操作目录和文件的常用命令。文中还介绍了linux的目录结构以及vi文本编辑器的使用方法,希望大家通过这篇文章能有所收获。
Linux目录结构采用树形目录结构,包含根目录和子目录。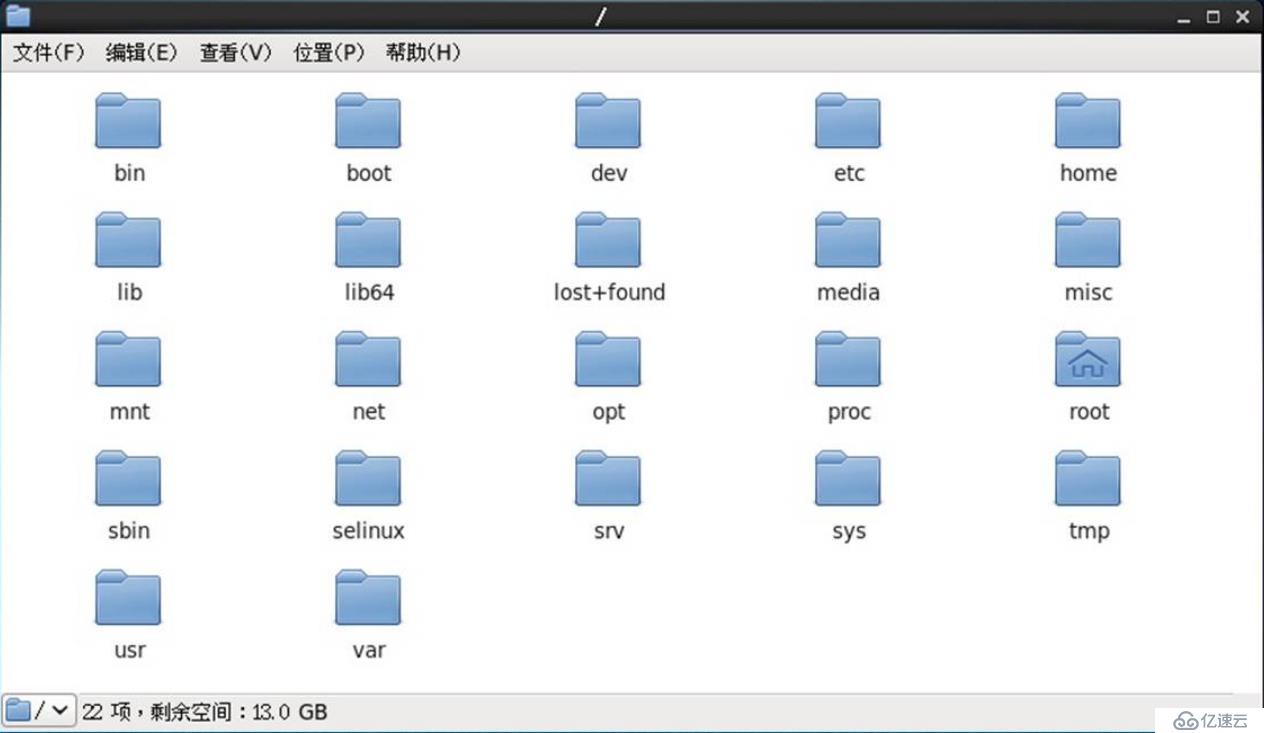
所有分区、目录、文件等的位置起点,整个树形目录结构中,使用独立的一个“/”表示。
常见的子目录如/root、/bin、/boot、/dev、/etc、/home、/var、/usr、/sbin。

cat用于一次性显示文件全部内容。基本语法格式如下:
应用举例:
[root@centos01 ~]# cat /etc/hosts
127.0.0.1 localhost localhost.localdomain localhost4 localhost4.localdomain4
::1 localhost localhost.localdomain localhost6 localhost6.localdomain6
[root@centos01 ~]# cat /etc/sysconfig/network
# Created by anaconda
[root@centos01 ~]# cat /etc/sysconfig/network /etc/hosts
# Created by anaconda
127.0.0.1 localhost localhost.localdomain localhost4 localhost4.localdomain4
::1 localhost localhost.localdomain localhost6 localhost6.localdomain6more用于全屏模式分页显示文件内容。基本语法格式如下:
交互操作方法:
按Enter键向下逐行滚动;
按空格键向下翻一屏;
- 按q键退出;
应用举例:
[root@centos01 ~]# more /etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf
#
# This is the main Apache HTTP server configuration file. It contains the
# configuration directives that give the server its instructions.
# See <URL:http://httpd.apache.org/docs/2.4/> for detailed information.
# In particular, see
# <URL:http://httpd.apache.org/docs/2.4/mod/directives.html>
--More--(2%)less命令的作用与more命令相同,但扩展功能更多。基本语法格式如下:
交互操作方法:
Page Up键:向上翻页;
Page Down键:向下翻页;
“/”键:查找关键内容;
“n”:查找下一个关键内容;
- “N”:查找上一个关键内容;
其他功能与more命令基本类似;
head、tail命令的基本语法格式如下:

head:查看文件开头的一部分内容(默认为10行);
- tail:查看文件结尾的一部分内容(默认为10行);
应用举例:
[root@centos01 ~]# head -2 /var/log/messages <!--显示文件的开始2行内容-->
Jan 10 20:20:01 centos01 systemd: Started Session 9 of user root.
Jan 10 20:20:01 centos01 systemd: Starting Session 9 of user root.
[root@centos01 ~]#
[root@centos01 ~]# tail -3 /var/log/messages <!--显示文件的最后3行内容-->
Jan 10 23:10:01 centos01 systemd: Starting Session 30 of user root.
Jan 10 23:20:01 centos01 systemd: Started Session 31 of user root.
Jan 10 23:20:01 centos01 systemd: Starting Session 31 of user root.
[root@centos01 ~]#
[root@centos01 ~]# tail -f /var/log/messages
<!--动态跟踪文件尾部内容,便于实时监控文件内容的变化
(按Ctrl+c组合键终止)-->
Jan 10 23:01:01 centos01 systemd: Starting Session 29 of user root.
Jan 10 23:03:19 centos01 yum[11583]: Installed: httpd-tools-2.4.6-67.el7.centos.x86_64
Jan 10 23:03:19 centos01 yum[11583]: Installed: mailcap-2.1.41-2.el7.noarch
Jan 10 23:03:20 centos01 systemd: Reloading.
Jan 10 23:03:20 centos01 yum[11583]: Installed: httpd-2.4.6-67.el7.centos.x86_64
Jan 10 23:03:20 centos01 journal: g_dbus_interface_skeleton_unexport: assertion 'interface_->priv->connections != NULL' failed
Jan 10 23:10:01 centos01 systemd: Started Session 30 of user root.
Jan 10 23:10:01 centos01 systemd: Starting Session 30 of user root.
Jan 10 23:20:01 centos01 systemd: Started Session 31 of user root.
Jan 10 23:20:01 centos01 systemd: Starting Session 31 of user root.wc用于统计文件中的单词数量、(Word Count)、行数、字节数等。基本语法格式如下:
wc常用选项如下:
-l:统计行数;
-w:统计单词个数;
- -c:统计字节数;
应用举例:
[root@centos01 ~]# wc -l /etc/passwd <!--统计文件行数-->
41 /etc/passwd
[root@centos01 ~]# wc -w /etc/passwd <!--统计文件中单词个数-->
81 /etc/passwd
[root@centos01 ~]# wc -c /etc/passwd <!--统计文件中字节数-->
2104 /etc/passwd
[root@centos01 ~]# wc /etc/passwd
<!--不加选项统计顺序依次是43行,85个单词,2223个字节-->
43 85 2223 /etc/passwd
[root@centos01 ~]# find /etc -name "*.conf" | wc -l
<!--统计/etc下有多少个以*.conf为后缀的文件数量-->
437 grep命令用于在文件中查找并显示包含指定字符串的行。基本语法格式如下:
grep命令常用选项如下:
-i:查找时忽略大小写;
- -v:反转查找,输出与条件不相符的行;
grep查找条件设置:
要查找的字符串以双引号括起来;
“^......”:表示查找以......开头的字符串;
“......$”:表示查找以......结尾的字符串;
- “^$”:表示查找空行;
应用举例:
[root@centos01 ~]# grep -i "SSHD" /etc/passwd
<!--查询sshd用户忽略大小写显示出来-->
sshd:x:74:74:Privilege-separated SSH:/var/empty/sshd:/sbin/nologin
[root@centos01 ~]# grep "ftp" /etc/passwd
<!--查询ftp用户显示出来-->
ftp:x:14:50:FTP User:/var/ftp:/sbin/nologin
[root@centos01 ~]# grep -v "^#" /etc/yum.conf | grep -v "^$"
<!--过滤/etc/yum.conf中的注释行和空行-->
[main]
cachedir=/var/cache/yum/$basearch/$releasever
keepcache=0
debuglevel=2
logfile=/var/log/yum.log
exactarch=1
obsoletes=1
gpgcheck=1
plugins=1
installonly_limit=5
bugtracker_url=http://bugs.centos.org/set_project.php?project_id=23&ref=http://bugs.centos.org/bug_report_page.php?category=yum
distroverpkg=centos-release
应用举例:
<!--压缩和解压缩方法一(“-9”选项代表高压缩)-->
[root@centos01 ~]# ls
anaconda-ks.cfg CentOS-7.4-x86_64-1708.iso initial-setup-ks.cfg
[root@centos01 ~]# gzip -9 initial-setup-ks.cfg
[root@centos01 ~]# ls
anaconda-ks.cfg CentOS-7.4-x86_64-1708.iso initial-setup-ks.cfg.gz
[root@centos01 ~]# gzip -d initial-setup-ks.cfg.gz
[root@centos01 ~]# ls
anaconda-ks.cfg CentOS-7.4-x86_64-1708.iso initial-setup-ks.cfg
<!--压缩和解压缩方法二(不加选项进行压缩,解压缩使用gunzip命令)-->
[root@centos01 ~]# ls
anaconda-ks.cfg CentOS-7.4-x86_64-1708.iso initial-setup-ks.cfg
[root@centos01 ~]# gzip initial-setup-ks.cfg
[root@centos01 ~]# ls
anaconda-ks.cfg CentOS-7.4-x86_64-1708.iso initial-setup-ks.cfg.gz
[root@centos01 ~]# gunzip initial-setup-ks.cfg.gz
[root@centos01 ~]# ls
anaconda-ks.cfg CentOS-7.4-x86_64-1708.iso initial-setup-ks.cfg
应用举例:
<!--方法一-->
[root@centos01 ~]# ls
anaconda-ks.cfg CentOS-7.4-x86_64-1708.iso initial-setup-ks.cfg
[root@centos01 ~]# bzip2 -9 initial-setup-ks.cfg <!--高速压缩-->
[root@centos01 ~]# ls
anaconda-ks.cfg CentOS-7.4-x86_64-1708.iso initial-setup-ks.cfg.bz2
[root@centos01 ~]# bzip2 -d initial-setup-ks.cfg.bz2 <!--解压缩-->
[root@centos01 ~]# ls
anaconda-ks.cfg CentOS-7.4-x86_64-1708.iso initial-setup-ks.cfg
<!--方法二-->
[root@centos01 ~]# ls
anaconda-ks.cfg CentOS-7.4-x86_64-1708.iso initial-setup-ks.cfg
[root@centos01 ~]# bzip2 initial-setup-ks.cfg <!--压缩-->
[root@centos01 ~]# ls
anaconda-ks.cfg CentOS-7.4-x86_64-1708.iso initial-setup-ks.cfg.bz2
[root@centos01 ~]# bunzip2 initial-setup-ks.cfg.bz2 <!--解压缩-->
[root@centos01 ~]# ls
anaconda-ks.cfg CentOS-7.4-x86_64-1708.iso initial-setup-ks.cfgtar命令制作归档文件、释放归档文件。基本语法格式如下:
tar命令常用选项如下:
-c:创建.tar格式的包文件;
-x:解开.tar格式的包文件;
-v:输出详细信息;
-f:表示使用归档文件;
-p:打包时保留原始文件及目录的权限;
-t:列表查看包内的文件;
-C:解包时指定释放的目标文件夹;
-z:调用gzip程序进行压缩或解压;
- -j:调用bzip2程序进行压缩或解压;
应用举例:
[root@centos01 ~]# tar zcvf yun.gz yun/ <!--使用tar命令调用gzip将yun归档为yun.gz-->
yun/
[root@centos01 ~]# ls
1.txt anaconda-ks.cfg initial-setup-ks.cfg www yun yun.gz
[root@centos01 ~]# tar zxvf yun.gz -C /usr/src/
<!--将压缩文件yun.gz解压缩到/usr/src目录中-->
yun/
[root@centos01 ~]# cd /usr/src/
[root@centos01 src]# ls
debug kernels yun
[root@centos01 ~]# tar jcvf yun.bz2 ./yun
<!--使用tar命令调用bzip将yun目录数据进行压缩-->
[root@centos01 ~]# tar jxvf yun.bz2 -C /usr/src/
<!--将yun.bz2压缩文件解压缩到/usr/src/目录中-->
./yun/
[root@centos01 ~]# cd /usr/src/
[root@centos01 src]# ls
debug kernels yun选项和参数:
if:input file(原文件)也可以是设备;
of:output file(备份后的文件)也可以是设备;
bs:规划的一个block(块)的大小,若未指定则默认是512Bytes(字节);
- count:多少块的意思。
应用举例:
[root@centos01 ~]# dd if=/dev/zero of=/usr/src/1.iso bs=30M count=10
<!--将/dev/zero文件中的信息复制到/usr/src目录下创建一个1.iso的文件,一次30M,10次-->
记录了10+0 的读入
记录了10+0 的写出
314572800字节(315 MB)已复制,0.212995 秒,1.5 GB/秒
[root@centos01 ~]# cd /usr/src/
[root@centos01 src]# ls
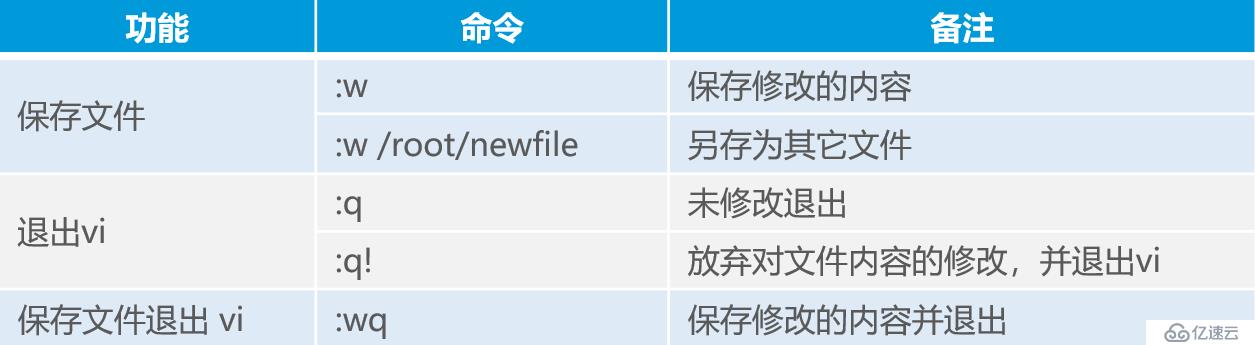
1.iso debug kernels创建或者修改文本文件,维护Linux系统中的各种配置文件。
vi:类Unix系统中默认的文本编辑器;
命令模式、输入模式、末行模式。不同模式之间的切换如下: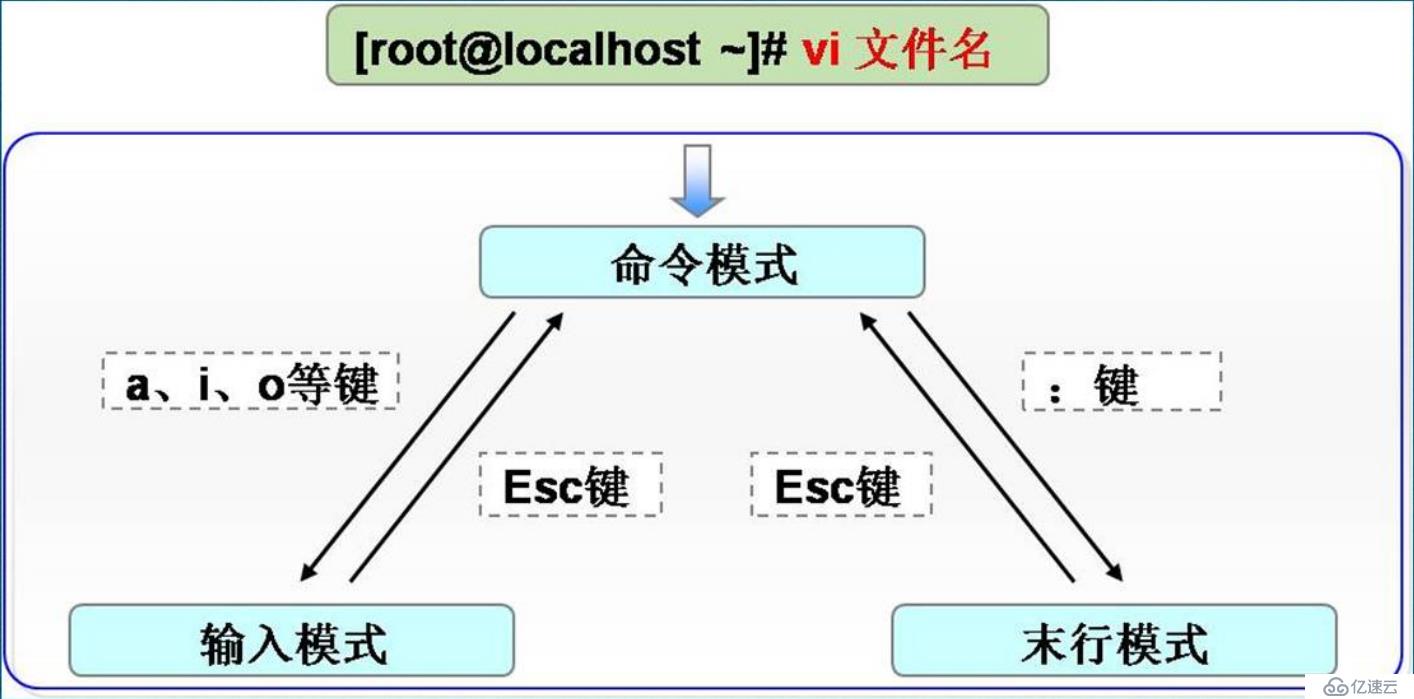
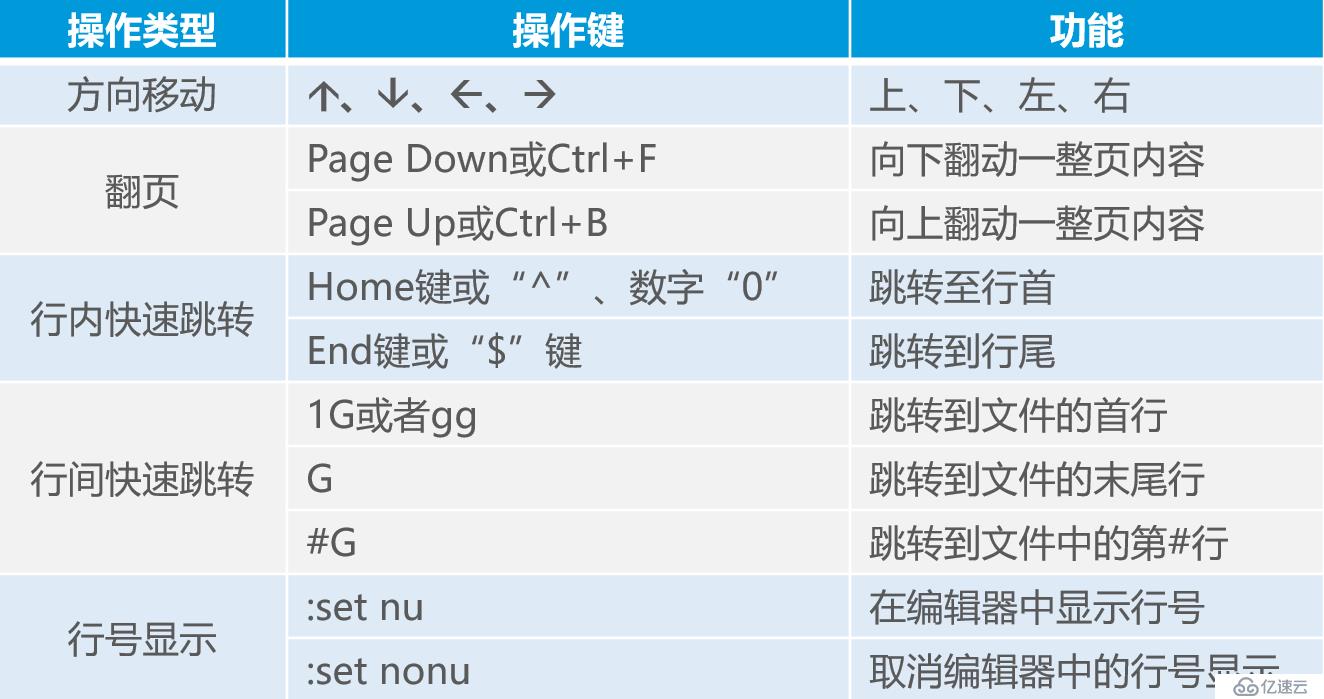
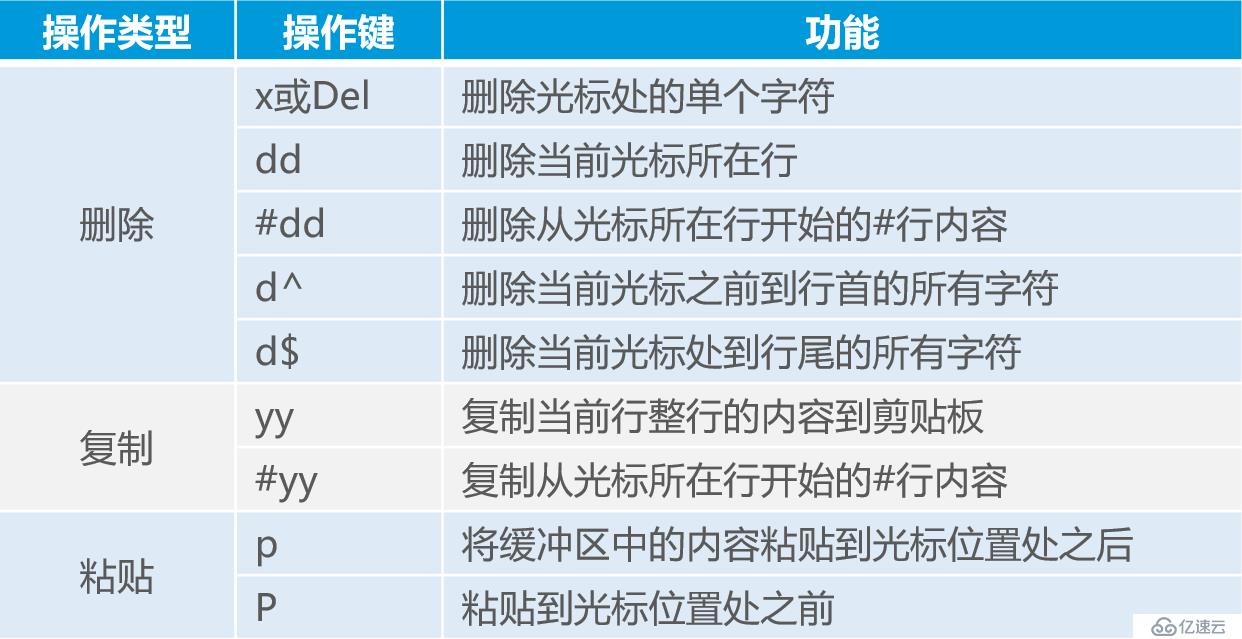




看完上述内容,你们对linux的常用命令有进一步的了解吗?如果还想学到更多技能或想了解更多相关内容,欢迎关注亿速云行业资讯频道,感谢各位的阅读。
免责声明:本站发布的内容(图片、视频和文字)以原创、转载和分享为主,文章观点不代表本网站立场,如果涉及侵权请联系站长邮箱:is@yisu.com进行举报,并提供相关证据,一经查实,将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容。