小编给大家分享一下如何建立一个Ansible实验室,相信大部分人都还不怎么了解,因此分享这篇文章给大家参考一下,希望大家阅读完这篇文章后大有收获,下面让我们一起去了解一下吧!
本方案使用以下工具和软件:
Ansible 是我们选择的自动化工具,因为它易于使用,而且足够灵活,可以满足实验室的要求。
Vagrant 易于使用,用于构建和维护虚拟机。
VirtualBox 是一个托管管理程序,可以在 Windows 和 Linux 环境中使用。
Fedora v30+ 是我本地机器上的操作系统。
你必须进行以下设置才能建立环境:
一个互联网连接
在 BIOS 中启用虚拟化技术支持(以下是在我的联想笔记本上的过程)
Vagrant v2.2.9
最新版本的 Ansible
最新版本的 VirtualBox
Fedora v30+ 宿主机操作系统
这个项目旨在部署一个带有 Ansible 引擎和多个 Linux 节点的 Ansible 主机,以及一些预加载和预配置的应用程序(httpd 和 MySQL)。它还启用了 Cockpit,这样你就可以在测试过程中监控虚拟机(VM)的状态。使用预部署的应用程序的原因是为了提高效率(所以你不必花时间安装这些组件)。这样你就可以专注于创建角色和剧本,并针对上述工具部署的环境进行测试。
我们确定,对于我们的用例来说,最好的方案是多机 Vagrant 环境。Vagrant 文件创建了三个 CentOS 虚拟机,以模拟两个目标主机和一个 Ansible 控制机。
Host1: 没有图形用户界面(GUI),安装 httpd 和 MySQL
Host2: 没有 GUI,安装了 httpd 和 MySQL
Ansible-host:没有 GUI,安装了 Ansible 引擎
如果使用了多个管理程序,一些管理程序可能不允许你拉起虚拟机。要解决这个问题,请遵循以下步骤(基于 Vagrant 的安装说明)。
首先,找出管理程序的名称:
$ lsmod | grep kvmkvm_intel 204800 6kvm 593920 1 kvm_intelirqbypass 16384 1 kvm
我感兴趣的是 kvm_intel,但你可能需要另一个(比如 kvm_amd)。
以 root 身份运行以下内容,将该管理程序列入黑名单:
$ echo 'blacklist kvm-intel' >> /etc/modprobe.d/blacklist.conf
重新启动你的机器并尝试再次运行 Vagrant。
cat Vagrantfile
# -*- mode: ruby -*-# vi: set ft=ruby : Vagrant.configure("2") do |config|# Define VMs with static private IP addresses, vcpu, memory and vagrant-box. boxes = [ { :name => "web1.demo.com", ⇒ Host1 this is one of the target nodes :box => "centos/8", ⇒ OS version :ram => 1024, ⇒ Allocated memory :vcpu => 1, ⇒ Allocated CPU :ip => "192.168.29.2" ⇒ Allocated IP address of the node }, { :name => "web2.demo.com", ⇒ Host2 this is one of the target nodes :box => "centos/8", :ram => 1024, :vcpu => 1, :ip => "192.168.29.3" }, { :name => "ansible-host", ⇒ Ansible Host with Ansible Engine :box => "centos/8", :ram => 8048, :vcpu => 1, :ip => "192.168.29.4" } ] # Provision each of the VMs. boxes.each do |opts| config.vm.define opts[:name] do |config|# Only Enable this if you are connecting to Proxy server# config.proxy.http = "http://usernam:password@x.y:80"⇒ Needed if you have a proxy# config.proxy.https = "http://usernam:password@x.y:80"# config.proxy.no_proxy = "localhost,127.0.0.1" config.vm.synced_folder ".", "/vagrant", id: "vagrant-root", disabled: true config.ssh.insert_key = false config.vm.box = opts[:box] config.vm.hostname = opts[:name] config.vm.provider :virtualbox do |v| ⇒ Defines the vagrant provider v.memory = opts[:ram] v.cpus = opts[:vcpu] end config.vm.network :private_network, ip: opts[:ip] config.vm.provision :file do |file| file.source = './keys/vagrant' ⇒ vagrant keys to allow access to the nodes file.destination = '/tmp/vagrant' ⇒ the location to copy the vagrant key end config.vm.provision :shell, path: "bootstrap-node.sh" ⇒ script that copy hosts entry config.vm.provision :ansible do |ansible| ⇒ declaration to run ansible playbook ansible.verbose = "v" ansible.playbook = "playbook.yml" ⇒ the playbook used to configure the hosts end end endend这些是你需要注意的重要文件。
inventory-test.yaml:连接到节点的清单文件
playbook.yaml:Vagrant 供应者调用的用于配置节点的剧本文件
`Vagrantfile':Vagrant 用来部署环境的文件
Vagrant 密钥文件:连接实验室环境中各节点的 Vagrant 密钥
你可以根据你的需要调整这些文件。Ansible 的灵活性使你有能力根据你的需要声明性地改变你的环境。
首先,克隆这个 GitHub 仓库 中的代码:
$ git clone https://github.com/mikecali/ansible-labs-101.gitCloning into 'ansible-labs-101'...remote: Enumerating objects: 15, done.remote: Counting objects: 100% (15/15), done.remote: Compressing objects: 100% (13/13), done.remote: Total 15 (delta 2), reused 10 (delta 0), pack-reused 0Unpacking objects: 100% (15/15), 6.82 KiB | 634.00 KiB/s, done.
接下来,将你的目录改为 vagrant-session-2,并查看其内容:
$ lsBootstrap-node.sh inventory keys playbook.yml README.md Vagrantfile
现在你已经拥有了实验室环境所需的所有工件和配置文件。要部署环境,请运行:
$ vagrant up
只要有一个像样的网络连接,只需要 20 分钟左右就可以得到一个运行环境:
$ vagrant upBringing machine 'web1.demo.com' up with 'virtualbox' provider...Bringing machine 'web2.demo.com' up with 'virtualbox' provider...Bringing machine 'ansible-host' up with 'virtualbox' provider...==> web1.demo.com: Importing base box 'centos/8'...==> web1.demo.com: Matching MAC address for NAT networking...==> web1.demo.com: Checking if box 'centos/8' version '1905.1' is up to date...==> web1.demo.com: Setting the name of the VM: ansible-labs_web1democom_1606434176593_70913==> web1.demo.com: Clearing any previously set network interfaces...==> web1.demo.com: Preparing network interfaces based on configuration... web1.demo.com: Adapter 1: nat web1.demo.com: Adapter 2: hostonly==> web1.demo.com: Forwarding ports... web1.demo.com: 22 (guest) => 2222 (host) (adapter 1)==> web1.demo.com: Running 'pre-boot' VM customizations...==> web1.demo.com: Booting VM...==> web1.demo.com: Waiting for machine to boot. This may take a few minutes... web1.demo.com: SSH address: 127.0.0.1:2222 web1.demo.com: SSH username: vagrant web1.demo.com: SSH auth method: private key[...]
一旦该剧本执行完成,你会看到这样的输出:
PLAY RECAP *********************************Ansible-host : ok=20 changed=11 unreachable=0 failed=0 skipped=0 rescued=0 ignored=3 Real 18m14.288sUser 2m26.978sSys 0m26.849s
确认所有虚拟机都在运行:
$ vagrant statusCurrent machine states: Web1.demo.com running (virtualbox)Web2.demo.com running (virtualbox)ansible-host running (virtualbox)[...]
你可以通过登录其中一个虚拟机进一步调查。访问 ansible-host:
> vagrant ssh ansible-hostActivate the web console with: systemctl enable --now cockpit.socket Last login: Thu Nov 26 12:21:23 2020 from 10.0.2.2[vagrant@ansible-host ~] uptime16:46:42 up 1:24, 1 user, load average: 0.00, 0.01, 0.04
最后,你可以使用 Ansible 模块来 ping 你创建的其他节点:
[vagrant@ansible-host]$ ansible -i inventory-test.yaml \webservers -m ping -u vagrant192.168.29.2 | SUCCESS => { "Ansible-facts": { "Discovered_interpreter_python": "/usr/libexec/platform-python" }, "Changed": false; "Ping": "pong"}[...]运行如下命令来清理环境:
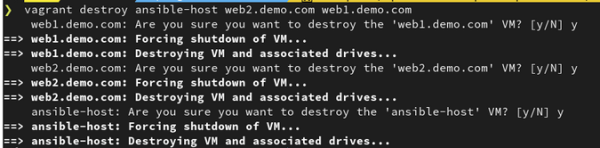
$ vagrant destroy [vagrant machine name]
你的输出会像这样:
以上是“如何建立一个Ansible实验室”这篇文章的所有内容,感谢各位的阅读!相信大家都有了一定的了解,希望分享的内容对大家有所帮助,如果还想学习更多知识,欢迎关注亿速云行业资讯频道!
免责声明:本站发布的内容(图片、视频和文字)以原创、转载和分享为主,文章观点不代表本网站立场,如果涉及侵权请联系站长邮箱:is@yisu.com进行举报,并提供相关证据,一经查实,将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容。