Golang中GinWeb框架如何使用,很多新手对此不是很清楚,为了帮助大家解决这个难题,下面小编将为大家详细讲解,有这方面需求的人可以来学习下,希望你能有所收获。
安装
Go版本要求: Go1.12及以上
1. 执行以下命令安装最新版本Gin
$ go get -u github.com/gin-gonic/gin
2. 在你的代码中导入
import "github.com/gin-gonic/gin"
3. (可选)导入net/http包, 如果你要使用其中的常量,比如http.StatusOK,则需要导入
import "net/http"
快速开始
编写main.go,写入以下代码并执行go run main.go, 访问http://localhost:8080/ping, 就可以得到响应消息{"message": "pong"}
package main import "github.com/gin-gonic/gin" func main() { r := gin.Default() //创建默认Gin引擎Engine,内部默认开启了日志和异常恢复中间件 r.GET("/ping", func(c *gin.Context) { c.JSON(200, gin.H{ "message": "pong", }) }) r.Run() //默认在localhost:8080监听 }基准测试
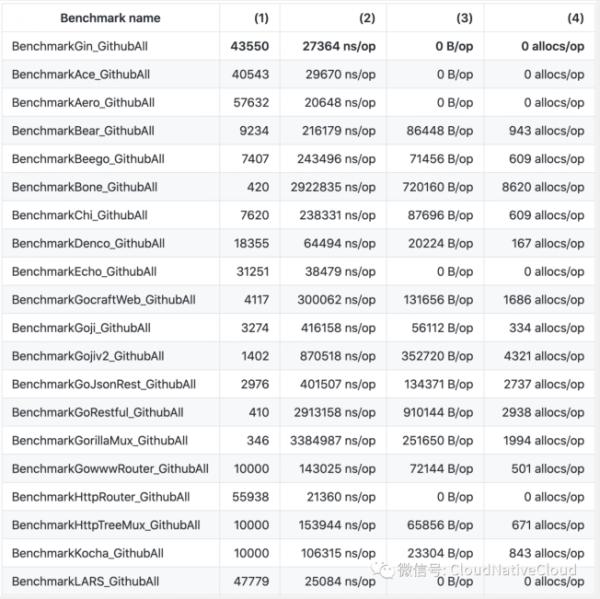
测试结果说明:
Benchmark name: 基准测试项
第(1)列:在固定时间内完成的重复次数, 值越大性能好
第(2)列:执行单次重复任务消耗的纳秒数, 单位ns/op, 值越低越好
第(3)列:执行单次重复任务消耗的堆内存字节数, 单位B/op, 值越低越好
第(4)列:每个重复任务平均分配内存的次数, 单位allocs/op, 值越低越好
Gin V1稳定版特性
零内存分配的路由器
仍然是最快的http路由器和框架
完整的单元测试
严格测试
API版本冻结,新发布的版本对你原来的代码兼容
使用jsoniter编译
jsoniter(https://github.com/json-iterator/go)是一个高性能可以替代Golang标准库encoding/json并且完全兼容的包
Gin默认使用encoding/json包,但是你可以使用以下tags修改为jsoniter重新编译源码
go build -tags=jsoniter .
API示例
你可以访问源码,查看更多接口示例代码:https://github.com/gin-gonic/examples
使用GET,POST,PUT,PATCH,DELETE,OPTIONS
func main() { // Creates a gin router with default middleware: // logger and recovery (crash-free) middleware router := gin.Default() router.GET("/someGet", getting) router.POST("/somePost", posting) router.PUT("/somePut", putting) router.DELETE("/someDelete", deleting) router.PATCH("/somePatch", patching) router.HEAD("/someHead", head) router.OPTIONS("/someOptions", options) // By default it serves on :8080 unless a // PORT environment variable was defined. router.Run() // router.Run(":3000") for a hard coded port 指定端口 }路径参数
func main() { router := gin.Default() // This handler will match /user/john but will not match /user/ or /user //以下路由只会匹配/user/用户名, 不会匹配/user/或者/user router.GET("/user/:name", func(c *gin.Context) { name := c.Param("name") //使用Param方法从路径中获取参数 c.String(http.StatusOK, "Hello %s", name) }) // However, this one will match /user/john/ and also /user/john/send // If no other routers match /user/john, it will redirect to /user/john/ // 以下带冒号:和带星号*组成的路由可以匹配/user/用户名/或/user/用户名/动作,如果/user/用户名没有匹配到其他路由,它会自动重定向到/user/用户名/进行匹配 router.GET("/user/:name/*action", func(c *gin.Context) { name := c.Param("name") action := c.Param("action") message := name + " is " + action c.String(http.StatusOK, message) }) // For each matched request Context will hold the route definition // 请求上下文request Context会保存所有匹配上的路由定义到c.FullPath()方法 router.POST("/user/:name/*action", func(c *gin.Context) { c.FullPath() == "/user/:name/*action" // true }) router.Run(":8080") }查询字符串参数
func main() { router := gin.Default() // Query string parameters are parsed using the existing underlying request object. // The request responds to a url matching: /welcome?firstname=Jane&lastname=Doe // 发送测试请求:/welcome?firstname=Jane&lastname=Doe router.GET("/welcome", func(c *gin.Context) { firstname := c.DefaultQuery("firstname", "Guest") //如果没有获取到该键值,则使用第二个参数作为默认值 lastname := c.Query("lastname") //上一行的完整写法:c.Request.URL.Query().Get("lastname") c.String(http.StatusOK, "Hello %s %s", firstname, lastname) }) router.Run(":8080") }URL编码的多种数据类型组成的表单请求
请求内容类型为:application/x-www-form-urlencoded
Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded
package main import "github.com/gin-gonic/gin" func main() { router := gin.Default() // 模拟提交表单:curl -XPOST http://localhost:8080/form_post -d "message=消息&nick=昵称" router.POST("/form_post", func(c *gin.Context) { message := c.PostForm("message") nick := c.DefaultPostForm("nick", "anonymous") c.JSON(200, gin.H{ "status": "posted", "message": message, "nick": nick, }) }) router.Run(":8080") } //返回结果: {"message":"消息","nick":"昵称","status":"posted"}查询和提交Post表单相结合
package main import ( "fmt" "github.com/gin-gonic/gin" ) func main() { router := gin.Default() router.POST("/post", func(c *gin.Context) { id := c.Query("id") page := c.DefaultQuery("page", "0") name := c.PostForm("name") message := c.PostForm("message") fmt.Printf("id: %s; page: %s; name: %s; message: %s\n", id, page, name, message) c.JSON(200, gin.H{ "id": id, "page": page, "name": name, "message": message, }) }) router.Run(":8080") }模拟发送请求:
curl -XPOST http://localhost:8080/post?id=1234&page=1 -d "name=manu&message=this_is_great"
返回结果:
{"id":"1234","message":"this_is_great","name":"manu","page":"1"}以Map映射作为查询字符串或Post表单参数
func main() {
router := gin.Default()
router.POST("/post", func(c *gin.Context) {
ids := c.QueryMap("ids") //获取查询参数中的Map
names := c.PostFormMap("names") //获取Post表单中的Map
fmt.Printf("ids: %v; names: %v\n", ids, names)
})
router.Run(":8080")
}
模拟请求: curl -XPOST http://localhost:8080/post?ids[a]=1234&ids[b]=hello -d "names[first]=thinkerou&names[second]=tianou" 打印结果: ids: map[a:1234 b:hello]; names: map[first:thinkerou second:tianou]
看完上述内容是否对您有帮助呢?如果还想对相关知识有进一步的了解或阅读更多相关文章,请关注亿速云行业资讯频道,感谢您对亿速云的支持。
免责声明:本站发布的内容(图片、视频和文字)以原创、转载和分享为主,文章观点不代表本网站立场,如果涉及侵权请联系站长邮箱:is@yisu.com进行举报,并提供相关证据,一经查实,将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容。