本篇文章为大家展示了Python中怎么调用C模块,内容简明扼要并且容易理解,绝对能使你眼前一亮,通过这篇文章的详细介绍希望你能有所收获。
一.c,ctypes和python的数据类型的对应关系
ctypes type ctype Python type
c_char char 1-character string
c_wchar wchar_t 1-character unicode string
c_byte char int/long
c_ubyte unsigned char int/long
c_short short int/long
c_ushort unsigned short int/long
c_int int int/long
c_uint unsigned int int/long
c_long long int/long
c_ulong unsigned long int/long
c_longlong __int64 or long long int/long
c_ulonglong unsigned __int64 or unsigned long long int/long
c_float float float
c_double double float
c_char_p char * (NUL terminated) string or None
c_wchar_p wchar_t * (NUL terminated) unicode or None
c_void_p void * int/long or None
2.操作int
>>> from ctypes import * >>> c=c_int(34) >>> c c_int(34) >>> c.value 34 >>> c.value=343 >>> c.value 3433.操作字符串
>>> p=create_string_buffer(10) >>> p.raw '\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00' >>> p.value='fefefe' >>> p.raw 'fefefe\x00\x00\x00\x00' >>> p.value='fefeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeee' #字符串太长,报错 Traceback (most recent call last): File "<stdin>", line 1, in <module> ValueError: string too long4.操作指针
>>> i=c_int(999) >>> pi=pointer(i) >>> pi <__main__.LP_c_int object at 0x7f7be1983b00> >>> pi.value Traceback (most recent call last): File "<stdin>", line 1, in <module> AttributeError: 'LP_c_int' object has no attribute 'value' >>> pi.contents c_int(999) >>> pi.contents=c_long(34343) >>> pi.contents c_int(34343)通过pointer获取一个值的指针
通过contents获取一个指针的值
5.c的结构体
#定义一个c的structure,包含两个成员变量x和y >>> class POINT(Structure): ... _fields_=[('x',c_int),('y',c_int)] ... >>> point=POINT(2,4) >>> point <__main__.POINT object at 0x7f7be1983b90> >>> point.x,point.y (2, 4) >>> porint=POINT(y=2) >>> porint <__main__.POINT object at 0x7f7be1983cb0> >>> point=POINT(y=2) >>> point.x,point.y (0, 2) 定义一个类型为POINT的数组 >>> POINT_ARRAY=POINT*3 >>> pa=POINT_ARRAY(POINT(2,3),POINT(2,4),POINT(2,5)) >>> for i in pa:print pa.y ... Traceback (most recent call last): File "<stdin>", line 1, in <module> AttributeError: 'POINT_Array_3' object has no attribute 'y' >>> for i in pa:print i.y ... 3 4 56.访问so文件
1.创建一个c文件
#include <stdio.h> int hello_world(){ printf("Hello World\n"); return 0; } int main(){ hello_world(); return 0; }2.编译成动态链接库
gcc hello_world.c -fPIC -shared -o hello_world.so3.python中调用库中的函数
from ctypes import cdll c_lib=cdll.LoadLibrary('./hello_world.so') c_lib.hello_world()二.测试c的性能和python的差别
sum.c
int sum(int num){ long sum=0; int i =0; for( i=1;i<=num;i++){ sum=sum+i; }; return sum; } int main(){ printf("%d",sum(10)); return 0; }测试方案:计算1-100的和
测试次数:100万次
1. 直接用c来执行,通linux 的time命令来记录执行的用时
sum.c:
#include <stdio.h> int sum(int num){ long sum=0; int i =0; for( i=1;i<=num;i++){ sum=sum+i; }; return sum; } int main(){ int i ; for (i=0;i<1000000;i++){ sum(100); } return 0; }测试结果的例子:
real 1.16
user 1.13
sys 0.01
2.通过Python调用so文件和python的测试结果
sum_test.py:
def sum_python(num): s = 0 for i in xrange(1,num+1): s += i return s from ctypes import cdll c_lib = cdll.LoadLibrary('./sum.so') def sum_c(num): return c_lib.sum(num) def test(num): import timeit t1 = timeit.Timer('c_lib.sum(%d)' % num, 'from __main__ import c_lib') t2 = timeit.Timer('sum_python(%d)' % num, 'from __main__ import sum_python') print 'c', t1.timeit(number=1000000) print 'python', t2.timeit(number=1000000) if __name__ == '__main__': test(100)测试结果的例子
c 1.02756714821 python 7.906728029253.测试erlang的测试结果
刚刚学了erlang,那就一起测试一下erlang的运算性能
sum.erl:
-module(sum). -export([sum/2,sum_test/2]). sum(0,Sum) -> Sum; sum(Num,Sum) -> sum(Num-1,Sum+Num). sum_test(Num,0) -> 0; sum_test(Num,Times) -> sum(Num,0), sum_test(Num,Times-1).调用:
timer:tc(sum,sum_test,[100,1000000]).测试结果的例子:
{2418486,0}4.测试结果
用上面的测试方法,进行10次测试,去除***值和最小值,再计算平均值,得出:
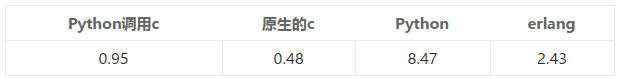
单位:秒
求和的运行,使用的内存比较小,但是占用CPU资源比较多。
原生的C是最快的,Python调用c会稍微慢一点,原因是计算100的和的操作是在c里面做的,而执行100万次的逻辑是在python做的
erlang的性能虽然比c稍慢,但是也是不错的,
Python的运行效率惨不忍睹。。。
上述内容就是Python中怎么调用C模块,你们学到知识或技能了吗?如果还想学到更多技能或者丰富自己的知识储备,欢迎关注亿速云行业资讯频道。
亿速云「云服务器」,即开即用、新一代英特尔至强铂金CPU、三副本存储NVMe SSD云盘,价格低至29元/月。点击查看>>
免责声明:本站发布的内容(图片、视频和文字)以原创、转载和分享为主,文章观点不代表本网站立场,如果涉及侵权请联系站长邮箱:is@yisu.com进行举报,并提供相关证据,一经查实,将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容。
原文链接:https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/qixz2cZstEGV3re9Rm_2aA