本篇内容主要讲解“Flink提交任务的方法是什么”,感兴趣的朋友不妨来看看。本文介绍的方法操作简单快捷,实用性强。下面就让小编来带大家学习“Flink提交任务的方法是什么”吧!
任务提交过程中有三个重要组件:Dispatcher、JobMaster、JobManagerRunnerImpl。通过下面调用路径先找到MiniDispatcher:
YarnJobClusterEntrypoint的main() -> ClusterEntrypoint的runCluster() -> DefaultDispatcherResourceManagerComponentFactory的create() -> DefaultDispatcherRunnerFactory的createDispatcherRunner() -> DefaultDispatcherRunner的grantLeadership() -> JobDispatcherLeaderProcess的onStart() -> DefaultDispatcherGatewayServiceFactory的create() -> JobDispatcherFactory的createDispatcher() -> MiniDispatcher的start()
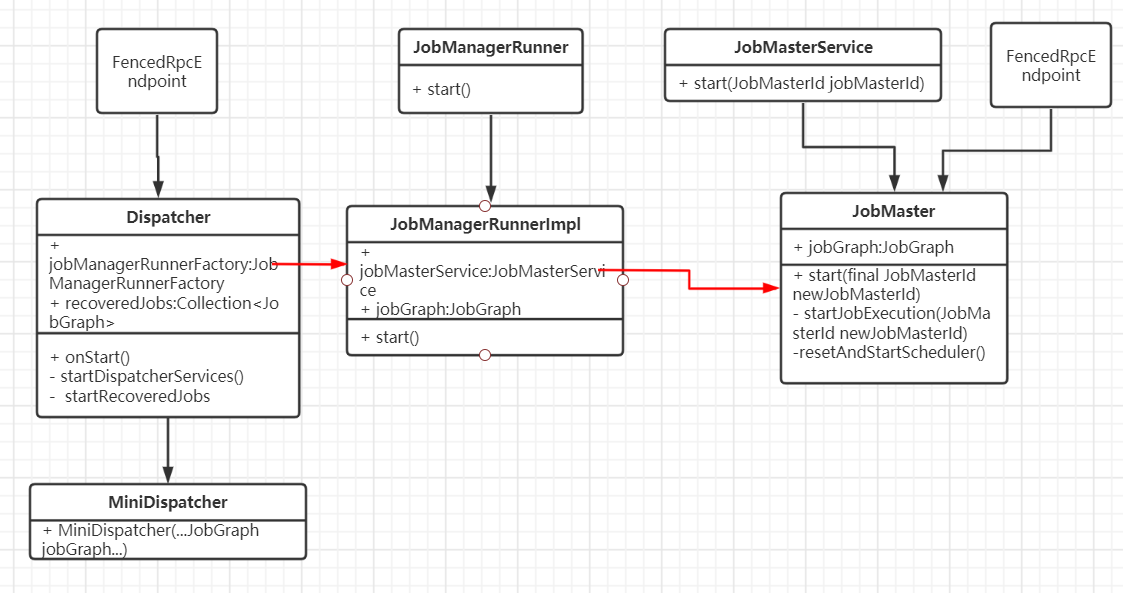
(1)Dispatcher
负责接收任务提交请求,并分给JobManager执行;
Dispatcher启动时,会运行startRecoveredJobs()来启动需要恢复的任务。当Flink on Yarn模式时,MiniDispatcher将当前任务传入到需要恢复的任务中,这样就实现了任务的提交启动
(2)JobManagerRunner
负责运行JobMaster
(3)JobMaster
负责运行任务,对应旧版的JobManager;
一个任务对应一个JobMaster;
在JobMaster中通过Scheduler、Execution组件来执行一个任务。将任务DAG中每个节点算子分配给TaskManager中的TaskExecutor运行。
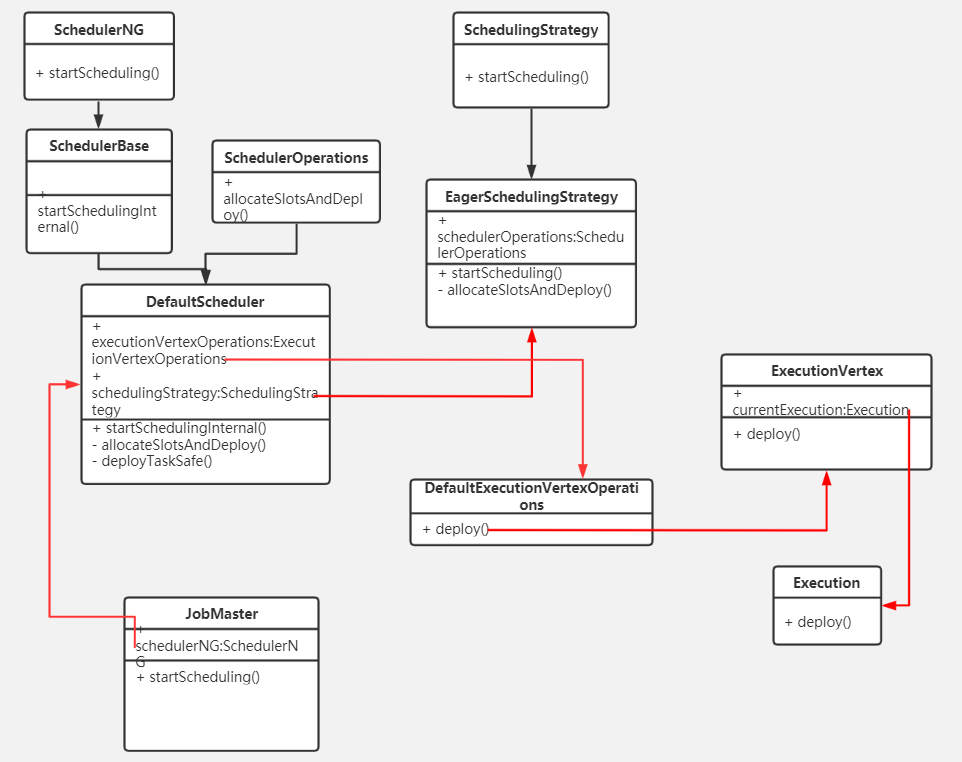
Execution的start()方法中通过rpc远程调用TaskExecutor的submitTask()方法:
public void deploy() throws JobException {
......
try {
......
final TaskManagerGateway taskManagerGateway = slot.getTaskManagerGateway();
final ComponentMainThreadExecutor jobMasterMainThreadExecutor =
vertex.getExecutionGraph().getJobMasterMainThreadExecutor();
CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> taskManagerGateway.submitTask(deployment, rpcTimeout), executor)
.thenCompose(Function.identity())
.whenCompleteAsync(
.....,
jobMasterMainThreadExecutor);
}
catch (Throwable t) {
......
}
}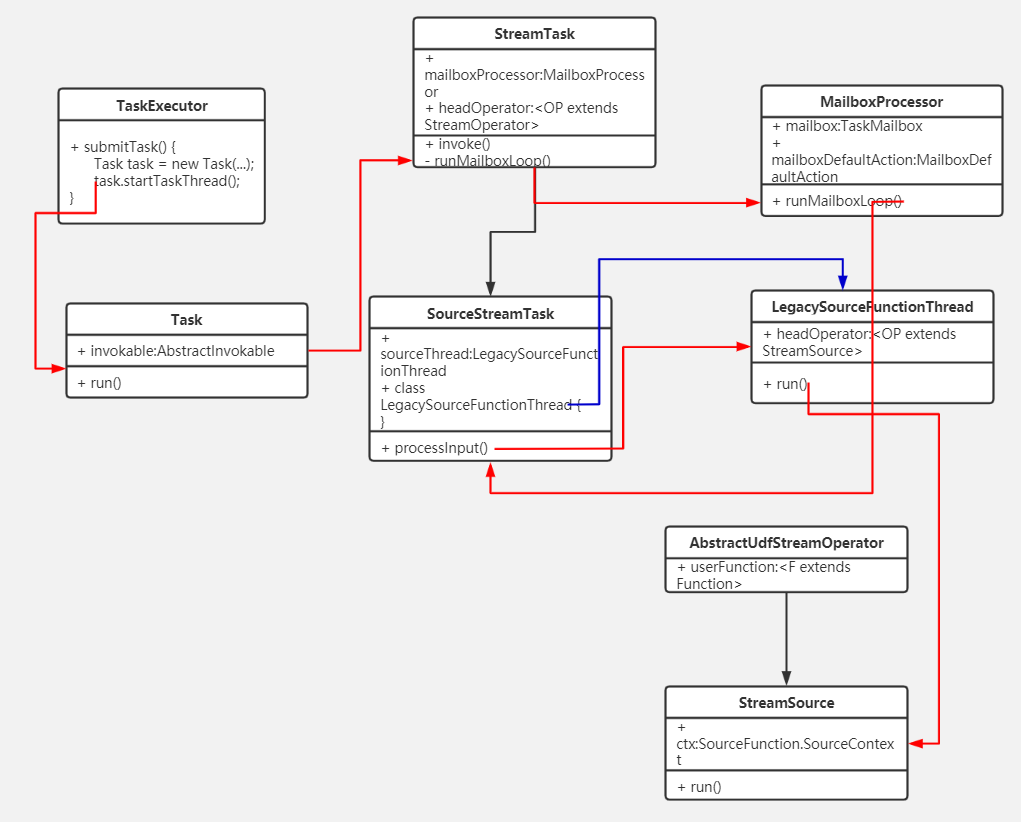
TaskExecutor的submitTask()方法中通过创建org.apache.flink.runtime.taskmanager.Task来运行算子任务。Task的doRun()方法中通过算子节点对应的执行类AbstractInvokable来运行算子的处理逻辑,每个算子对应的执行类AbstractInvokable在客户端提交任务时确定,StreamExecutionEnvironment的addOperator():
public <IN, OUT> void addOperator(
Integer vertexID,
@Nullable String slotSharingGroup,
@Nullable String coLocationGroup,
StreamOperatorFactory<OUT> operatorFactory,
TypeInformation<IN> inTypeInfo,
TypeInformation<OUT> outTypeInfo,
String operatorName) {
Class<? extends AbstractInvokable> invokableClass =
operatorFactory.isStreamSource() ? SourceStreamTask.class : OneInputStreamTask.class;
addOperator(vertexID, slotSharingGroup, coLocationGroup, operatorFactory, inTypeInfo,
outTypeInfo, operatorName, invokableClass);
}当是流式任务时,调用StreamTask的invoke()方法。当是source节点时,通过调用链 StreamTask.invoke() -> StreamTask.runMailboxLoop() -> MailboxProcessor.runMailboxLoop() -> SourceStreamTask.processInput() :
protected void processInput(MailboxDefaultAction.Controller controller) throws Exception {
controller.suspendDefaultAction();
// Against the usual contract of this method, this implementation is not step-wise but blocking instead for
// compatibility reasons with the current source interface (source functions run as a loop, not in steps).
sourceThread.setTaskDescription(getName());
sourceThread.start();
sourceThread.getCompletionFuture().whenComplete((Void ignore, Throwable sourceThreadThrowable) -> {
if (isCanceled() && ExceptionUtils.findThrowable(sourceThreadThrowable, InterruptedException.class).isPresent()) {
mailboxProcessor.reportThrowable(new CancelTaskException(sourceThreadThrowable));
} else if (!isFinished && sourceThreadThrowable != null) {
mailboxProcessor.reportThrowable(sourceThreadThrowable);
} else {
mailboxProcessor.allActionsCompleted();
}
});
}创建线程LegacySourceFunctionThread实例,来开启单独生产数据的线程。LegacySourceFunctionThread的run()方法中调用StreamSource的run()方法:
public void run(final Object lockingObject,
final StreamStatusMaintainer streamStatusMaintainer,
final Output<StreamRecord<OUT>> collector,
final OperatorChain<?, ?> operatorChain) throws Exception {
final TimeCharacteristic timeCharacteristic = getOperatorConfig().getTimeCharacteristic();
final Configuration configuration = this.getContainingTask().getEnvironment().getTaskManagerInfo().getConfiguration();
final long latencyTrackingInterval = getExecutionConfig().isLatencyTrackingConfigured()
? getExecutionConfig().getLatencyTrackingInterval()
: configuration.getLong(MetricOptions.LATENCY_INTERVAL);
LatencyMarksEmitter<OUT> latencyEmitter = null;
if (latencyTrackingInterval > 0) {
latencyEmitter = new LatencyMarksEmitter<>(
getProcessingTimeService(),
collector,
latencyTrackingInterval,
this.getOperatorID(),
getRuntimeContext().getIndexOfThisSubtask());
}
final long watermarkInterval = getRuntimeContext().getExecutionConfig().getAutoWatermarkInterval();
this.ctx = StreamSourceContexts.getSourceContext(
timeCharacteristic,
getProcessingTimeService(),
lockingObject,
streamStatusMaintainer,
collector,
watermarkInterval,
-1);
try {
userFunction.run(ctx);
// if we get here, then the user function either exited after being done (finite source)
// or the function was canceled or stopped. For the finite source case, we should emit
// a final watermark that indicates that we reached the end of event-time, and end inputs
// of the operator chain
if (!isCanceledOrStopped()) {
// in theory, the subclasses of StreamSource may implement the BoundedOneInput interface,
// so we still need the following call to end the input
synchronized (lockingObject) {
operatorChain.endHeadOperatorInput(1);
}
}
} finally {
if (latencyEmitter != null) {
latencyEmitter.close();
}
}
}StreamSource的run()方法中调用 userFunction.run(ctx); 当数据源是kafka时,userFunction为FlinkKafkaConsumerBase
最后执行run()的headOperator和算子程序userFunction是在添加算子时确定的,比如添加kafka数据源时
environment.addSource(new FlinkKafkaConsumer<String>(......));
最后调用的addSource()方法:
public <OUT> DataStreamSource<OUT> addSource(SourceFunction<OUT> function, String sourceName, TypeInformation<OUT> typeInfo) {
TypeInformation<OUT> resolvedTypeInfo = getTypeInfo(function, sourceName, SourceFunction.class, typeInfo);
boolean isParallel = function instanceof ParallelSourceFunction;
clean(function);
final StreamSource<OUT, ?> sourceOperator = new StreamSource<>(function);
return new DataStreamSource<>(this, resolvedTypeInfo, sourceOperator, isParallel, sourceName);
}headOperator为StreamSource,StreamSource中的userFunction为FlinkKafkaConsumer
到此,相信大家对“Flink提交任务的方法是什么”有了更深的了解,不妨来实际操作一番吧!这里是亿速云网站,更多相关内容可以进入相关频道进行查询,关注我们,继续学习!
免责声明:本站发布的内容(图片、视频和文字)以原创、转载和分享为主,文章观点不代表本网站立场,如果涉及侵权请联系站长邮箱:is@yisu.com进行举报,并提供相关证据,一经查实,将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容。