如何利用Prometheus Operator实现自定义指标监控,很多新手对此不是很清楚,为了帮助大家解决这个难题,下面小编将为大家详细讲解,有这方面需求的人可以来学习下,希望你能有所收获。
在过去的文章中,我们花了相当大的篇幅来聊关于监控的话题。这是因为当你正在管理Kubernetes集群时,一切都会以极快的速度发生变化。因此有一个工具来监控集群的健康状态和资源指标极为重要。
在Rancher 2.5中,我们引入了基于Prometheus Operator的新版监控,它可以提供Prometheus以及相关监控组件的原生Kubernetes部署和管理。Prometheus Operator可以让你监控集群节点、Kubernetes组件和应用程序工作负载的状态和进程。同时,它还能够通过Prometheus收集的指标来定义告警并且创建自定义仪表盘,通过Grafana可以轻松地可视化收集到的指标。
新版本的监控也采用prometheus-adapter,开发人员可以利用其基于自定义指标和HPA扩展他们的工作负载。
我们将探索如何利用Prometheus Operator来抓取自定义指标并利用这些指标进行高级工作负载管理。
在Rancher 2.5中安装Prometheus极为简单。仅需访问Cluster Explorer -> Apps并安装rancher-monitoring即可。

你需要了解以下默认设置:
prometheus-adapter将会作为chart安装的一部分启用
ServiceMonitorNamespaceSelector 留为空,允许 Prometheus 在所有命名空间中收集 ServiceMonitors
安装完成后,我们可以从Cluster Explorer访问监控组件。

现在让我们部署一个从应用层暴露自定义指标的示例工作负载。该工作负载暴露了一个简单的应用程序,该应用程序已经使用Prometheus client_golang库进行了检测,并在/metric端点上提供了一些自定义指标。
它有两个指标:
http_requests_total
http_request_duration_seconds
以下manifest部署了工作负载、相关服务以及访问该工作负载的ingress:
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
labels:
app.kubernetes.io/name: prometheus-example-app
name: prometheus-example-app
spec:
replicas: 1
selector:
matchLabels:
app.kubernetes.io/name: prometheus-example-app
template:
metadata:
labels:
app.kubernetes.io/name: prometheus-example-app
spec:
containers:
- name: prometheus-example-app
image: gmehta3/demo-app:metrics
ports:
- name: web
containerPort: 8080
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: prometheus-example-app
labels:
app.kubernetes.io/name: prometheus-example-app
spec:
selector:
app.kubernetes.io/name: prometheus-example-app
ports:
- protocol: TCP
port: 8080
targetPort: 8080
name: web
---
apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1beta1
kind: Ingress
metadata:
name: prometheus-example-app
spec:
rules:
- host: hpa.demo
http:
paths:
- path: /
backend:
serviceName: prometheus-example-app
servicePort: 8080ServiceMonitor是一个自定义资源定义(CRD),可以让我们声明性地定义如何监控一组动态服务。
你可以访问以下链接查看完整的ServiceMonitor规范:
https://github.com/prometheus-operator/prometheus-operator/blob/master/Documentation/api.md#servicemonitor
现在,我们来部署ServiceMonitor,Prometheus用它来收集组成prometheus-example-app Kubernetes服务的pod。
kind: ServiceMonitor
metadata:
name: prometheus-example-app
spec:
selector:
matchLabels:
app.kubernetes.io/name: prometheus-example-app
endpoints:
- port: web如你所见,现在用户可以在Rancher监控中浏览ServiceMonitor。
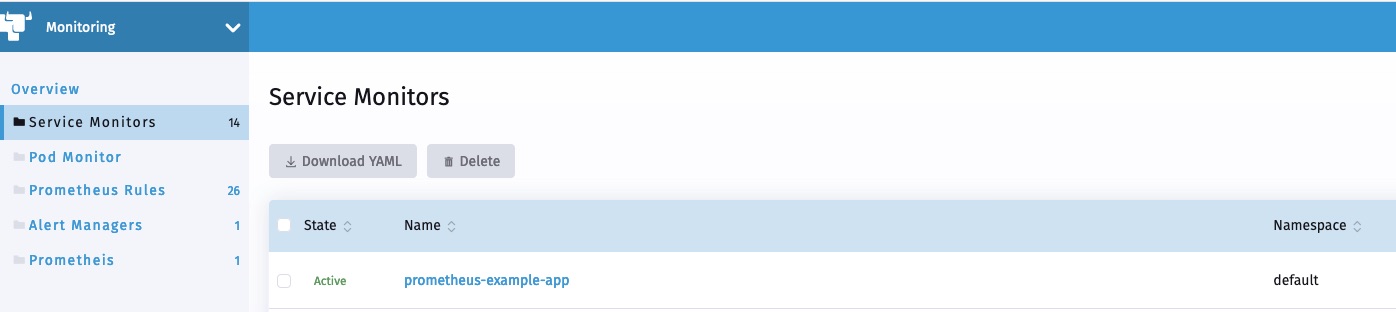
不久之后,新的service monitor和服务相关联的pod应该会反映在Prometheus服务发现中。
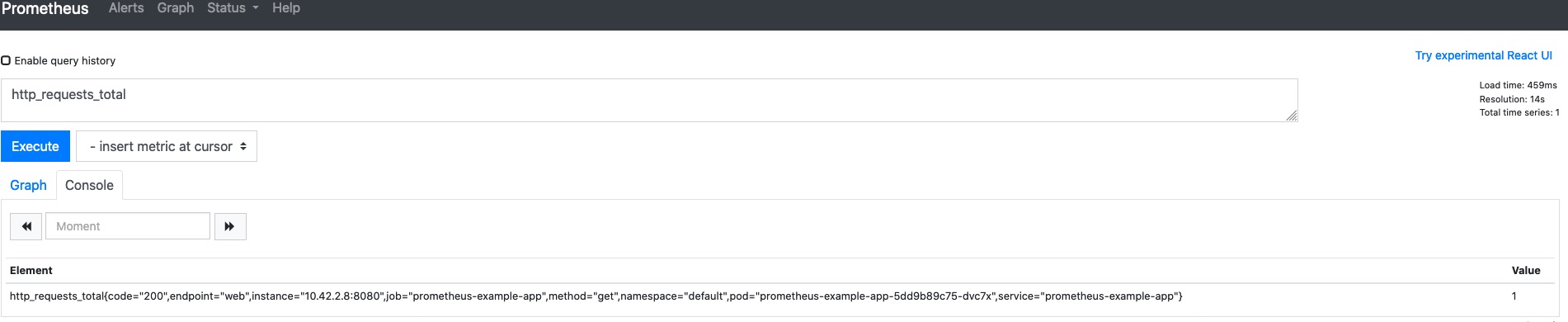
我们也能够在Prometheus中看到指标。
在Rancher 2.5中,监控可以让用户将Grafana仪表盘存储为cattle-dashboards命名空间中的ConfigMaps。
用户或集群管理员现在可以在这一命名空间中添加更多的仪表盘以扩展Grafana的自定义仪表盘。
Dashboard ConfigMap Example
apiVersion: v1
kind: ConfigMap
metadata:
name: prometheus-example-app-dashboard
namespace: cattle-dashboards
labels:
grafana_dashboard: "1"
data:
prometheus-example-app.json: |
{
"annotations": {
"list": [
{
"builtIn": 1,
"datasource": "-- Grafana --",
"enable": true,
"hide": true,
"iconColor": "rgba(0, 211, 255, 1)",
"name": "Annotations & Alerts",
"type": "dashboard"
}
]
},
"editable": true,
"gnetId": null,
"graphTooltip": 0,
"links": [],
"panels": [
{
"aliasColors": {},
"bars": false,
"dashLength": 10,
"dashes": false,
"datasource": null,
"fieldConfig": {
"defaults": {
"custom": {}
},
"overrides": []
},
"fill": 1,
"fillGradient": 0,
"gridPos": {
"h": 9,
"w": 12,
"x": 0,
"y": 0
},
"hiddenSeries": false,
"id": 2,
"legend": {
"avg": false,
"current": false,
"max": false,
"min": false,
"show": true,
"total": false,
"values": false
},
"lines": true,
"linewidth": 1,
"nullPointMode": "null",
"percentage": false,
"pluginVersion": "7.1.5",
"pointradius": 2,
"points": false,
"renderer": "flot",
"seriesOverrides": [],
"spaceLength": 10,
"stack": false,
"steppedLine": false,
"targets": [
{
"expr": "rate(http_requests_total{code=\"200\",service=\"prometheus-example-app\"}[5m])",
"instant": false,
"interval": "",
"legendFormat": "",
"refId": "A"
}
],
"thresholds": [],
"timeFrom": null,
"timeRegions": [],
"timeShift": null,
"title": "http_requests_total_200",
"tooltip": {
"shared": true,
"sort": 0,
"value_type": "individual"
},
"type": "graph",
"xaxis": {
"buckets": null,
"mode": "time",
"name": null,
"show": true,
"values": []
},
"yaxes": [
{
"format": "short",
"label": null,
"logBase": 1,
"max": null,
"min": null,
"show": true
},
{
"format": "short",
"label": null,
"logBase": 1,
"max": null,
"min": null,
"show": true
}
],
"yaxis": {
"align": false,
"alignLevel": null
}
},
{
"aliasColors": {},
"bars": false,
"dashLength": 10,
"dashes": false,
"datasource": null,
"description": "",
"fieldConfig": {
"defaults": {
"custom": {}
},
"overrides": []
},
"fill": 1,
"fillGradient": 0,
"gridPos": {
"h": 8,
"w": 12,
"x": 0,
"y": 9
},
"hiddenSeries": false,
"id": 4,
"legend": {
"avg": false,
"current": false,
"max": false,
"min": false,
"show": true,
"total": false,
"values": false
},
"lines": true,
"linewidth": 1,
"nullPointMode": "null",
"percentage": false,
"pluginVersion": "7.1.5",
"pointradius": 2,
"points": false,
"renderer": "flot",
"seriesOverrides": [],
"spaceLength": 10,
"stack": false,
"steppedLine": false,
"targets": [
{
"expr": "rate(http_requests_total{code!=\"200\",service=\"prometheus-example-app\"}[5m])",
"interval": "",
"legendFormat": "",
"refId": "A"
}
],
"thresholds": [],
"timeFrom": null,
"timeRegions": [],
"timeShift": null,
"title": "http_requests_total_not_200",
"tooltip": {
"shared": true,
"sort": 0,
"value_type": "individual"
},
"type": "graph",
"xaxis": {
"buckets": null,
"mode": "time",
"name": null,
"show": true,
"values": []
},
"yaxes": [
{
"format": "short",
"label": null,
"logBase": 1,
"max": null,
"min": null,
"show": true
},
{
"format": "short",
"label": null,
"logBase": 1,
"max": null,
"min": null,
"show": true
}
],
"yaxis": {
"align": false,
"alignLevel": null
}
}
],
"schemaVersion": 26,
"style": "dark",
"tags": [],
"templating": {
"list": []
},
"time": {
"from": "now-15m",
"to": "now"
},
"timepicker": {
"refresh_intervals": [
"5s",
"10s",
"30s",
"1m",
"5m",
"15m",
"30m",
"1h",
"2h",
"1d"
]
},
"timezone": "",
"title": "prometheus example app",
"version": 1
}现在,用户应该能够在Grafana中访问prometheus example app的仪表盘。
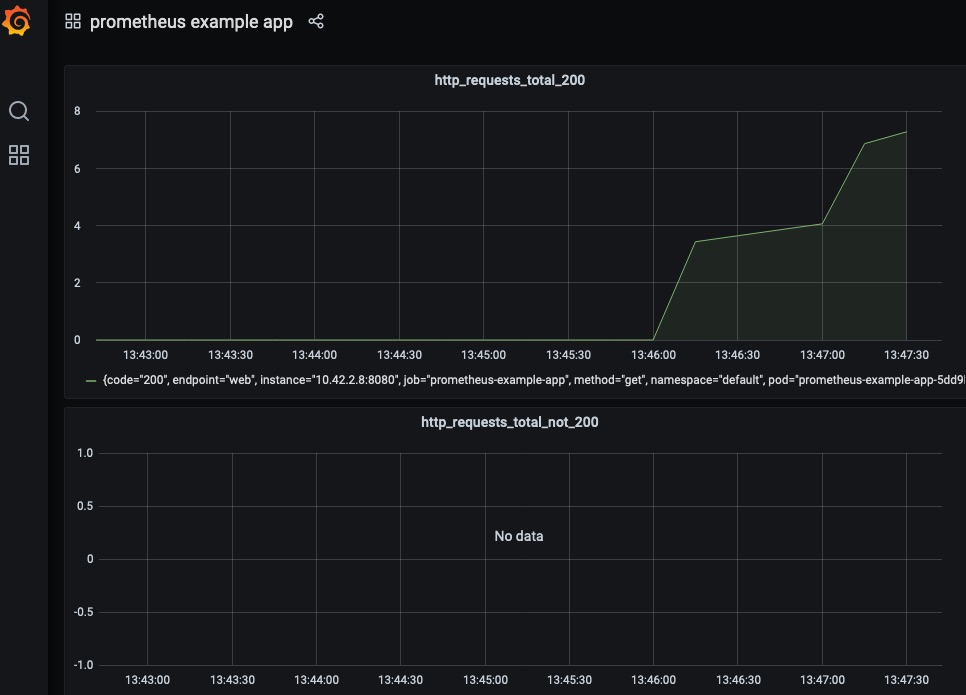
这一部分假设你已经将prometheus-adapter作为监控的一部分安装完毕了。实际上,在默认情况下,监控安装程序会安装prometheus-adapter。
用户现在可以创建一个HPA spec,如下所示:
apiVersion: autoscaling/v2beta2
kind: HorizontalPodAutoscaler
metadata:
name: prometheus-example-app-hpa
spec:
scaleTargetRef:
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
name: prometheus-example-app
minReplicas: 1
maxReplicas: 5
metrics:
- type: Object
object:
describedObject:
kind: Service
name: prometheus-example-app
metric:
name: http_requests
target:
averageValue: "5"
type: AverageValue你可以查看以下链接获取关于HPA的更多信息:
https://kubernetes.io/docs/tasks/run-application/horizontal-pod-autoscale/
我们将使用自定义的http_requests_total指标来执行pod自动伸缩。

现在我们可以生成一个样本负载来查看HPA的运行情况。我可以使用hey进行同样的操作。
hey -c 10 -n 5000 http://hpa.demo
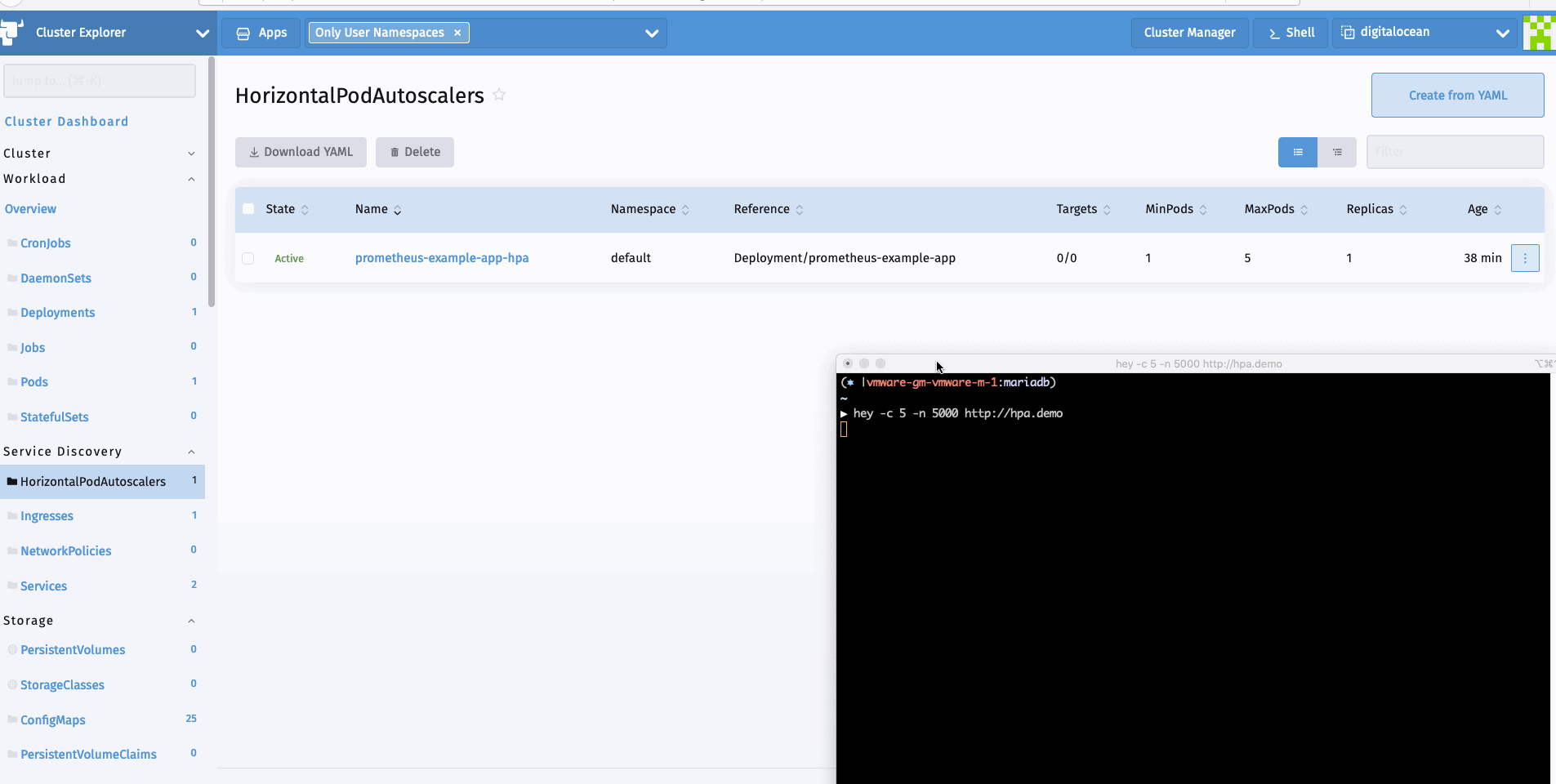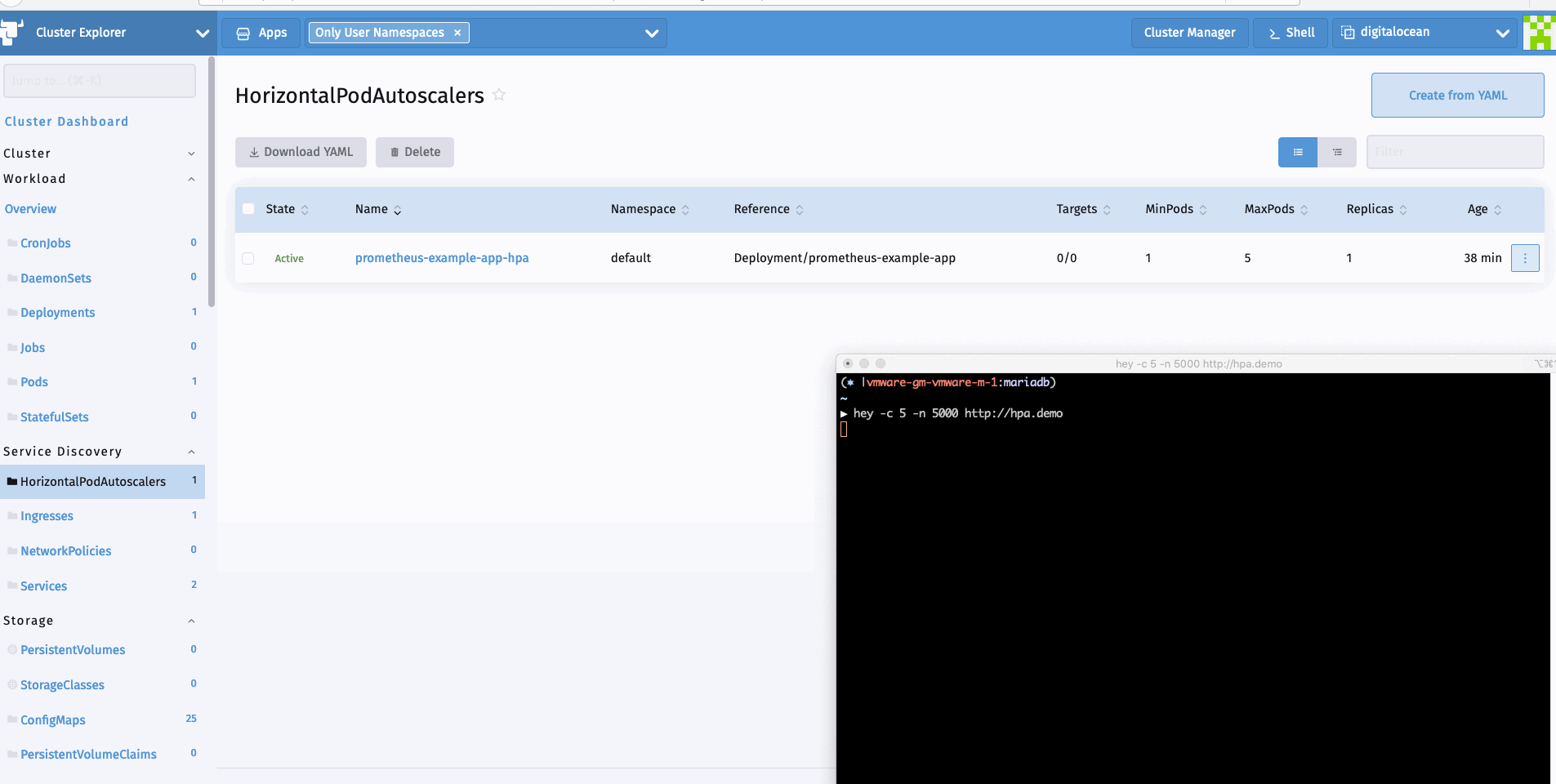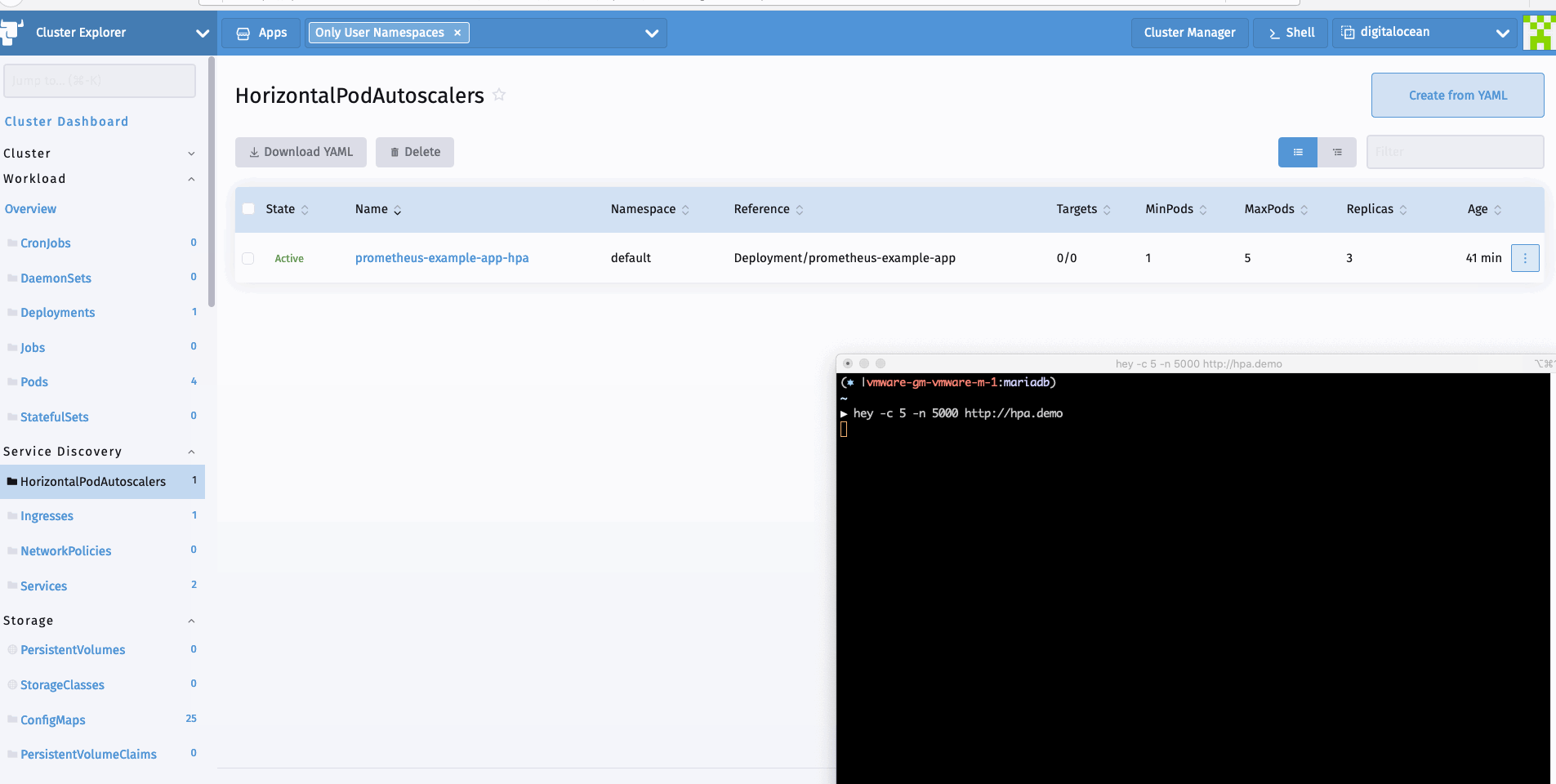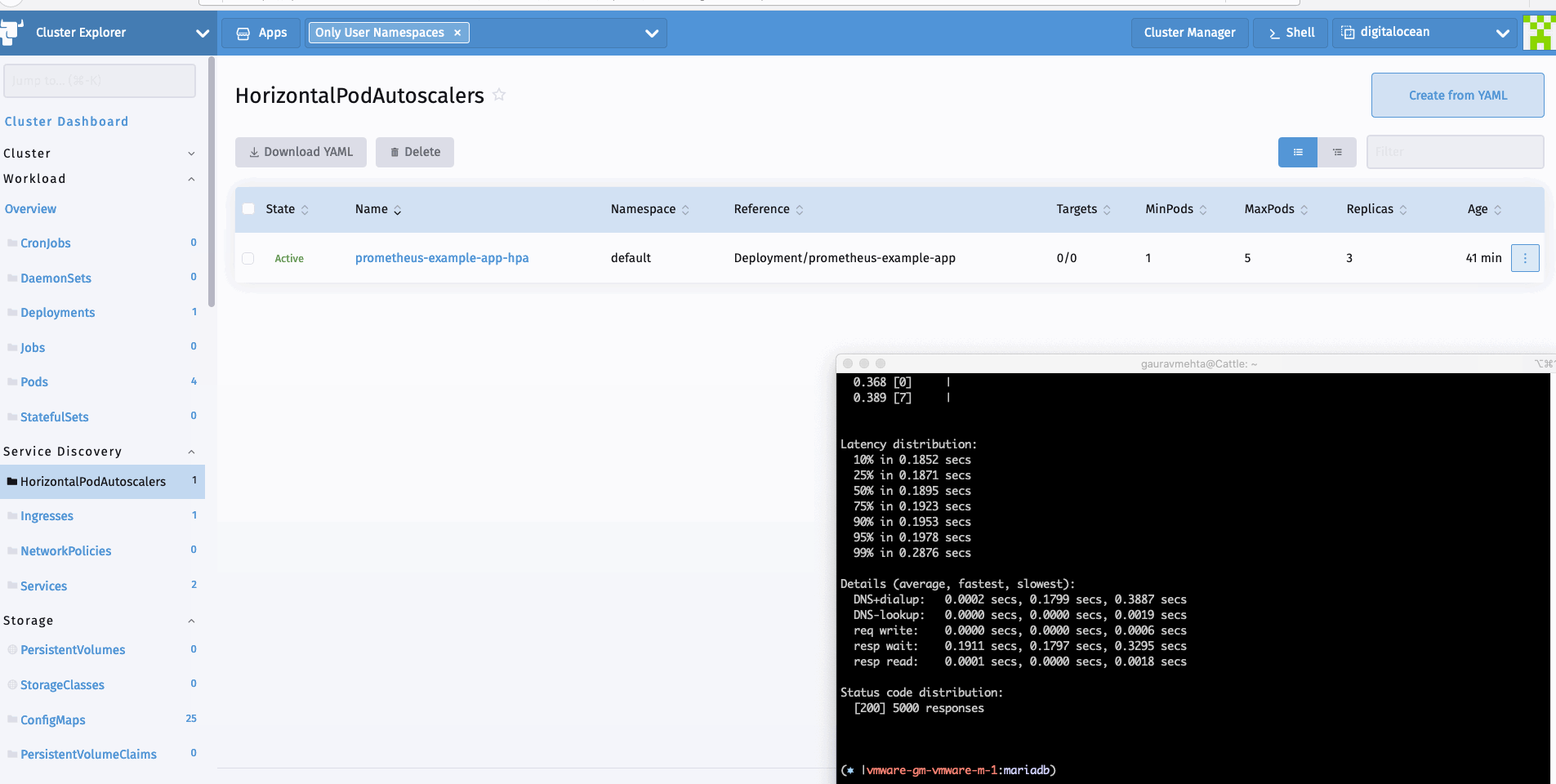
看完上述内容是否对您有帮助呢?如果还想对相关知识有进一步的了解或阅读更多相关文章,请关注亿速云行业资讯频道,感谢您对亿速云的支持。
亿速云「云服务器」,即开即用、新一代英特尔至强铂金CPU、三副本存储NVMe SSD云盘,价格低至29元/月。点击查看>>
免责声明:本站发布的内容(图片、视频和文字)以原创、转载和分享为主,文章观点不代表本网站立场,如果涉及侵权请联系站长邮箱:is@yisu.com进行举报,并提供相关证据,一经查实,将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容。
原文链接:https://my.oschina.net/rancher/blog/4875093