这篇文章主要介绍“如何实现网关Restful接口拦截”,在日常操作中,相信很多人在如何实现网关Restful接口拦截问题上存在疑惑,小编查阅了各式资料,整理出简单好用的操作方法,希望对大家解答”如何实现网关Restful接口拦截”的疑惑有所帮助!接下来,请跟着小编一起来学习吧!
我们看下实际的案例,演示下这种场景。在 account-service模块下增加一个博客用户管理功能,有如下的接口方法:
| 接口URL | HTTP方法 | 接口说明 |
|---|---|---|
| /blog/user | POST | 保存用户 |
| /blog/user/{id} | GET | 查询用户 |
| /blog/user/{id} | DELETE | 删除用户 |
| /blog/user/{id} | PUT | 更新用户信息 |
然后我们在 sys_permission表中添加2个用户权限,再将其授予给用户角色
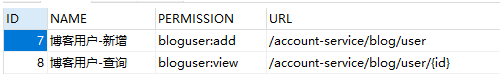
在网关层的校验方法中可以看到已经增加了2个权限
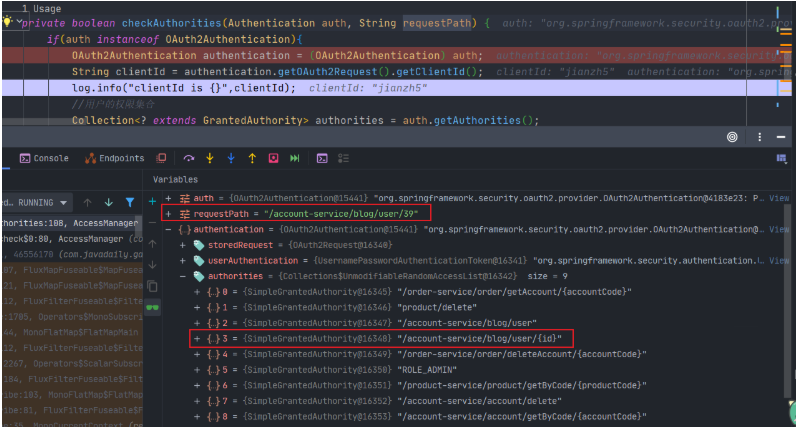
由于DELETE 和 PUT对应的权限路径都是 /blog/user/{id},这样就是当给用户授予了查询权限后此用户也拥有了删除和更新的权限。
看到这里大部分同学应该想到了,要想实现Restful风格的精细化权限管理单单通过URL路径是不行的,需要搭配Method一起使用。
最关键的点就是「需要给权限表加上方法字段,然后在网关校验的时候即判断请求路径又匹配请求方法。」 实现步骤如下:
loadUserByUsername()方法构建用户权限的时候将权限对应的Method也拼接在权限上,关键代码如下:@Overridepublic UserDetails loadUserByUsername(String userName) throws UsernameNotFoundException { //获取本地用户 SysUser sysUser = sysUserMapper.selectByUserName(userName); if(sysUser != null){ //获取当前用户的所有角色 List<SysRole> roleList = sysRoleService.listRolesByUserId(sysUser.getId()); sysUser.setRoles(roleList.stream().map(SysRole::getRoleCode).collect(Collectors.toList())); List<Integer> roleIds = roleList.stream().map(SysRole::getId).collect(Collectors.toList()); //获取所有角色的权限 List<SysPermission> permissionList = sysPermissionService.listPermissionsByRoles(roleIds); //拼接method List<String> permissionUrlList = permissionList.stream() .map(item -> "["+item.getMethod()+"]"+item.getUrl()) .collect(Collectors.toList()); sysUser.setPermissions(permissionUrlList); //构建oauth3的用户 return buildUserDetails(sysUser); }else{ throw new UsernameNotFoundException("用户["+userName+"]不存在"); }} 通过上面的代码构建的用户权限如下:
[GET]/account-service/blog/user/{id}
[POST]/account-service/blog/user
可以通过代码调试查看:
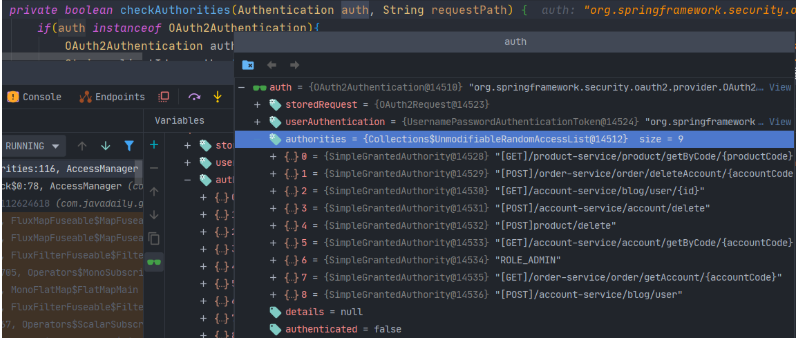
AccessManager#check(),校验
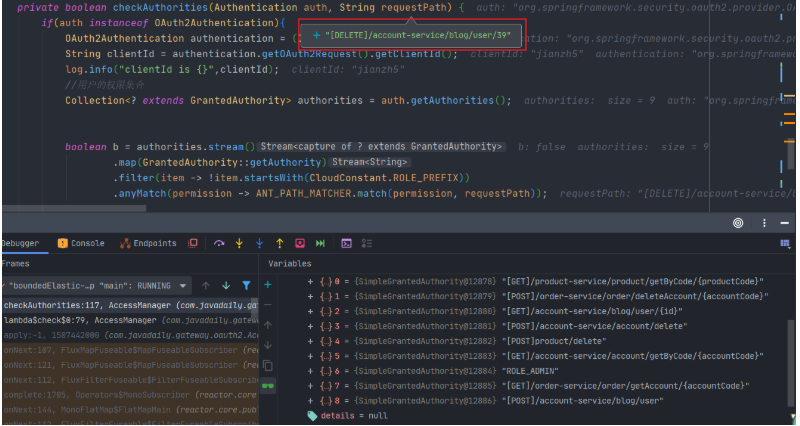
[MEHOTD]RequestPath 格式@Overridepublic Mono<AuthorizationDecision> check(Mono<Authentication> authenticationMono, AuthorizationContext authorizationContext) { ServerWebExchange exchange = authorizationContext.getExchange(); ServerHttpRequest request = exchange.getRequest(); //请求资源 String requestPath = request.getURI().getPath(); //拼接method String methodPath = "["+request.getMethod()+"]" + requestPath; // 1. 对应跨域的预检请求直接放行 if(request.getMethod() == HttpMethod.OPTIONS){ return Mono.just(new AuthorizationDecision(true)); } // 是否直接放行 if (permitAll(requestPath)) { return Mono.just(new AuthorizationDecision(true)); } return authenticationMono.map(auth -> new AuthorizationDecision(checkAuthorities(auth, methodPath))) .defaultIfEmpty(new AuthorizationDecision(false));} 校验方法 checkAuthorities():
private boolean checkAuthorities(Authentication auth, String requestPath) { if(auth instanceof OAuth3Authentication){ OAuth3Authentication authentication = (OAuth3Authentication) auth; String clientId = authentication.getOAuth3Request().getClientId(); log.info("clientId is {}",clientId); //用户的权限集合 Collection<? extends GrantedAuthority> authorities = auth.getAuthorities(); return authorities.stream() .map(GrantedAuthority::getAuthority) //ROLE_开头的为角色,需要过滤掉 .filter(item -> !item.startsWith(CloudConstant.ROLE_PREFIX)) .anyMatch(permission -> ANT_PATH_MATCHER.match(permission, requestPath)); } return true;} 
这里还有另外一种方案,实现的原理跟上面差不多,只简单提一下。
首先还是得在权限表中新增METHOD字段,这是必须的。
然后项目中使用的权限类是 SimpleGrantedAuthority,这个只能存储一个权限字段,我们可以自定义一个权限实体类,让其可以存储url 和 method。
@Datapublic class MethodGrantedAuthority implements GrantedAuthority { private String method; private String url; public MethodGrantedAuthority(String method, String url){ this.method = method; this.url = url; } @Override public String getAuthority() { return "["+method+"]" + url; }} 在 UserDetailServiceImpl中构建用户权限时使用自定义的 MethodGrantedAuthority
网关层校验的方法还是需要跟上面一样,既校验Method 又 校验 URL。
到此,关于“如何实现网关Restful接口拦截”的学习就结束了,希望能够解决大家的疑惑。理论与实践的搭配能更好的帮助大家学习,快去试试吧!若想继续学习更多相关知识,请继续关注亿速云网站,小编会继续努力为大家带来更多实用的文章!
亿速云「云服务器」,即开即用、新一代英特尔至强铂金CPU、三副本存储NVMe SSD云盘,价格低至29元/月。点击查看>>
免责声明:本站发布的内容(图片、视频和文字)以原创、转载和分享为主,文章观点不代表本网站立场,如果涉及侵权请联系站长邮箱:is@yisu.com进行举报,并提供相关证据,一经查实,将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容。
原文链接:https://my.oschina.net/u/1388595/blog/4910147