本篇内容主要讲解“Python的Jupyter Notebook举例分析”,感兴趣的朋友不妨来看看。本文介绍的方法操作简单快捷,实用性强。下面就让小编来带大家学习“Python的Jupyter Notebook举例分析”吧!
Jupyter Notebook(此前被称为IPython notebook)是一个交互式笔记本,支持运行40多种编程语言。
在开始使用notebook之前,需要先安装该库:(1)在命令行中执行pip install jupyter来安装;(2)安装Anaconda后自带Jupyter Notebook。
在命令行中执行jupyter notebook,就会在当前目录下启动Jupyter服务并使用默认浏览器打开页面,还可以复制链接在其他浏览器中打开。
notebook界面由以下部分组成:(1)notebook名称;(2)主工具栏,提供了保存、导出、重载notebook,以及重启内核等选项;(3)notebook主要区域,包含了notebook的内容编辑区。
在Jupyter页面下方的主要区域,由被称为单元格的部分组成。每个notebook由多个单元格构成,而每个单元格又可以有不同的用途。上图中看到的是一个代码单元格(code cell),以[ ]开头,在这种类型的单元格中,可以输入任意代码并执行。例如,输入1 + 2并按下Shift + Enter,单元格中的代码就会被计算,光标也会被移动到一个新的单元格中。
如果想新建一个notebook,只需要点击New,选择希望启动的notebook类型即可。
notebook可以修改之前的单元格,对其重新计算,这样就可以更新整个文档了。如果你不想重新运行整个脚本,只想用不同的参数测试某个程式的话,这个特性显得尤其强大。不过,也可以重新计算整个notebook,只要点击Cell -> Run all即可。
再测试标题和其他代码如下:
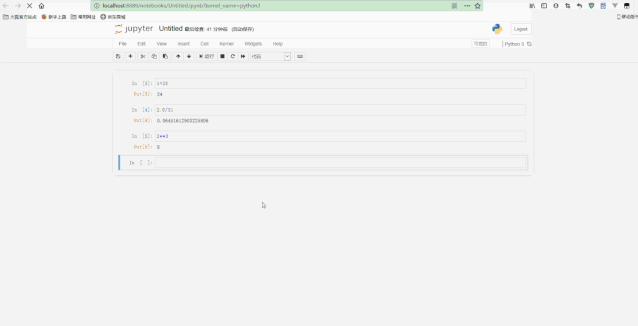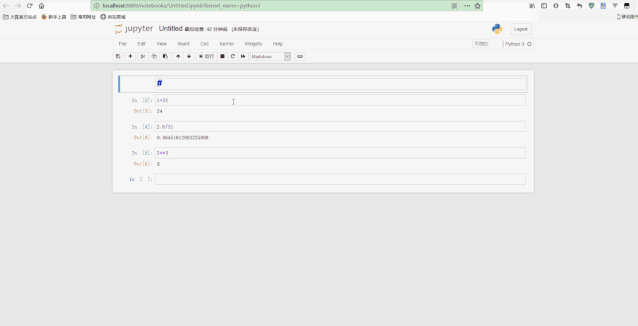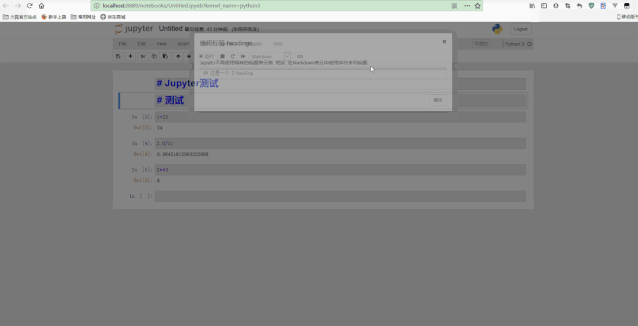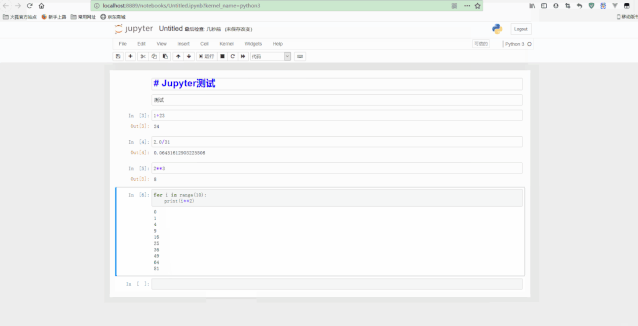
可以看到,在顶部添加了一个notebook的标题,还可以执行for循环等语句。
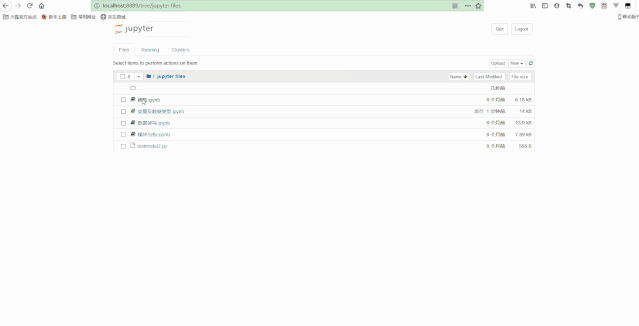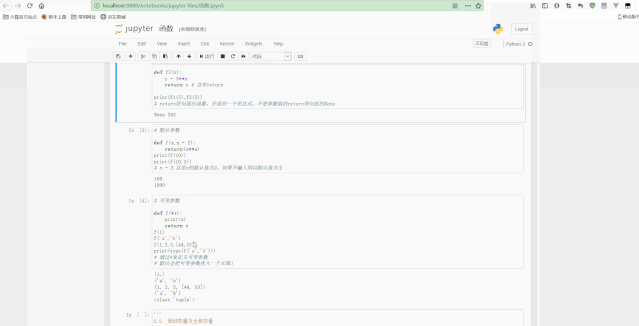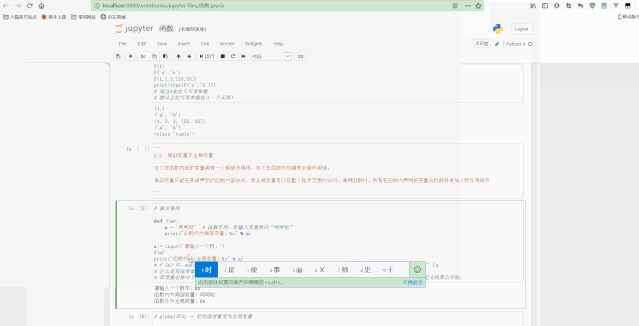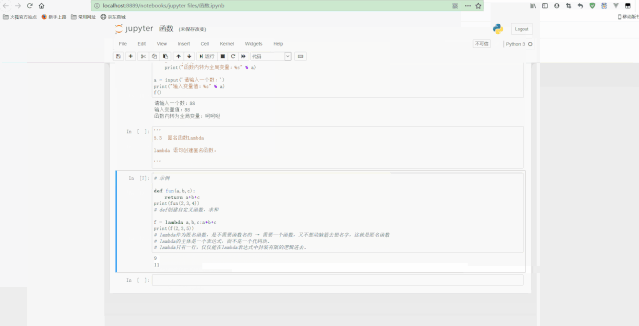
Jupyter测试Python变量和数据类型如下:
测试Python模块如下:
数据读写很重要,因为进行数据分析时必须先读取数据,进行数据处理后也要进行保存。
加载csv数据,处理数据,保存到MongoDB数据库
有csv文件shopproducts.csv和userratings.csv,分别是商品数据和用户评分数据,如下:
现在需要通过Python将其读取出来,并将指定的字段保存到MongoDB中,需要在Anaconda中执行命令conda install pymongo安装pymongo。
Python代码如下:
import pymongo
class Product:
def __init__(self,productId:int ,name, imageUrl, categories, tags):
self.productId = productId
self.name = name
self.imageUrl = imageUrl
self.categories = categories
self.tags = tags
def __str__(self) -> str:
return self.productId +'^' + self.name +'^' + self.imageUrl +'^' + self.categories +'^' + self.tags
class Rating:
def __init__(self, userId:int, productId:int, score:float, timestamp:int):
self.userId = userId
self.productId = productId
self.score = score
self.timestamp = timestamp
def __str__(self) -> str:
return self.userId +'^' + self.productId +'^' + self.score +'^' + self.timestamp
if __name__ == '__main__':
myclient = pymongo.MongoClient("mongodb://127.0.0.1:27017/")
mydb = myclient["goods-users"]
## val attr = item.split("\\^")
## // 转换成Product
## Product(attr(0).toInt, attr(1).trim, attr(4).trim, attr(5).trim, attr(6).trim)
shopproducts = mydb['shopproducts']
with open('shopproducts.csv', 'r',encoding='UTF-8') as f:
item = f.readline()
while item:
attr = item.split('^')
product = Product(int(attr[0]), attr[1].strip(), attr[4].strip(), attr[5].strip(), attr[6].strip())
shopproducts.insert_one(product.__dict__)
## print(product)
## print(json.dumps(obj=product.__dict__,ensure_ascii=False))
item = f.readline()
## val attr = item.split(",")
## Rating(attr(0).toInt, attr(1).toInt, attr(2).toDouble, attr(3).toInt)
userratings = mydb['userratings']
with open('userratings.csv', 'r',encoding='UTF-8') as f:
item = f.readline()
while item:
attr = item.split(',')
rating = Rating(int(attr[0]), int(attr[1].strip()), float(attr[2].strip()), int(attr[3].strip()))
userratings.insert_one(rating.__dict__)
## print(rating)
item = f.readline()在启动MongoDB服务后,运行Python代码,运行完成后,再通过Robo 3T查看数据库如下:
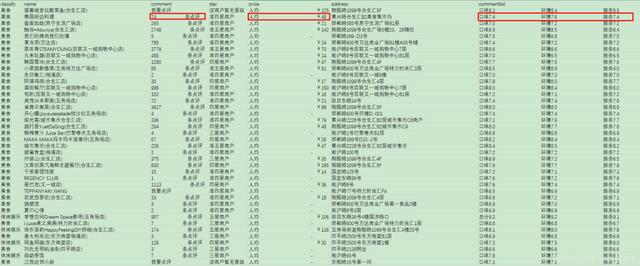
包括名称、评论数、价格、地址、评分列表等,其中评论数、价格和评分均不规则、需要进行数据清洗。
Jupyter中处理如下:
可以看到,最后得到了经过清洗后的规则数据。
完整Python代码如下:
## 数据读取
f = open('商铺数据.csv', 'r', encoding='utf8')
for i in f.readlines()[1:15]:
print(i.split(','))
## 创建comment、price、commentlist清洗函数
def fcomment(s):
'''comment清洗函数:用空格分段,选取结果list的第一个为点评数,并且转化为整型'''
if '条' in s:
return int(s.split(' ')[0])
else:
return '缺失数据'
def fprice(s):
'''price清洗函数:用¥分段,选取结果list的最后一个为人均价格,并且转化为浮点型'''
if '¥' in s:
return float(s.split('¥')[-1])
else:
return '缺失数据'
def fcommentl(s):
'''commentlist清洗函数:用空格分段,分别清洗出质量、环境及服务数据,并转化为浮点型'''
if ' ' in s:
quality = float(s.split(' ')[0][2:])
environment = float(s.split(' ')[1][2:])
service = float(s.split(' ')[2][2:-1])
return [quality, environment, service]
else:
return '缺失数据'
## 数据处理清洗
datalist = [] ## 创建空列表
f.seek(0)
n = 0 ## 创建计数变量
for i in f.readlines():
data = i.split(',')
## print(data)
classify = data[0] ## 提取分类
name = data[1] ## 提取店铺名称
comment_count = fcomment(data[2]) ## 提取评论数量
star = data[3] ## 提取星级
price = fprice(data[4]) ## 提取人均
address = data[5] ## 提取地址
quality = fcommentl(data[6])[0] ## 提取质量评分
env = fcommentl(data[6])[1] ## 提取环境评分
service = fcommentl(data[6])[2] ## 提取服务评分
if '缺失数据' not in [comment_count, price, quality]: ## 用于判断是否有数据缺失
n += 1
data_re = [['classify', classify],
['name', name],
['comment_count', comment_count],
['star', star],
['price', price],
['address', address],
['quality', quality],
['environment', env],
['service', service]]
datalist.append(dict(data_re)) ## 字典生成,并存入列表datalist
print('成功加载%i条数据' % n)
else:
continue
print(datalist)
print('总共加载%i条数据' % n)
f.close()到此,相信大家对“Python的Jupyter Notebook举例分析”有了更深的了解,不妨来实际操作一番吧!这里是亿速云网站,更多相关内容可以进入相关频道进行查询,关注我们,继续学习!
亿速云「云服务器」,即开即用、新一代英特尔至强铂金CPU、三副本存储NVMe SSD云盘,价格低至29元/月。点击查看>>
免责声明:本站发布的内容(图片、视频和文字)以原创、转载和分享为主,文章观点不代表本网站立场,如果涉及侵权请联系站长邮箱:is@yisu.com进行举报,并提供相关证据,一经查实,将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容。
原文链接:https://my.oschina.net/u/4848094/blog/4745618