这期内容当中小编将会给大家带来有关如何正确的使用ElastchSearch,文章内容丰富且以专业的角度为大家分析和叙述,阅读完这篇文章希望大家可以有所收获。
首次添加文档时,若索引不存在会自动创建; 借助 kibana 的dev-tools来实现 es 的交互
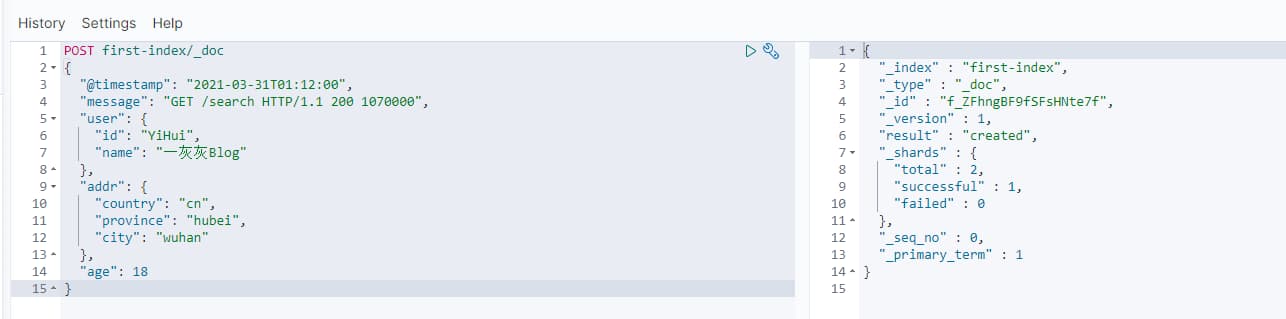
POST first-index/_doc
{
"@timestamp": "2021-03-31T01:12:00",
"message": "GET /search HTTP/1.1 200 1070000",
"user": {
"id": "YiHui",
"name": "一灰灰Blog"
},
"addr": {
"country": "cn",
"province": "hubei",
"city": "wuhan"
},
"age": 18
}
## 添加两个数据进行测试
POST first-index/_doc
{
"@timestamp": "2021-03-31T02:12:00",
"message": "GET /search HTTP/1.1 200 1070000",
"user": {
"id": "ErHui",
"name": "二灰灰Blog"
},
"addr": {
"country": "cn",
"province": "hubei",
"city": "wuhan"
},
"age": 19
}当然也可以直接使用 http 进行交互,下面的方式和上面等价(后面都使用 kibanan 进行交互,更直观一点)
curl -X POST 'http://localhost:9200/first-index/_doc?pretty' -H 'Content-Type: application/json' -d '
{
"@timestamp": "2021-03-31T01:12:00",
"message": "GET /search HTTP/1.1 200 1070000",
"user": {
"id": "YiHui",
"name": "一灰灰Blog"
},
"addr": {
"country": "cn",
"province": "hubei",
"city": "wuhan"
},
"age": 18
}'
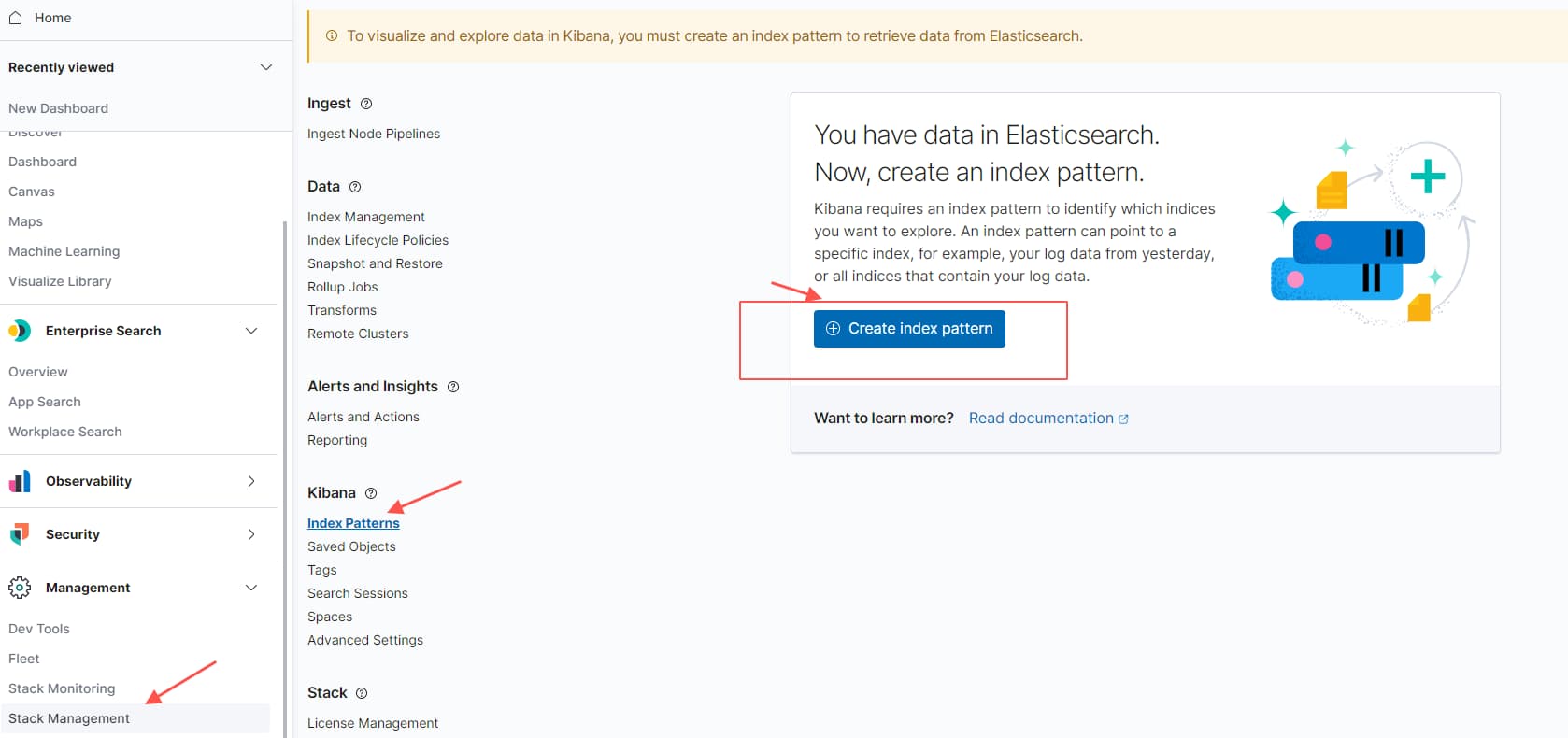
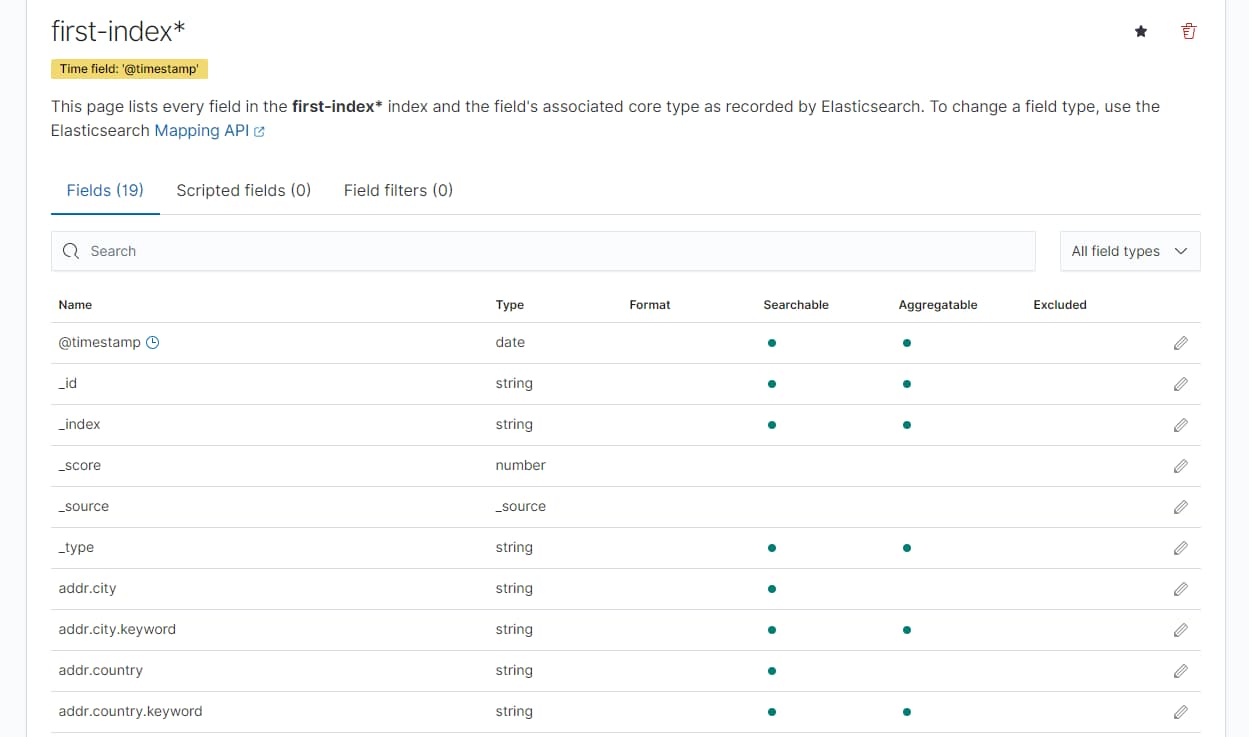
除了基础的查询语法之外,直接使用 kibana 进行查询,对于使用方而言,门槛最低;首先配置上面的 es 索引
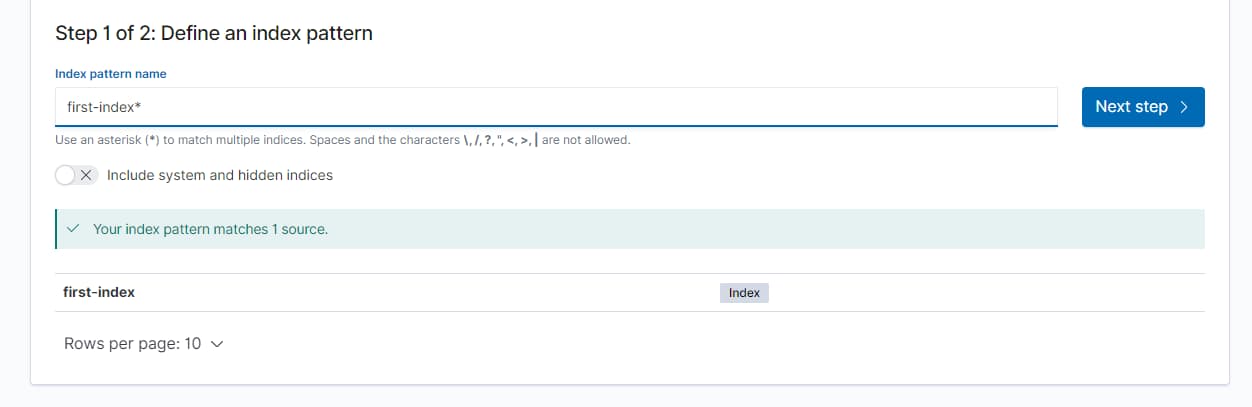
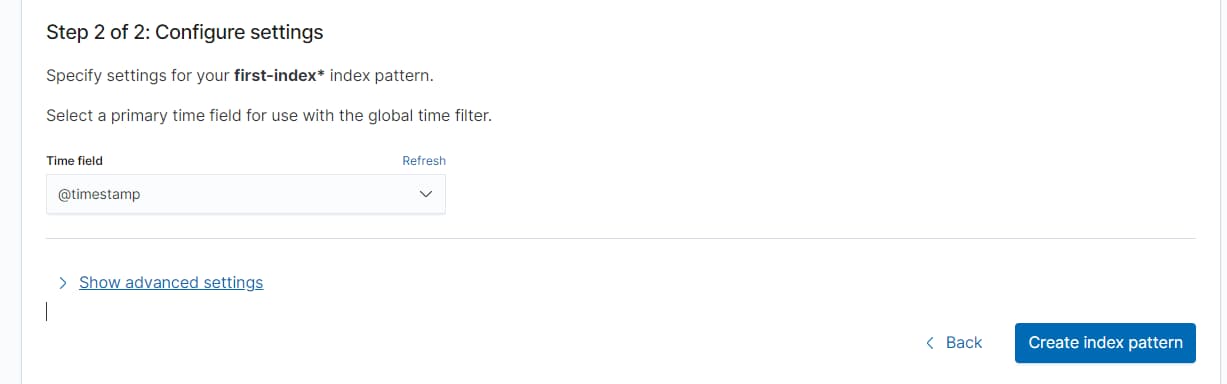
Management -> Stack Management -> Kiabana Index Patterns
index pattern name
时间字段,选择 @timestamp 这个与实际的文档中的 field 有关
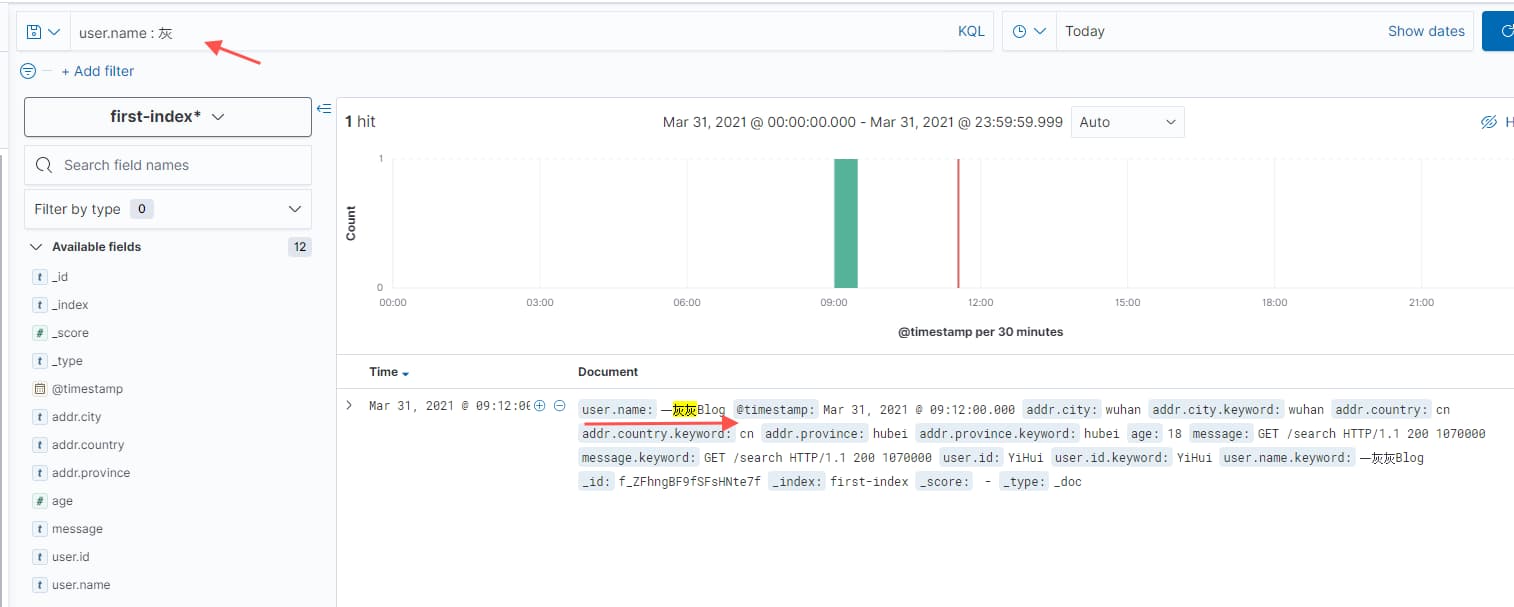
接下来进入Discover 进行查询

比如字段查询
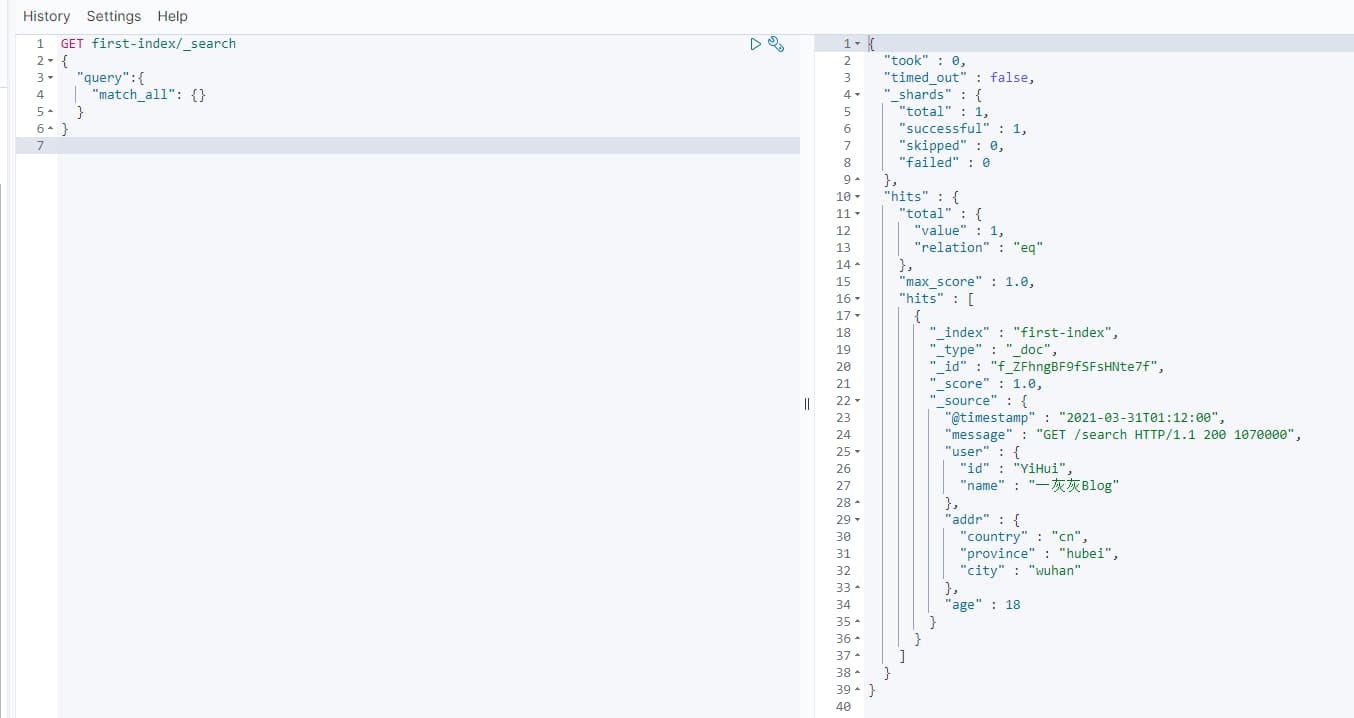
不加任何匹配,捞出文档(当数据量很多时,当然也不会真的全部返回,也是会做分页的)
GET my-index/_search
{
"query": {
"match_all": {
}
}
}
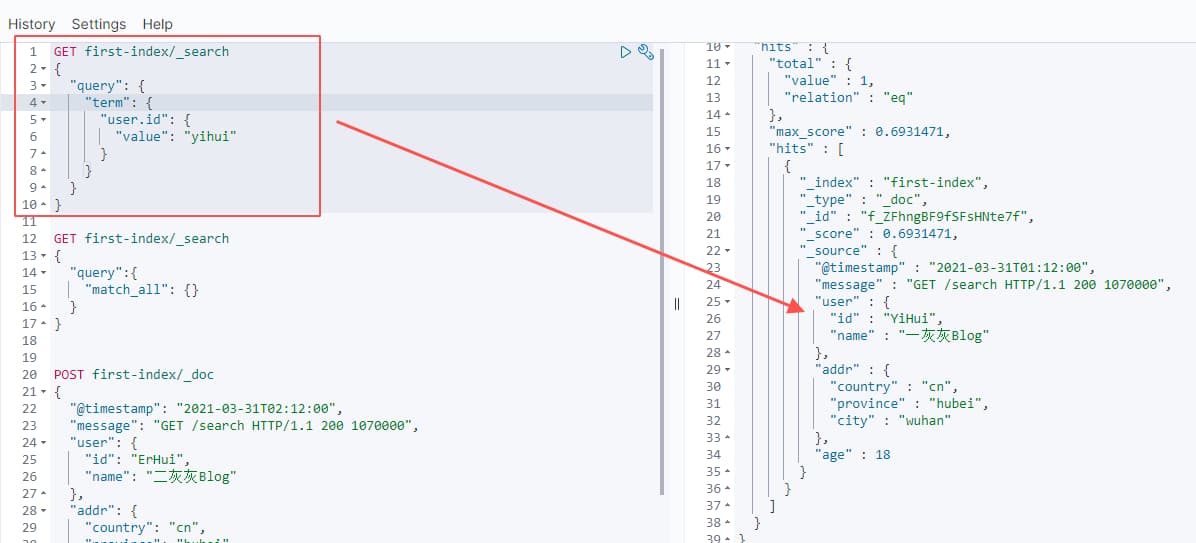
根据 field 进行 value 匹配,忽略大小写;
查询语法,形如: `{"query": {"term": {"成员名": {"value": "查询值"}}}}
query, term, value 三个 key 为固定值
成员名: 为待查询的成员
查询值: 需要匹配的值
(说明:后面语法中,中文的都是需要替换的,英文的为固定值)
GET first-index/_search
{
"query": {
"term": {
"user.id": {
"value": "yihui"
}
}
}
}
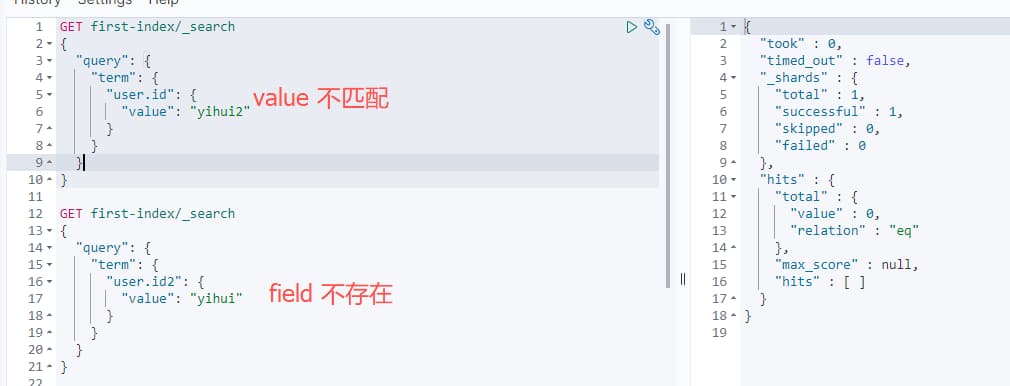
当 value 不匹配,或者查询的 field 不存在,则查不到的对应的信息,如
term 表示 value 的精确匹配,如果我希望类似value in (xxx)的查询,则可以使用 terms
语法:
{
"query": {
"terms": {
"成员名": [成员值, 成员值]
}
}
}实例如
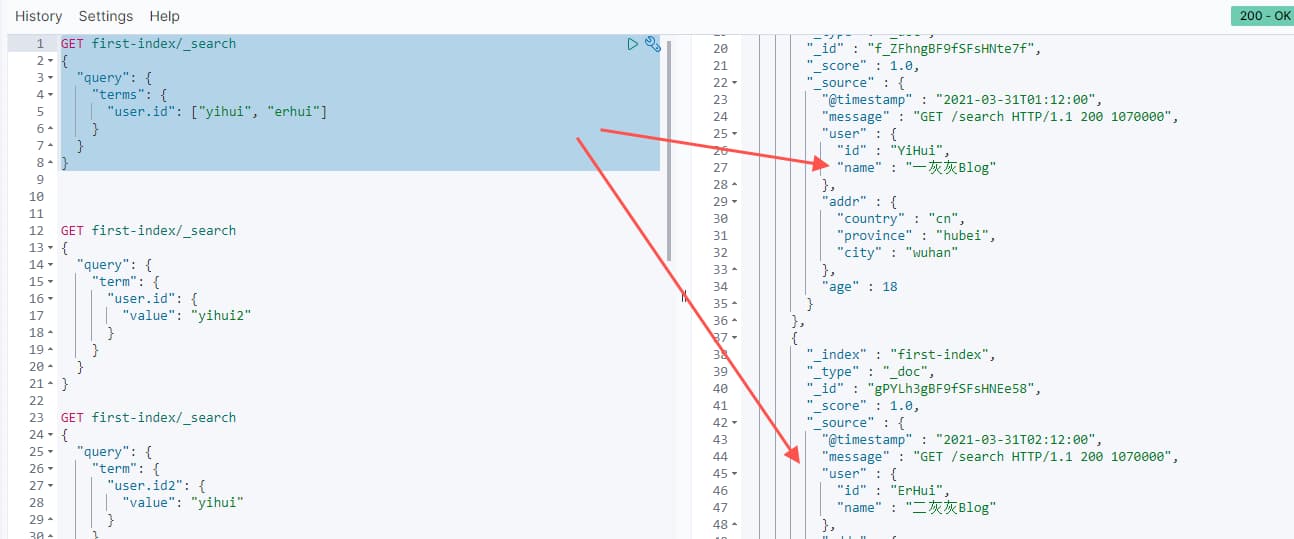
GET first-index/_search
{
"query": {
"terms": {
"user.id": ["yihui", "erhui"]
}
}
}
适用于数值、日期的比较查询,如常见的 >, >=, <, <=
查询语法
{
"query": {
"range": {
"成员名": {
"gte": "查询下界" ,
"lte": "查询下界"
}
}
}
}| 范围操作符 | 说明 |
|---|---|
gt | 大于 > |
gte | 大于等于 >= |
lt | 小于 < |
lte | 小于等于 <= |
实例如下
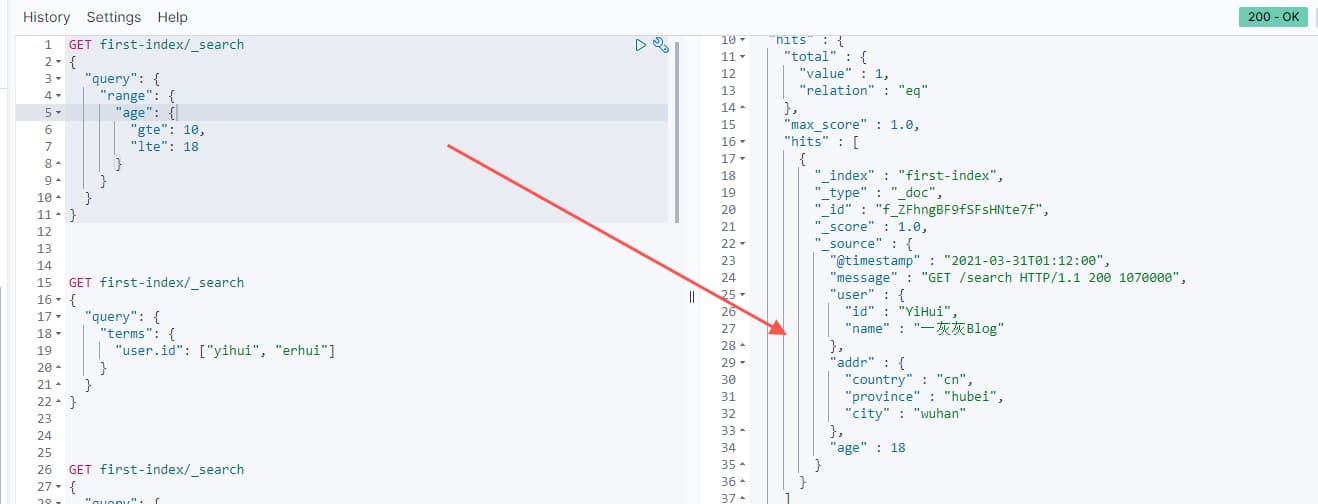
GET first-index/_search
{
"query": {
"range": {
"age": {
"gte": 10,
"lte": 18
}
}
}
}
根据是否包含某个字段来查询, 主要有两个 exists 表示要求存在, missing表示要求不存在
查询语法
{
"query": {
"exists/missing": {
"field": "字段值"
}
}
}实例如下
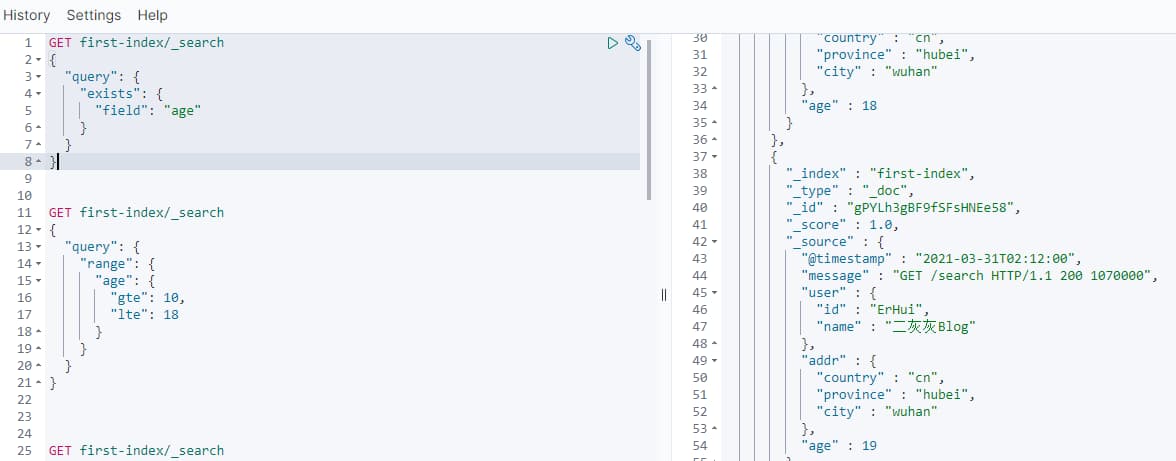
GET first-index/_search
{
"query": {
"exists": {
"field": "age"
}
}
}
上面都是单个查询条件,单我们需要多个查询条件组合使用时,可以使用bool + must/must_not/should来实现
查询语法
{
"query": {
"bool": {
"must": [ # 相当于and查询
"查询条件1",
"查询条件2"
],
"must_not": [ # 多个查询条件相反匹配,相当与not
...
],
"should": [ # 有一个匹配即可, 相当于or
...
]
}
}
}实例如下
## user.id = yihui and age < 20
GET first-index/_search
{
"query": {
"bool": {
"must": [
{
"term": {
"user.id": {
"value": "yihui"
}
}
},
{
"range": {
"age": {
"lt": 20
}
}
}
]
}
}
}
# !(user.id) = yihui and !(age>20)
GET first-index/_search
{
"query": {
"bool": {
"must_not": [
{
"term": {
"user.id": {
"value": "yihui"
}
}
},
{
"range": {
"age": {
"gt": 20
}
}
}
]
}
}
}
# user.id = 'yihui' or age>20
GET first-index/_search
{
"query": {
"bool": {
"should": [
{
"term": {
"user.id": {
"value": "yihui"
}
}
},
{
"range": {
"age": {
"gt": 20
}
}
}
]
}
}
}下面截图以 must_not 输出示意
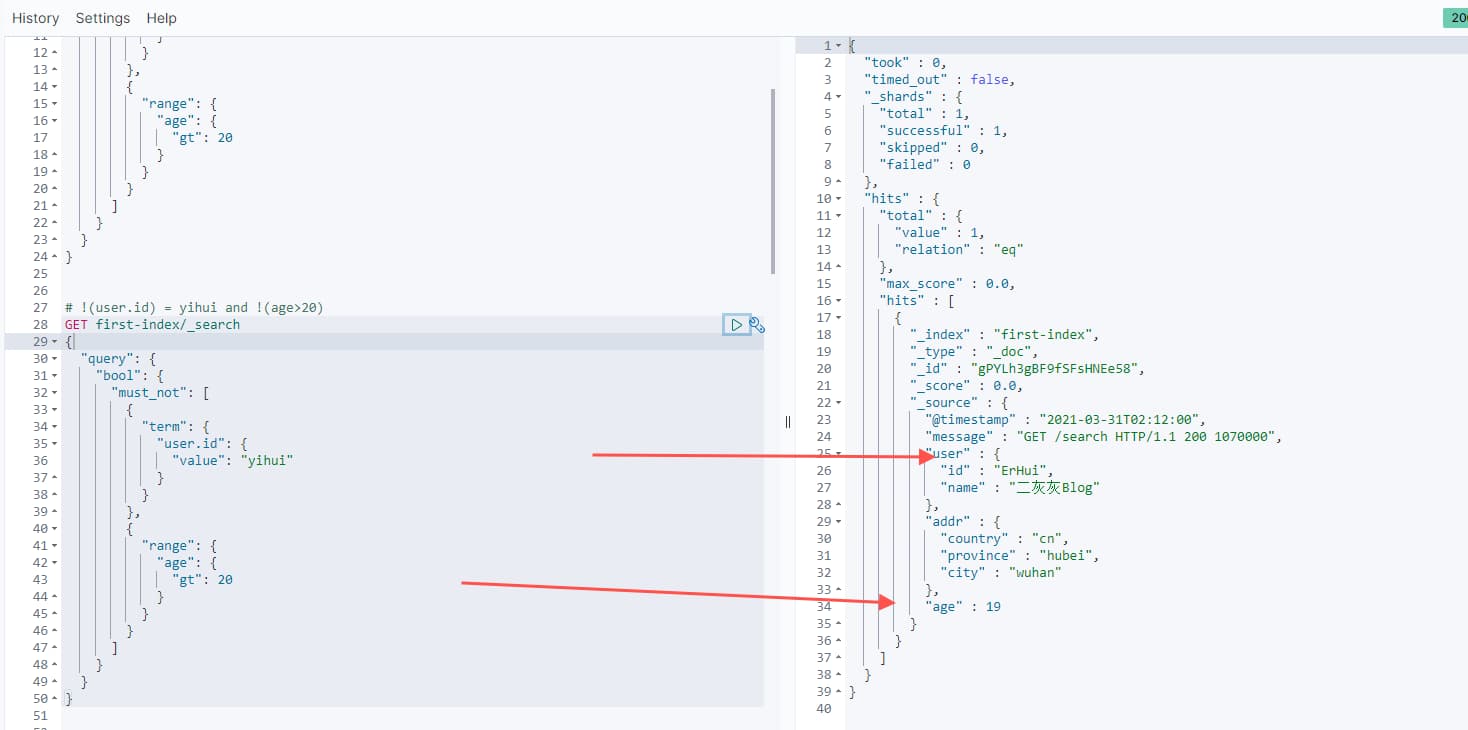
说明
前面根据字段查询 existing 只能单个匹配,可以借助这里的组合来实现多个的判断
最大的特点是它更适用于模糊查询,比如查询某个 field 中的字段匹配
语法
{
"query": {
"match": {
"字段名": "查询值"
}
}
}举例说明
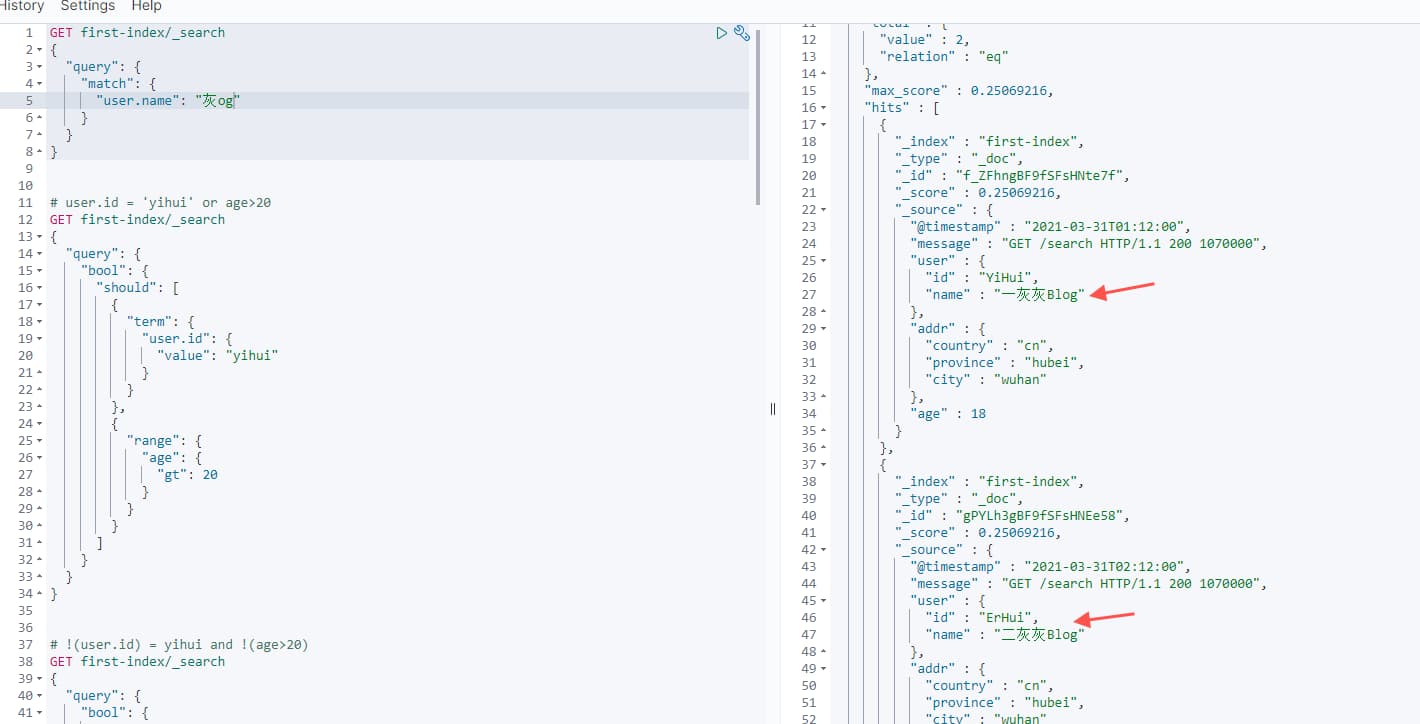
GET first-index/_search
{
"query": {
"match": {
"user.name": "灰og"
}
}
}
说明,如果有精确查询的需求,使用前面的 term,可以缓存结果
更多相关信息,可以查看: 官网-multi_match 查询
多个字段中进行查询
语法
type: best_fields 、 most_fields 和 cross_fields (最佳字段、多数字段、跨字段)
最佳字段 :当搜索词语具体概念的时候,比如 “brown fox” ,词组比各自独立的单词更有意义
多数字段:为了对相关度进行微调,常用的一个技术就是将相同的数据索引到不同的字段,它们各自具有独立的分析链。
混合字段:对于某些实体,我们需要在多个字段中确定其信息,单个字段都只能作为整体的一部分
{
"query": {
"multi_match": {
"query": "Quick brown fox",
"type": "best_fields",
"fields": [ "title", "body" ],
"tie_breaker": 0.3,
"minimum_should_match": "30%"
}
}
}实例演示
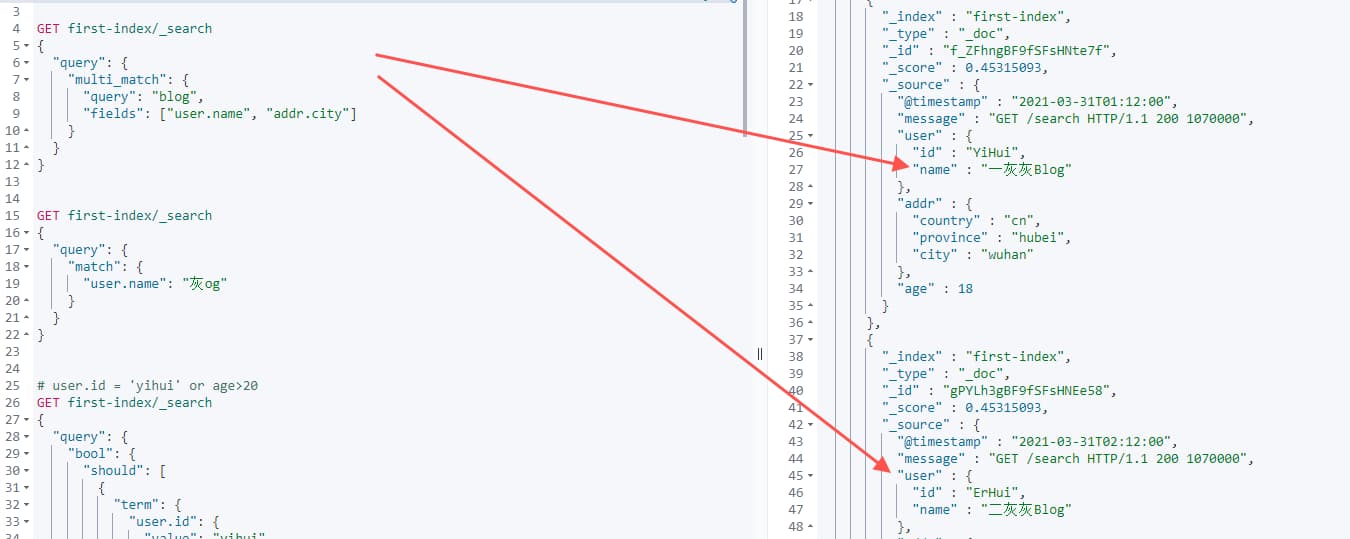
GET first-index/_search
{
"query": {
"multi_match": {
"query": "汉",
"fields": ["user.id", "addr.city"]
}
}
}
上面除了写上精确的字段之外,还支持模糊匹配,比如所有字段中进行匹配
GET first-index/_search
{
"query": {
"multi_match": {
"query": "blog",
"fields": ["*"]
}
}
}shell 统配符
?: 0/1 个字符
*: 0/n 个字符
GET first-index/_search
{
"query": {
"wildcard": {
"user.id": {
"value": "*Hu?"
}
}
}
}说明,对中文可能有问题
正则匹配
GET first-index/_search
{
"query": {
"regexp": {
"user.name": ".*log"
}
}
}前缀匹配
GET first-index/_search
{
"query": {
"prefix": {
"user.name": "一"
}
}
}查询结果排序,根据 sort 来指定
{
"sort": [
{
"成员变量": {
"order": "desc"
}
}
]
}实例如下
GET first-index/_search
{
"query":{
"match_all": {}
},
"sort": [
{
"@timestamp": {
"order": "desc"
}
}
]
}更多操作姿势,可以在官方文档上获取
官方教程
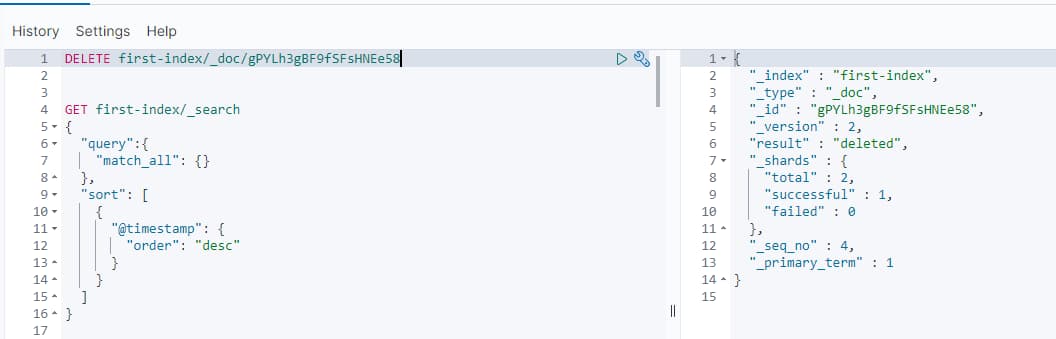
需要根据文档 id 进行指定删除
DELETE first-index/_doc/gPYLh4gBF9fSFsHNEe58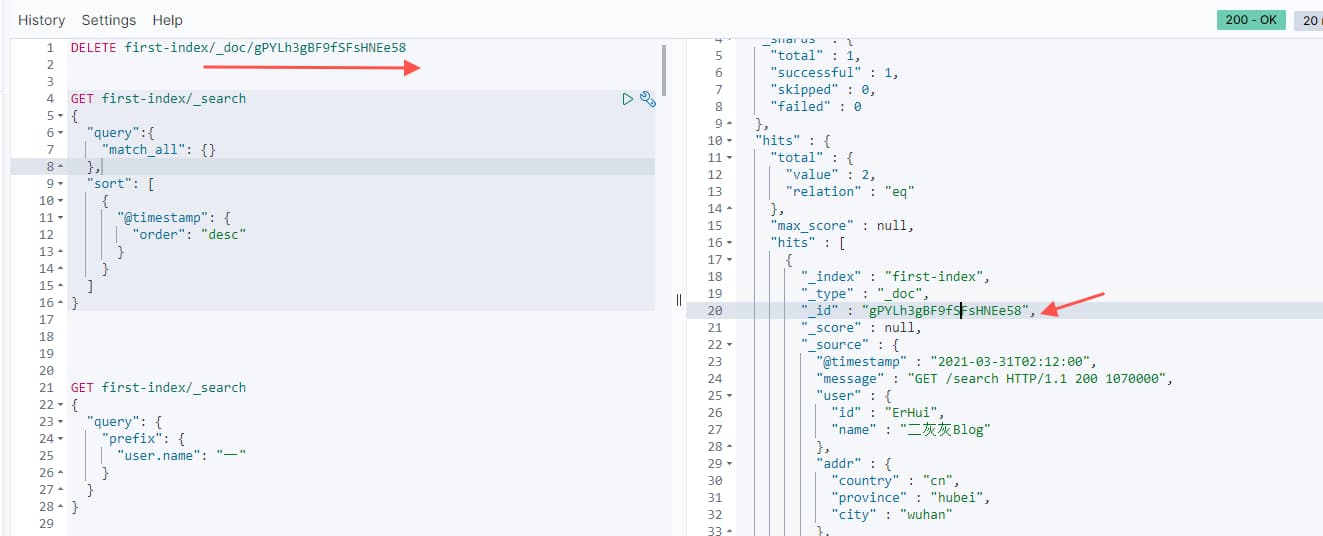
删除成功
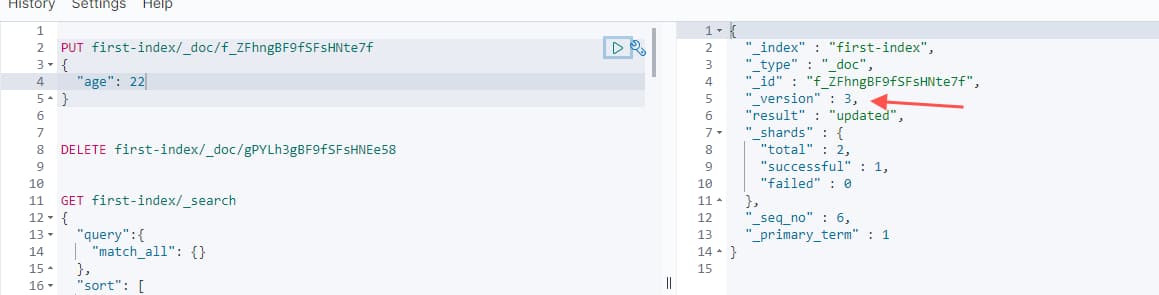
使用 PUT 来实现更新,同样通过 id 进行
覆盖更新
version 版本会+1
如果 id 对应的文档不存在,则新增
PUT first-index/_doc/f_ZFhngBF9fSFsHNte7f
{
"age": 28
}
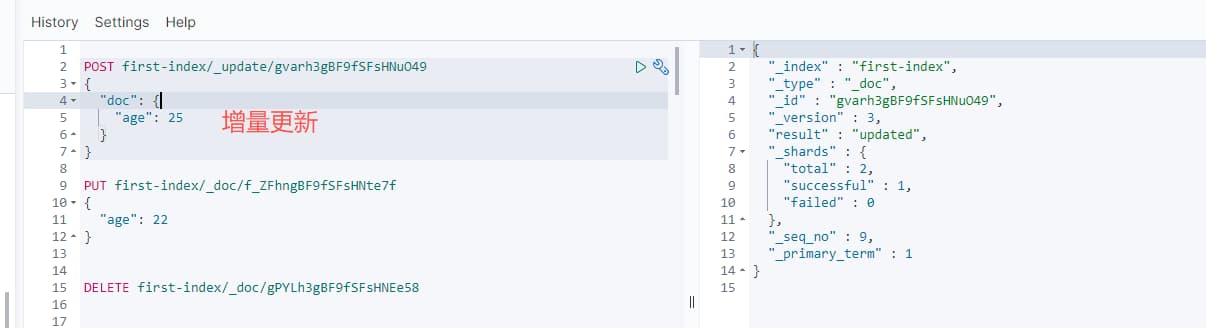
采用 POST 来实现增量更新
field 存在,则更新
field 不存在,则新增
POST first-index/_update/gvarh4gBF9fSFsHNuO49
{
"doc": {
"age": 25
}
}
此外还可以采用 script 脚本更新
在原来的 age 基础上 + 5
POST first-index/_update/gvarh4gBF9fSFsHNuO49
{
"script": "ctx._source.age += 5"
}上述就是小编为大家分享的如何正确的使用ElastchSearch了,如果刚好有类似的疑惑,不妨参照上述分析进行理解。如果想知道更多相关知识,欢迎关注亿速云行业资讯频道。
亿速云「云服务器」,即开即用、新一代英特尔至强铂金CPU、三副本存储NVMe SSD云盘,价格低至29元/月。点击查看>>
免责声明:本站发布的内容(图片、视频和文字)以原创、转载和分享为主,文章观点不代表本网站立场,如果涉及侵权请联系站长邮箱:is@yisu.com进行举报,并提供相关证据,一经查实,将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容。
原文链接:https://my.oschina.net/u/566591/blog/5012774