这篇文章给大家介绍springboot2.0.6如何启动监听器,内容非常详细,感兴趣的小伙伴们可以参考借鉴,希望对大家能有所帮助。
public ConfigurableApplicationContext run(String... args) {
......//省略
// 获取一个run监听器,主要监听SpringApplication对象,(内部只有一个EventPublishingRunListener)
SpringApplicationRunListeners listeners = getRunListeners(args);
//调用监听器的启动,当SpringApplication对象的run方法刚启动的时候(依靠SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster)
listeners.starting();
......//省略
}SpringApplicationRunListeners 是一个集合类,内部包含一个 log 和包含 SpringApplicationRunListener 的 List。而 SpringApplicationRunListener 主要是监听 SpringApplication 对象的,里面的方法都定义了在何时调用 SpringApplicationRunListener 的各种方法。
下面的每一个方法 SpringApplicationRunListener 都把其包装成一个事件,在spring容器还未成功 refreshed 之前都是使用SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster 去寻找对该事件感兴趣的ApplicationListener,然后调用其onApplicationEvent方法
starting:当SpringApplication对象的run方法刚启动的时候(依靠SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster)
environmentPrepared:在environment Prepared 但是spring容器还未创建的时候(依靠SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster)
contextPrepared:当spring容器已经创建且准备好了,(目前是空的实现)
contextLoaded:当spring容器已经loaded 且未refresh 。load就是将我们的primaryClass注册到spring容器中,(依靠SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster) 同时将之前获取到的ApplicationListener都加入到spring容器中,此时如果ApplicationListener还是ApplicationContextAware的也要调用其setApplicationContext方法。
started:spring容器已经刷新过且应用已经启动,但是CommandLineRunners和ApplicationRunners还未调用,直接通过spring容器自己发送(因为ApplicationListener已经加入spring容器)
running:我们已经调用了CommandLineRunners,直接通过spring容器自己发送(因为ApplicationListener已经加入spring容器)
failed:当异常发生的时候就调用这个,如果spring容器没有loaded 或者没有激活就使用SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster,否则还是依靠spring容器自己
public class SpringApplication {
// 获取监听
private SpringApplicationRunListeners getRunListeners(String[] args) {
// 定义class数组
Class<?>[] types = new Class<?>[] { SpringApplication.class, String[].class };
// 创建SpringApplicationRunListeners对象
return new SpringApplicationRunListeners(logger, getSpringFactoriesInstances(
SpringApplicationRunListener.class, types, this, args));
}
}默认情况下,getRunListeners 方法从 spring.factories 文件中找出key为 SpringApplicationRunListener 的类有:
org.springframework.boot.context.event.EventPublishingRunListener
这里我们看到了一个熟悉的方法getSpringFactoriesInstances(SpringApplicationRunListener.class, types, this, args),前面的博文我们已经详细介绍过该方法是怎么一步步的获取到META-INF/spring.factories中的指定的key的value,获取到以后怎么实例化类的(参考)。执行 获取的值如下图
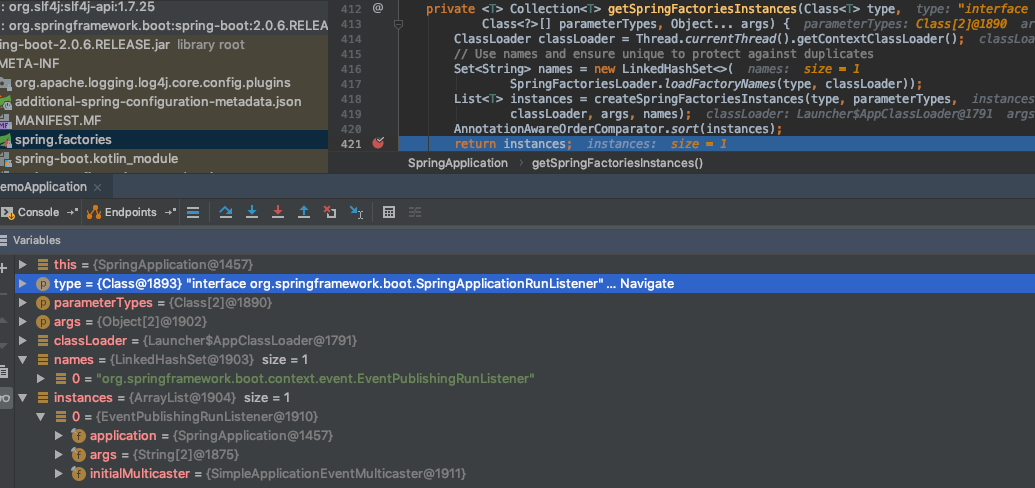
从上图debug结果,我们可以看到我们获取到了一个监听器EventPublishingRunListener,该监听器是Spring容器的启动监听器。listeners.starting()方法开启了监听事件
public class EventPublishingRunListener implements SpringApplicationRunListener, Ordered {
private final SpringApplication application;
private final String[] args;
private final SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster initialMulticaster;
// 加载监听器类
public EventPublishingRunListener(SpringApplication application, String[] args) {
this.application = application;
this.args = args;
this.initialMulticaster = new SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster();
// 给initialMulticaster 添加listener
for (ApplicationListener<?> listener : application.getListeners()) {
this.initialMulticaster.addApplicationListener(listener);
}
}
// 实现类调用EventPublishingRunListener的方法
public void starting() {
this.initialMulticaster.multicastEvent(
// 创建了一个ApplicationStartingEvent事件,将springapplication的this.application传入,因此监听的时候获取的是SpringApplication实例
new ApplicationStartingEvent(this.application, this.args));
}
......//省略
}EventPublishingRunListener的初始化方法中 对application、args进行了赋值,并对SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster进行了初始化,然后获取application中的监听器添加给SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster对象。
进入SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster类的初始化方法,如下
public class SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster extends AbstractApplicationEventMulticaster {
private Executor taskExecutor;
private ErrorHandler errorHandler;
public void multicastEvent(ApplicationEvent event) {
multicastEvent(event, resolveDefaultEventType(event));
}
public void multicastEvent(final ApplicationEvent event, @Nullable ResolvableType eventType) {
ResolvableType type = (eventType != null ? eventType : resolveDefaultEventType(event));
// 注意getApplicationListeners获取对应的事件监听器
for (final ApplicationListener<?> listener : getApplicationListeners(event, type)) {
Executor executor = getTaskExecutor();
if (executor != null) {
executor.execute(() -> invokeListener(listener, event));
}
else {
invokeListener(listener, event);
}
}
}
}SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster类继承 AbstractApplicationEventMulticaster
public abstract class AbstractApplicationEventMulticaster
implements ApplicationEventMulticaster, BeanClassLoaderAware, BeanFactoryAware {
protected Collection<ApplicationListener<?>> getApplicationListeners(
ApplicationEvent event, ResolvableType eventType) {
Object source = event.getSource();
Class<?> sourceType = (source != null ? source.getClass() : null);
ListenerCacheKey cacheKey = new ListenerCacheKey(eventType, sourceType);
// Quick check for existing entry on ConcurrentHashMap…
// 快速检测 COncurrentHashMap 的现有条目
ListenerRetriever retriever = this.retrieverCache.get(cacheKey);
if (retriever != null) {
return retriever.getApplicationListeners();
}
if (this.beanClassLoader == null ||
(ClassUtils.isCacheSafe(event.getClass(), this.beanClassLoader) &&
(sourceType == null || ClassUtils.isCacheSafe(sourceType, this.beanClassLoader)))) {
// Fully synchronized building and caching of a ListenerRetriever
synchronized (this.retrievalMutex) {
retriever = this.retrieverCache.get(cacheKey);
if (retriever != null) {
return retriever.getApplicationListeners();
}
retriever = new ListenerRetriever(true);
Collection<ApplicationListener<?>> listeners =
retrieveApplicationListeners(eventType, sourceType, retriever);
this.retrieverCache.put(cacheKey, retriever);
return listeners;
}
}
else {
// No ListenerRetriever caching -> no synchronization necessary
return retrieveApplicationListeners(eventType, sourceType, null);
}
}
// 实际上检索给定事件和源类型的应用程序监听器是否匹配
private Collection<ApplicationListener<?>> retrieveApplicationListeners(
ResolvableType eventType, @Nullable Class<?> sourceType, @Nullable ListenerRetriever retriever) {
List<ApplicationListener<?>> allListeners = new ArrayList<>();
Set<ApplicationListener<?>> listeners;
Set<String> listenerBeans;
synchronized (this.retrievalMutex) {
// 这个listener集合就是前文提到的从配置中过滤的10个监听器(图1)
listeners = new LinkedHashSet<>(this.defaultRetriever.applicationListeners);
listenerBeans = new LinkedHashSet<>(this.defaultRetriever.applicationListenerBeans);
}
// 循环10个listener调用supportsEvent方法
for (ApplicationListener<?> listener : listeners) {
if (supportsEvent(listener, eventType, sourceType)) {
if (retriever != null) {
retriever.applicationListeners.add(listener);
}
allListeners.add(listener);
}
}
......//省略
AnnotationAwareOrderComparator.sort(allListeners);
if (retriever != null && retriever.applicationListenerBeans.isEmpty()) {
retriever.applicationListeners.clear();
retriever.applicationListeners.addAll(allListeners);
}
return allListeners;
}
protected boolean supportsEvent(
ApplicationListener<?> listener, ResolvableType eventType, @Nullable Class<?> sourceType) {
GenericApplicationListener smartListener = (listener instanceof GenericApplicationListener ?
(GenericApplicationListener) listener : new GenericApplicationListenerAdapter(listener));
return (smartListener.supportsEventType(eventType) && smartListener.supportsSourceType(sourceType));
}
} -->程序启动
-->调用getRunListeners(args)获取SpringApplicationRunListeners实例
-->getSpringFactoriesInstances()获取Spring工厂实例集合
-->loadFactoryNames()通过classLoader加载/META-INF/spring.factories文件,获取指定class对应的类全限定名称集合
-->loadSpringFactories() 通过classLoader循环加载/META-INF/spring.factories文件,获取文件中类全限定名称集合返回
-->createSpringFactoriesInstances()根据加载文件返回的类全限定名称集合创建工厂实例,反射
-->listeners.starting()启动监听器
-->multicastEvent(ApplicationEvent event)组播ApplicationEvent事件
-->getApplicationListeners()判断监听器类型是否与当前监听器类型相同
-->retrieveApplicationListeners(eventType, sourceType, retriever)检索给定事件和源类型的应用程序监听器。
-->supportsEvent(listener, eventType, sourceType)确认给定的监听器是否支持给定的事件。
-->GenericApplicationListenerAdapter(ApplicationListener<?> delegate)为给定的委托创建一个新的GenericApplicationListener。
-->resolveDeclaredEventType(ApplicationListener<ApplicationEvent> listener)发布事件监听
-->supportsEventType(eventType)从指定类型解析事件
-->结束
SpringApplicationRunListener的那些方法底层还是依靠spring容器去发布事件
底层还是会被ApplicationListener给监听到
在spring容器prepareContext调用之后会将ApplicationListener都加入到SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster,在这之后所有的事件都会lazy发送,即先存在earlyApplicationEvents。等到spring容器refresh之后注册所有ApplicationListener,然后在统一发送之前存储的事件。
关于springboot2.0.6如何启动监听器就分享到这里了,希望以上内容可以对大家有一定的帮助,可以学到更多知识。如果觉得文章不错,可以把它分享出去让更多的人看到。
免责声明:本站发布的内容(图片、视频和文字)以原创、转载和分享为主,文章观点不代表本网站立场,如果涉及侵权请联系站长邮箱:is@yisu.com进行举报,并提供相关证据,一经查实,将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容。