这篇文章主要讲解了“Spring使用BeanPostProcessor实现AB测试的方法”,文中的讲解内容简单清晰,易于学习与理解,下面请大家跟着小编的思路慢慢深入,一起来研究和学习“Spring使用BeanPostProcessor实现AB测试的方法”吧!
第一步:
创建要实现AB测试的接口、实现类、controller
@RoutingSwitch("hello.switch")
public interface HelloService {
@RoutingSwitch("B")
String sayHello();
@RoutingSwitch("A")
String sayHi();
}@Service
public class HelloServiceImplV1 implements HelloService {
@Override
public String sayHello() {
String helloV1= "hello from V1";
System.out.println("hello from V1");
return helloV1;
}
@Override
public String sayHi() {
String hiV1= "hi from V1";
System.out.println("hi from V1");
return hiV1;
}
}@Service
public class HelloServiceImplV2 implements HelloService {
@Override
public String sayHello() {
String helloV2 = "hello from V2";
System.out.println("hello from V2");
return helloV2;
}
@Override
public String sayHi() {
String hiV2 = "hi from V2";
System.out.println("hi from V2");
return hiV2;
}
}@RestController
@RequestMapping("/test")
public class HelloControllerV2 {
@RoutingInject
private HelloService helloService;
@GetMapping("/hello")
public String sayHello() {
return helloService.sayHello();
}
@GetMapping("/hi")
public String sayHi() {
return helloService.sayHi();
}
}第二步:
创建RoutingBeanPostProcessor类实现接口BeanPostProcessor。注册controller的bean时,对使用@RoutingInject注解的接口,创建动态代理类实现类。在使用该接口时,通过invoke方法创建接口实现类。
对接口设置动态代理类注解:
@Target({ElementType.FIELD})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@Component
public @interface RoutingInject {
}开关设置注解:
@Target({ElementType.FIELD, ElementType.METHOD, ElementType.TYPE})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@Component
public @interface RoutingSwitch {
String value();
}bean初始化后,对使用RoutingInject的注解类,进行处理后置处理
@Component
public class RoutingBeanPostProcessor implements BeanPostProcessor {
@Autowired
private ApplicationContext applicationContext;
@Override
public Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
return bean;
}
@Override
public Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
Class clazz = bean.getClass();
Field[] fields = clazz.getDeclaredFields();
for (Field f : fields) {
if(f.isAnnotationPresent(RoutingInject.class)) {
if(!f.getType().isInterface()) {
throw new BeanCreationException("RoutingInject field must be declared as an interface:" + "@Class" + clazz.getName());
}
try {
this.handleRoutingInjected(f, bean, f.getType());
} catch (IllegalAccessException e) {
throw new BeanCreationException("Exception thrown when handleAutowiredRouting", e);
}
}
}
return bean;
}
private void handleRoutingInjected(Field field, Object bean, Class type) throws IllegalAccessException {
Map<String, Object> candidates = applicationContext.getBeansOfType(type);
field.setAccessible(true);
if(candidates.size() == 1) {
field.set(bean, candidates.entrySet().iterator().next());
}else if(candidates.size() == 2) {
Object proxy = RoutingBeanProxyFactory.createProxy(type, candidates);
field.set(bean, proxy);
}else{
throw new IllegalAccessException("Find more bean 2 bean for type: " + type);
}
}
}代理工程实现类:
public class RoutingBeanProxyFactory {
public static Object createProxy(Class targetClass, Map<String, Object> beans) {
ProxyFactory proxyFactory = new ProxyFactory();
proxyFactory.setInterfaces(new Class[]{targetClass});
proxyFactory.addAdvice(new VersionRoutingMethodInterceptor(targetClass, beans));
return proxyFactory.getProxy();
}
static class VersionRoutingMethodInterceptor implements MethodInterceptor {
private String classSwitch;
private Object beanSwitchOn;
private Object beanSwitchOff;
public VersionRoutingMethodInterceptor(Class targetClass, Map<String, Object> beans) {
String interfaceName = StringUtils.uncapitalize(targetClass.getSimpleName());
if(targetClass.isAnnotationPresent(RoutingSwitch.class)) {
this.classSwitch = ((RoutingSwitch) targetClass.getAnnotation(RoutingSwitch.class)).value();
}
this.beanSwitchOn = beans.get(this.buildBeanName(interfaceName, true));
this.beanSwitchOff = beans.get(this.buildBeanName(interfaceName, false));
}
private String buildBeanName(String interfaceName, boolean isSwitchOn) {
return interfaceName + "Impl" + (isSwitchOn ? "V2" : "V1");
}
@Override
public Object invoke(MethodInvocation invocation) throws Throwable {
Method method = invocation.getMethod();
String switchName = this.classSwitch;
if(method.isAnnotationPresent(RoutingSwitch.class)) {
switchName = method.getAnnotation(RoutingSwitch.class).value();
}
if(StringUtils.isBlank(switchName)) {
throw new IllegalStateException("RoutingSwitch's value is blank, method:" + method.getName());
}
return invocation.getMethod().invoke(getTargetName(switchName), invocation.getArguments());
}
public Object getTargetName(String switchName) {
boolean switchOn;
if(RoutingVersion.A.name().equals(switchName)) {
switchOn = false;
}else{
switchOn = true;
}
return switchOn ? beanSwitchOn : beanSwitchOff;
}
}
enum RoutingVersion{
A,B
}
}第三步:
测试接口正常
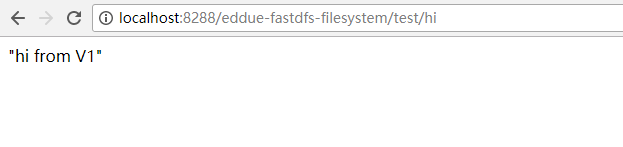
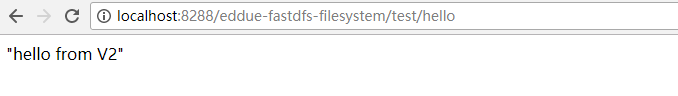
感谢各位的阅读,以上就是“Spring使用BeanPostProcessor实现AB测试的方法”的内容了,经过本文的学习后,相信大家对Spring使用BeanPostProcessor实现AB测试的方法这一问题有了更深刻的体会,具体使用情况还需要大家实践验证。这里是亿速云,小编将为大家推送更多相关知识点的文章,欢迎关注!
亿速云「云服务器」,即开即用、新一代英特尔至强铂金CPU、三副本存储NVMe SSD云盘,价格低至29元/月。点击查看>>
免责声明:本站发布的内容(图片、视频和文字)以原创、转载和分享为主,文章观点不代表本网站立场,如果涉及侵权请联系站长邮箱:is@yisu.com进行举报,并提供相关证据,一经查实,将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容。
原文链接:https://my.oschina.net/u/1017791/blog/3124265