这篇文章将为大家详细讲解有关C++中怎么利用LeetCode拷贝带有随机指针的链表,文章内容质量较高,因此小编分享给大家做个参考,希望大家阅读完这篇文章后对相关知识有一定的了解。
A linked list is given such that each node contains an additional random pointer which could point to any node in the list or null.
Return a deep copy of the list.
Example 1:
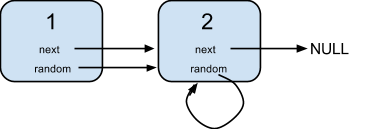
Input:
{"$id":"1","next":{"$id":"2","next":null,"random":{"$ref":"2"},"val":2},"random":{"$ref":"2"},"val":1} Explanation: Node 1's value is 1, both of its next and random pointer points to Node 2. Node 2's value is 2, its next pointer points to null and its random pointer points to itself.
Note:
You must return the copy of the given head as a reference to the cloned list.
这道链表的深度拷贝题的难点就在于如何处理随机指针的问题,由于每一个节点都有一个随机指针,这个指针可以为空,也可以指向链表的任意一个节点,如果在每生成一个新节点给其随机指针赋值时,都要去遍历原链表的话,OJ 上肯定会超时,所以可以考虑用 HashMap 来缩短查找时间,第一遍遍历生成所有新节点时同时建立一个原节点和新节点的 HashMap,第二遍给随机指针赋值时,查找时间是常数级。代码如下:
解法一:
class Solution {
public:
Node* copyRandomList(Node* head) {
if (!head) return nullptr;
Node *res = new Node(head->val, nullptr, nullptr);
Node *node = res, *cur = head->next;
unordered_map<Node*, Node*> m;
m[head] = res;
while (cur) {
Node *t = new Node(cur->val, nullptr, nullptr);
node->next = t;
m[cur] = t;
node = node->next;
cur = cur->next;
}
node = res; cur = head;
while (cur) {
node->random = m[cur->random];
node = node->next;
cur = cur->next;
}
return res;
}
};我们可以使用递归的解法,写起来相当的简洁,还是需要一个 HashMap 来建立原链表结点和拷贝链表结点之间的映射。在递归函数中,首先判空,若为空,则返回空指针。然后就是去 HashMap 中查找是否已经在拷贝链表中存在了该结点,是的话直接返回。否则新建一个拷贝结点 res,然后建立原结点和该拷贝结点之间的映射,然后就是要给拷贝结点的 next 和 random 指针赋值了,直接分别调用递归函数即可,参见代码如下:
解法二:
class Solution {
public:
Node* copyRandomList(Node* head) {
unordered_map<Node*, Node*> m;
return helper(head, m);
}
Node* helper(Node* node, unordered_map<Node*, Node*>& m) {
if (!node) return nullptr;
if (m.count(node)) return m[node];
Node *res = new Node(node->val, nullptr, nullptr);
m[node] = res;
res->next = helper(node->next, m);
res->random = helper(node->random, m);
return res;
}
};当然,如果使用 HashMap 占用额外的空间,如果这道题限制了空间的话,就要考虑别的方法。下面这个方法很巧妙,可以分为以下三个步骤:
1. 在原链表的每个节点后面拷贝出一个新的节点。
2. 依次给新的节点的随机指针赋值,而且这个赋值非常容易 cur->next->random = cur->random->next。
3. 断开链表可得到深度拷贝后的新链表。
举个例子来说吧,比如原链表是 1(2) -> 2(3) -> 3(1),括号中是其 random 指针指向的结点,那么这个解法是首先比遍历一遍原链表,在每个结点后拷贝一个同样的结点,但是拷贝结点的 random 指针仍为空,则原链表变为 1(2) -> 1(null) -> 2(3) -> 2(null) -> 3(1) -> 3(null)。然后第二次遍历,是将拷贝结点的 random 指针赋上正确的值,则原链表变为 1(2) -> 1(2) -> 2(3) -> 2(3) -> 3(1) -> 3(1),注意赋值语句为:
cur->next->random = cur->random->next;
这里的 cur 是原链表中结点,cur->next 则为拷贝链表的结点,cur->next->random 则为拷贝链表的 random 指针。cur->random 为原链表结点的 random 指针指向的结点,因为其指向的还是原链表的结点,所以我们要再加个 next,才能指向拷贝链表的结点。最后再遍历一次,就是要把原链表和拷贝链表断开即可,参见代码如下:
解法二:
class Solution {
public:
Node* copyRandomList(Node* head) {
if (!head) return nullptr;
Node *cur = head;
while (cur) {
Node *t = new Node(cur->val, nullptr, nullptr);
t->next = cur->next;
cur->next = t;
cur = t->next;
}
cur = head;
while (cur) {
if (cur->random) cur->next->random = cur->random->next;
cur = cur->next->next;
}
cur = head;
Node *res = head->next;
while (cur) {
Node *t = cur->next;
cur->next = t->next;
if (t->next) t->next = t->next->next;
cur = cur->next;
}
return res;
}
};关于C++中怎么利用LeetCode拷贝带有随机指针的链表就分享到这里了,希望以上内容可以对大家有一定的帮助,可以学到更多知识。如果觉得文章不错,可以把它分享出去让更多的人看到。
免责声明:本站发布的内容(图片、视频和文字)以原创、转载和分享为主,文章观点不代表本网站立场,如果涉及侵权请联系站长邮箱:is@yisu.com进行举报,并提供相关证据,一经查实,将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容。