这篇文章给大家分享的是有关C#中ThreadPool之QueueUserWorkItem怎么用的内容。小编觉得挺实用的,因此分享给大家做个参考,一起跟随小编过来看看吧。
先看代码:
//设置可以同时处于活动状态的线程池的请求数目。
bool pool = ThreadPool.SetMaxThreads(8, 8);
if (pool) {
ThreadPool.QueueUserWorkItem(o => this.DoSomethingLong("参数1"));
ThreadPool.QueueUserWorkItem(o => this.DoSomethingLong("参数2"));
ThreadPool.QueueUserWorkItem(o => this.DoSomethingLong("参数3"));
ThreadPool.QueueUserWorkItem(o => this.DoSomethingLong("参数4"));
ThreadPool.QueueUserWorkItem(o => this.DoSomethingLong("参数5"));
ThreadPool.QueueUserWorkItem(o => this.DoSomethingLong("参数6"));
ThreadPool.QueueUserWorkItem(o => this.DoSomethingLong("参数7"));
ThreadPool.QueueUserWorkItem(o => this.DoSomethingLong("参数8"));
ThreadPool.QueueUserWorkItem(o => this.DoSomethingLong("参数9"));
ThreadPool.QueueUserWorkItem(o => this.DoSomethingLong("参数10"));
ThreadPool.QueueUserWorkItem(o => this.DoSomethingLong("参数11"));
};上面代码先设置线程池中最大并发量为8个,然后通过QueueUserWorkItem向线程池中添加11个方法,运行,输出结果:
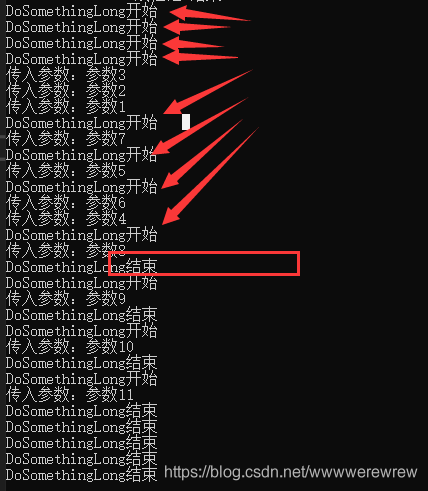
可以看出,先运行了8个,当有一个任务结束后线程池中有空闲线程时,排队的下一个任务才会执行,
把最大并发量改成9试试:
{
//设置可以同时处于活动状态的线程池的请求数目。
bool pool = ThreadPool.SetMaxThreads(9, 9);
if (pool) {
ThreadPool.QueueUserWorkItem(o => this.DoSomethingLong("参数1"));
ThreadPool.QueueUserWorkItem(o => this.DoSomethingLong("参数2"));
ThreadPool.QueueUserWorkItem(o => this.DoSomethingLong("参数3"));
ThreadPool.QueueUserWorkItem(o => this.DoSomethingLong("参数4"));
ThreadPool.QueueUserWorkItem(o => this.DoSomethingLong("参数5"));
ThreadPool.QueueUserWorkItem(o => this.DoSomethingLong("参数6"));
ThreadPool.QueueUserWorkItem(o => this.DoSomethingLong("参数7"));
ThreadPool.QueueUserWorkItem(o => this.DoSomethingLong("参数8"));
ThreadPool.QueueUserWorkItem(o => this.DoSomethingLong("参数9"));
ThreadPool.QueueUserWorkItem(o => this.DoSomethingLong("参数10"));
ThreadPool.QueueUserWorkItem(o => this.DoSomethingLong("参数11"));
};
}运行结果:
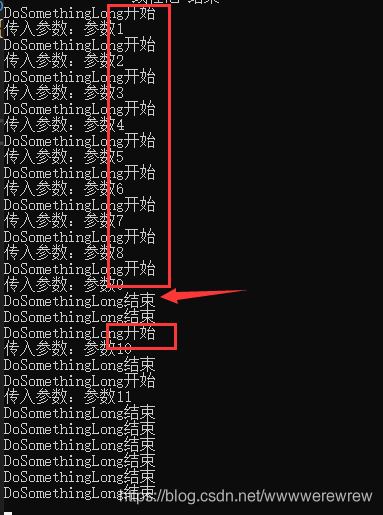
感谢各位的阅读!关于“C#中ThreadPool之QueueUserWorkItem怎么用”这篇文章就分享到这里了,希望以上内容可以对大家有一定的帮助,让大家可以学到更多知识,如果觉得文章不错,可以把它分享出去让更多的人看到吧!
免责声明:本站发布的内容(图片、视频和文字)以原创、转载和分享为主,文章观点不代表本网站立场,如果涉及侵权请联系站长邮箱:is@yisu.com进行举报,并提供相关证据,一经查实,将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容。