这篇文章主要介绍“Python中extend()、 "+"、"+=" 的区别”,在日常操作中,相信很多人在Python中extend()、 "+"、"+=" 的区别问题上存在疑惑,小编查阅了各式资料,整理出简单好用的操作方法,希望对大家解答”Python中extend()、 "+"、"+=" 的区别”的疑惑有所帮助!接下来,请跟着小编一起来学习吧!
使用 Python 的时候,我们知道 list 是一个长度可变对的数组, 可以通过 insert,append 和 extend 轻易的拓展其中的元素个数。 也可以使用运算符 如: [1] + [2] 生成新的数组[1, 2]
"+"将两个 list 相加,会返回到一个新的 list 对象
append 在原 list 上进行修改,没有返回值
从以下代码可以看到, 调用 b = b + [3, 4] 之后, 通过id(b) 查看 b 变成了一个新对象。
In [5]: b = [1, 2] In [6]: id(b) Out[6]: 1628740249224 In [7]: b = b + [3, 4] In [8]: id(b) Out[8]: 1628740456520
使用extend() 完成相同的步骤, 可以看到 对象c 的id保持和原来的一致
In [9]: c = [1, 2] In [10]: id(c) Out[10]: 1628740392584 In [11]: c.extend([3, 4]) In [12]: id(c) Out[12]: 1628740392584
使用 "+=" 连接列表, 看到效果和 extend() 是相同的。
In [1]: a = [1, 2] In [2]: id(a) Out[2]: 1628740021448 In [3]: a += [3, 4] In [4]: id(a) Out[4]: 1628740021448
结论: 减少内存的拷贝, 修改一个列表的数据时, 应避免使用 list1 = list1 + list2 这样的语法。
一个示例:
In [1]: import sys In [2]: lst1 = [1] In [3]: lst2 = [] In [4]: lst2.append(1) In [5]: lst1 == lst2 Out[5]: True In [6]: sys.getsizeof(lst1) Out[6]: 72 In [7]: sys.getsizeof(lst2) Out[7]: 96
可以看到,lst1 == lst2, 但是当使用 sys.getsizeof 获取对象的内存大小时, 两者却是不同的。
如下图所示, list_a 长度为4, 当执行 append(4) 时, 底层的数据长度其实申请了4个元素的空间,当再次执行 append(5) 的时候,不需要再次申请内存。
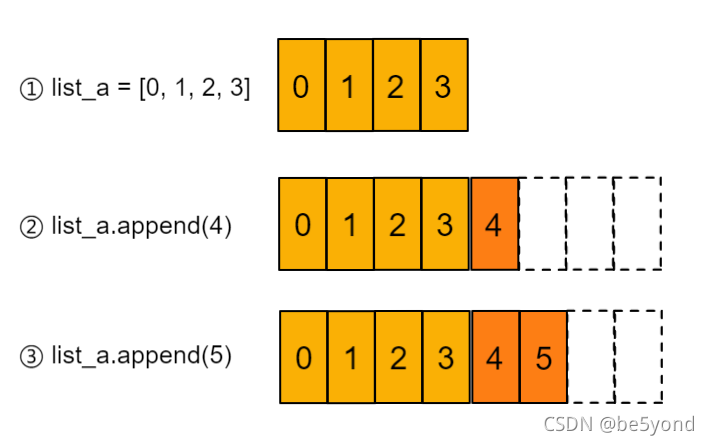
因为 执行 append() 操作时,Python将一次拓展N个元素的内存,因为一个 append 操作很可能是很多 append 操作的开始,通过额外分配内存来减少可能的内存分配和内存copy的次数。
In [1]: import sys
In [2]: l = []
...: print(f'list initial size {sys.getsizeof(l)}')
...: for i in range(80):
...: cur_size = sys.getsizeof(l)
...: l.append(i)
...: new_size = sys.getsizeof(l)
...: print(f'list len {i+1}:\t current_size {new_size}\t new_allocated 8 * {(new_size-cur_size)/8}')
...:
list initial size 64
list len 1: current_size 96 new_allocated 8 * 4.0
list len 2: current_size 96 new_allocated 8 * 0.0
list len 3: current_size 96 new_allocated 8 * 0.0
list len 4: current_size 96 new_allocated 8 * 0.0
list len 5: current_size 128 new_allocated 8 * 4.0
list len 6: current_size 128 new_allocated 8 * 0.0
list len 7: current_size 128 new_allocated 8 * 0.0
list len 8: current_size 128 new_allocated 8 * 0.0
list len 9: current_size 192 new_allocated 8 * 8.0
list len 10: current_size 192 new_allocated 8 * 0.0
list len 11: current_size 192 new_allocated 8 * 0.0
list len 12: current_size 192 new_allocated 8 * 0.0
list len 13: current_size 192 new_allocated 8 * 0.0
list len 14: current_size 192 new_allocated 8 * 0.0
list len 15: current_size 192 new_allocated 8 * 0.0
list len 16: current_size 192 new_allocated 8 * 0.0
list len 17: current_size 264 new_allocated 8 * 9.0
list len 18: current_size 264 new_allocated 8 * 0.0
list len 19: current_size 264 new_allocated 8 * 0.0
list len 20: current_size 264 new_allocated 8 * 0.0
list len 21: current_size 264 new_allocated 8 * 0.0
list len 22: current_size 264 new_allocated 8 * 0.0
list len 23: current_size 264 new_allocated 8 * 0.0
list len 24: current_size 264 new_allocated 8 * 0.0
list len 25: current_size 264 new_allocated 8 * 0.0
list len 26: current_size 344 new_allocated 8 * 10.0
list len 27: current_size 344 new_allocated 8 * 0.0
list len 28: current_size 344 new_allocated 8 * 0.0
list len 29: current_size 344 new_allocated 8 * 0.0
list len 30: current_size 344 new_allocated 8 * 0.0
list len 31: current_size 344 new_allocated 8 * 0.0
list len 32: current_size 344 new_allocated 8 * 0.0
list len 33: current_size 344 new_allocated 8 * 0.0
list len 34: current_size 344 new_allocated 8 * 0.0
list len 35: current_size 344 new_allocated 8 * 0.0
list len 36: current_size 432 new_allocated 8 * 11.0
list len 37: current_size 432 new_allocated 8 * 0.0
list len 38: current_size 432 new_allocated 8 * 0.0
list len 39: current_size 432 new_allocated 8 * 0.0
list len 40: current_size 432 new_allocated 8 * 0.0
list len 41: current_size 432 new_allocated 8 * 0.0
list len 42: current_size 432 new_allocated 8 * 0.0
list len 43: current_size 432 new_allocated 8 * 0.0
list len 44: current_size 432 new_allocated 8 * 0.0
list len 45: current_size 432 new_allocated 8 * 0.0
list len 46: current_size 432 new_allocated 8 * 0.0
list len 47: current_size 528 new_allocated 8 * 12.0
list len 48: current_size 528 new_allocated 8 * 0.0
list len 49: current_size 528 new_allocated 8 * 0.0
list len 50: current_size 528 new_allocated 8 * 0.0
list len 51: current_size 528 new_allocated 8 * 0.0
list len 52: current_size 528 new_allocated 8 * 0.0
list len 53: current_size 528 new_allocated 8 * 0.0
list len 54: current_size 528 new_allocated 8 * 0.0
list len 55: current_size 528 new_allocated 8 * 0.0
list len 56: current_size 528 new_allocated 8 * 0.0
list len 57: current_size 528 new_allocated 8 * 0.0
list len 58: current_size 528 new_allocated 8 * 0.0
list len 59: current_size 640 new_allocated 8 * 14.0
list len 60: current_size 640 new_allocated 8 * 0.0
list len 61: current_size 640 new_allocated 8 * 0.0
list len 62: current_size 640 new_allocated 8 * 0.0
list len 63: current_size 640 new_allocated 8 * 0.0
list len 64: current_size 640 new_allocated 8 * 0.0
list len 65: current_size 640 new_allocated 8 * 0.0
list len 66: current_size 640 new_allocated 8 * 0.0
list len 67: current_size 640 new_allocated 8 * 0.0
list len 68: current_size 640 new_allocated 8 * 0.0
list len 69: current_size 640 new_allocated 8 * 0.0
list len 70: current_size 640 new_allocated 8 * 0.0
list len 71: current_size 640 new_allocated 8 * 0.0
list len 72: current_size 640 new_allocated 8 * 0.0
list len 73: current_size 768 new_allocated 8 * 16.0
list len 74: current_size 768 new_allocated 8 * 0.0
list len 75: current_size 768 new_allocated 8 * 0.0
list len 76: current_size 768 new_allocated 8 * 0.0
list len 77: current_size 768 new_allocated 8 * 0.0
list len 78: current_size 768 new_allocated 8 * 0.0
list len 79: current_size 768 new_allocated 8 * 0.0
list len 80: current_size 768 new_allocated 8 * 0.0
通过观察可以发现, 列表从0 增加到 80长度的过程中, 新申请的内存长度为 [4, 4, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 16] 。 反之, 当执行 remove 或者 pop 减少列表中的数据时, 列表也会自动缩容。
扩容条件 ,新长度大于底层数组长度;
缩容条件 ,新长度小于底层数组长度的一半;
结论: 避免使用类似 append 语法初始化列表, 优先使用列表表达式
# Bad ❌ list_a = [] for i in range(50): list_a.append(i) # Good ✔️ list_b = [i for i in range(50)]
① 避免使用 "+" 修改数组
② 尽量避免多次使用 append 函数
到此,关于“Python中extend()、 "+"、"+=" 的区别”的学习就结束了,希望能够解决大家的疑惑。理论与实践的搭配能更好的帮助大家学习,快去试试吧!若想继续学习更多相关知识,请继续关注亿速云网站,小编会继续努力为大家带来更多实用的文章!
免责声明:本站发布的内容(图片、视频和文字)以原创、转载和分享为主,文章观点不代表本网站立场,如果涉及侵权请联系站长邮箱:is@yisu.com进行举报,并提供相关证据,一经查实,将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容。