这篇文章将为大家详细讲解有关SpringCloud如何实现微服务数据权限控制,小编觉得挺实用的,因此分享给大家做个参考,希望大家阅读完这篇文章后可以有所收获。
举个例子:
有一批业务员跟进全国的销售订单。他们被按城市进行划分,一个业务员跟进3个城市的订单,为了保护公司的业务数据不能被所有人都掌握,故每个业务员只能看到自己负责城市的订单数据。所以从系统来讲每个业务员都有访问销售订单的功能,然后再需要配置每个业务员负责的城市,以此对订单数据进行筛选。
要实现此功能有很多方法,如果系统中多个地方都需要类似的需求,那我们就可以将其提出来做成一个通用的功能。这里我介绍一个相对简单的解决方案,以供参考。
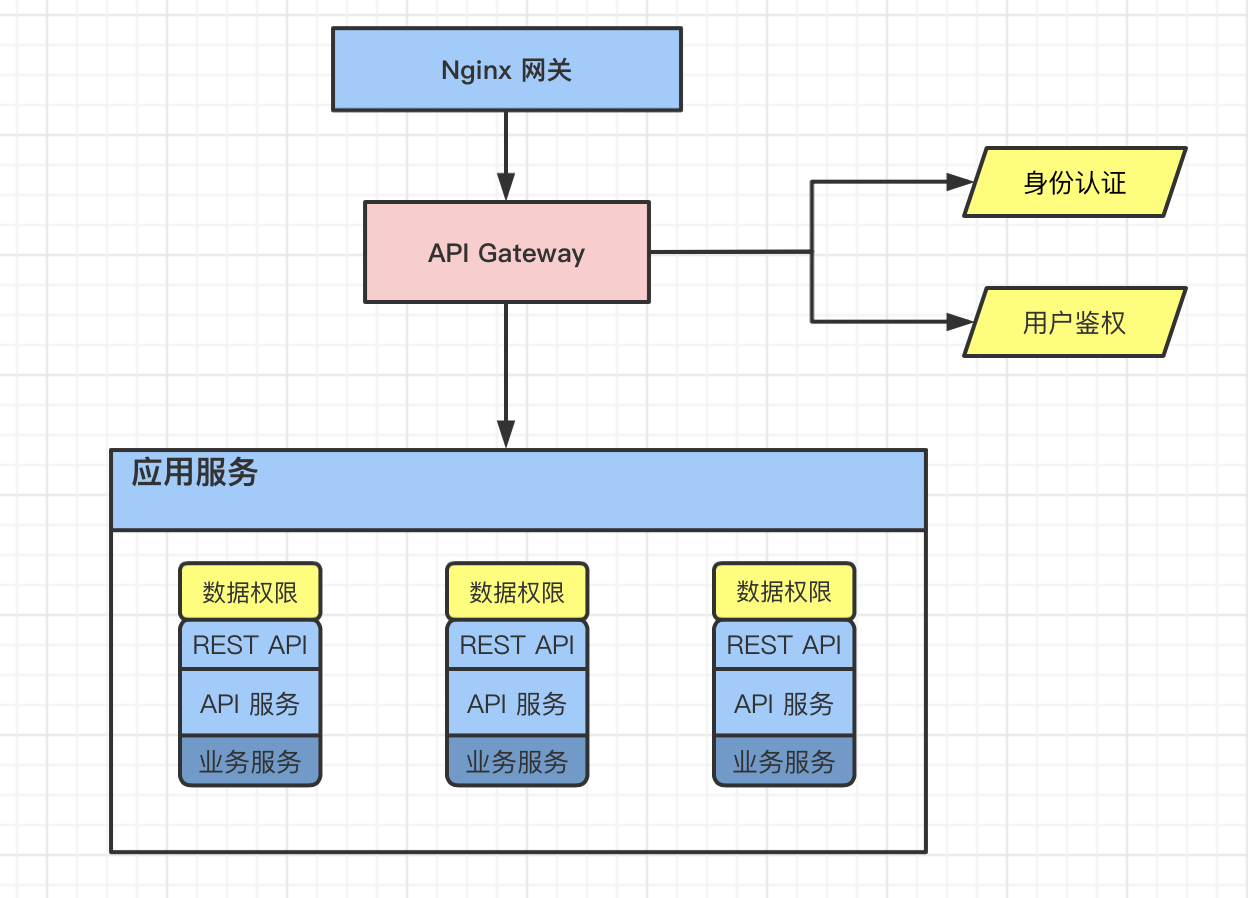
数据权限为作一个注解的形式挂在每一个需要数据权限控制的Controller上,由于和具体的程序逻辑有关故有一定的入侵性,且需要数据库配合使用。
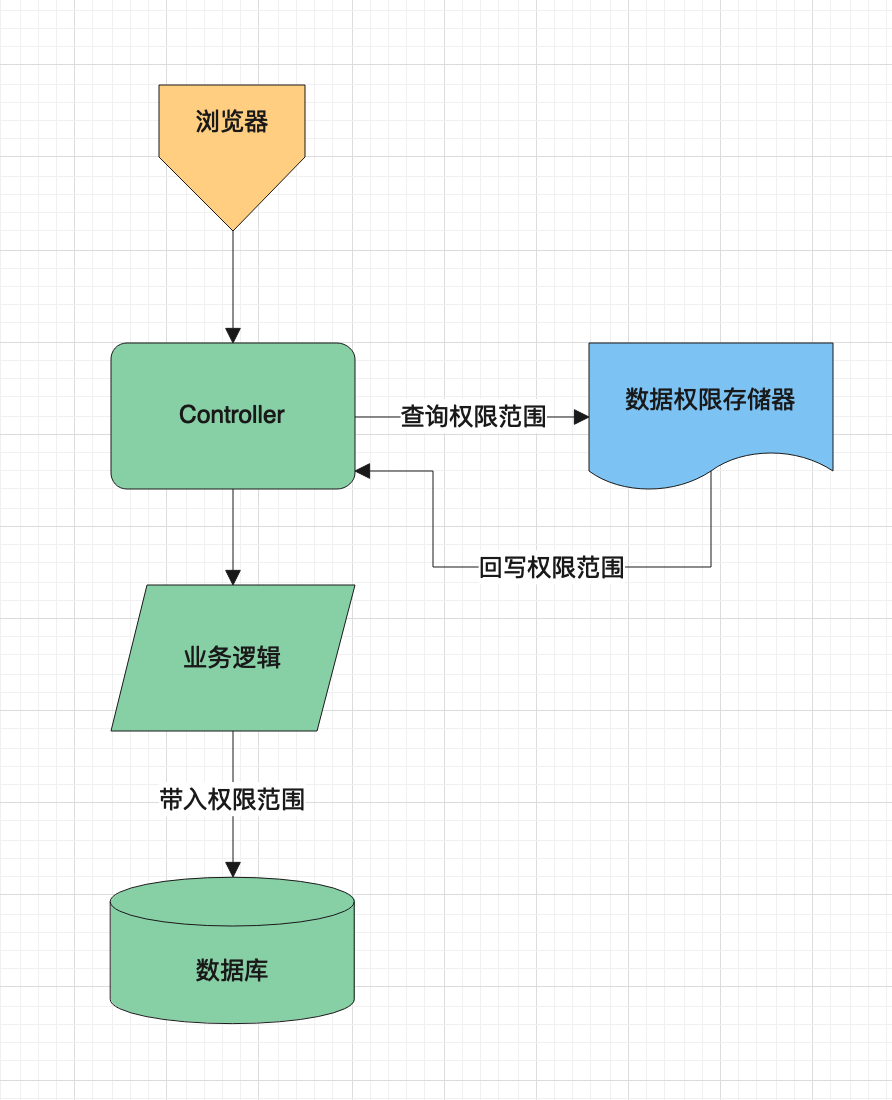
1.浏览器传带查询权限范围参数访问Controller,如cities
POST http://127.0.0.1:8000/order/query
accept: */*
Content-Type: application/json
token: 1e2b2298-8274-4599-a26f-a799167cc82f
{"cities":["cq","cd","bj"],"userName":"string"}2.通过注解拦截权限范围参数,并根据预授权范围比较,回写在授权范围内的权限范围参数
cities = ["cq","cd"]3.通过参数传递到DAO层,在SQL语句中拼装出查询条件,实现数据的过滤
select * from order where city in ('cq','cd')注解的完整代码,请详见源代码
1)创建注解
@Retention(value = RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Target(value = {ElementType.METHOD})
@Documented
public @interface ScopeAuth {
String token() default "AUTH_TOKEN";
String scope() default "";
String[] scopes() default {};
}此注解为运行时RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME作用在方法上ElementType.METHOD的
token:获取识别唯一用户的标识,与用户数据权限存储有关
scope,scopes:预请求的数据权限范围
2) AOP实现注解
public class ScopeAuthAdvice {
@Around("@annotation(scopeAuth)")
public Object before(ProceedingJoinPoint thisJoinPoint, ScopeAuth scopeAuth) throws Throwable {
// ... 省略过程
// 获取token
String authToken = getToken(args, scopeAuth.token(), methodSignature.getMethod());
// 回写范围参数
setScope(scopeAuth.scope(), methodSignature, args, authToken);
return thisJoinPoint.proceed();
}
/**
* 设置范围
*/
private void setScope(String scope, MethodSignature methodSignature, Object[] args, String authToken) {
// 获取请求范围
Set<String> requestScope = getRequestScope(args, scope, methodSignature.getMethod());
ScopeAuthAdapter adapter = new ScopeAuthAdapter(supplier);
// 已授权范围
Set<String> authorizedScope = adapter.identifyPermissionScope(authToken, requestScope);
// 回写新范围
setRequestScope(args, scope, authorizedScope, methodSignature.getMethod());
}
/**
* 回写请求范围
*/
private void setRequestScope(Object[] args, String scopeName, Collection<String> scopeValues, Method method) {
// 解析 SPEL 表达式
if (scopeName.indexOf(SPEL_FLAG) == 0) {
ParseSPEL.setMethodValue(scopeName, scopeValues, method, args);
}
}
}此为演示代码省略了过程,主要功能为通过token拿到预先授权的数据范围,再与本次请求的范围做交集,最后回写回原参数。
过程中用到了较多的SPEL表达式,用于计算表达式结果,具体请参考ParseSPEL文件
3)权限范围交集计算
public class ScopeAuthAdapter {
private final AuthQuerySupplier supplier;
public ScopeAuthAdapter(AuthQuerySupplier supplier) {
this.supplier = supplier;
}
/**
* 验证权限范围
* @param token
* @param requestScope
* @return
*/
public Set<String> identifyPermissionScope(String token, Set<String> requestScope) {
Set<String> authorizeScope = supplier.queryScope(token);
String ALL_SCOPE = "AUTH_ALL";
String USER_ALL = "USER_ALL";
if (authorizeScope == null) {
return null;
}
if (authorizeScope.contains(ALL_SCOPE)) {
// 如果是全开放则返回请求范围
return requestScope;
}
if (requestScope == null) {
return null;
}
if (requestScope.contains(USER_ALL)){
// 所有授权的范围
return authorizeScope;
}
// 移除不同的元素
requestScope.retainAll(authorizeScope);
return requestScope;
}
}此处为了方便设置,有两个关键字范围
AUTH_ALL:预设所有范围,全开放的意思,为数据库预先设置值,请求传什么值都通过
USER_ALL:请求所有授权的范围,请求时传此值则会以数据库预设值为准
4) spring.factories自动导入类配置
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.AutoConfigurationImportSelector=\
fun.barryhome.cloud.annotation.ScopeAuthAdvice如果注解功能是单独项目存在,在使用时有可能会存在找不到引入文件的问题,可通过此配置文件自动载入需要初始化的类
@ScopeAuth(scopes = {"#orderDTO.cities"}, token = "#request.getHeader(\"X-User-Name\")")
@PostMapping(value = "/query")
public String query(@RequestBody OrderDTO orderDTO, HttpServletRequest request) {
return Arrays.toString(orderDTO.getCities());
}在需要使用数据权限的controller方法上增加@ScopeAuth注解
scopes = {"#orderDTO.cities"}:表示取输入参数orderDTO的cities值,这里是表达式必须加#
实际开发过程中,需要将orderDTO.getCities()带入后续逻辑中,在DAO层将此拼装在SQL中,以实现数据过滤功能
AuthStoreSupplier接口为数据权限的存储接口,与AuthQuerySupplier配合使用,可按实际情况实现
此接口为非必要接口,可由数据库或Redis存储(推荐),一般在登录的同时保存在Redis中
AuthQuerySupplier接口为数据权限查询接口,可按存储方法进行查询,推荐使用Redis
@Component
public class RedisAuthQuerySupplier implements AuthQuerySupplier {
@Autowired
private RedisTemplate<String, String> redisTemplate;
/**
* 查询范围
*/
@Override
public Set<String> queryScope(String key) {
String AUTH_USER_KEY = "auth:logic:user:%s";
String redisKey = String.format(AUTH_USER_KEY, key);
List<String> range = redisTemplate.opsForList().range(redisKey, 0, -1);
if (range != null) {
return new HashSet<>(range);
} else {
return null;
}
}
}在分布式结构里,也可将此实现提出到权限模块,采用远程调用方式,进一步解耦
@EnableScopeAuth
@EnableDiscoveryClient
@SpringBootApplication
public class OrderApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(OrderApplication.class, args);
}
}关于“SpringCloud如何实现微服务数据权限控制”这篇文章就分享到这里了,希望以上内容可以对大家有一定的帮助,使各位可以学到更多知识,如果觉得文章不错,请把它分享出去让更多的人看到。
亿速云「云服务器」,即开即用、新一代英特尔至强铂金CPU、三副本存储NVMe SSD云盘,价格低至29元/月。点击查看>>
免责声明:本站发布的内容(图片、视频和文字)以原创、转载和分享为主,文章观点不代表本网站立场,如果涉及侵权请联系站长邮箱:is@yisu.com进行举报,并提供相关证据,一经查实,将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容。