今天小编给大家分享一下C++的运算符怎么正确使用的相关知识点,内容详细,逻辑清晰,相信大部分人都还太了解这方面的知识,所以分享这篇文章给大家参考一下,希望大家阅读完这篇文章后有所收获,下面我们一起来了解一下吧。
运算符的作用:用于执行代码的运算
主要有:
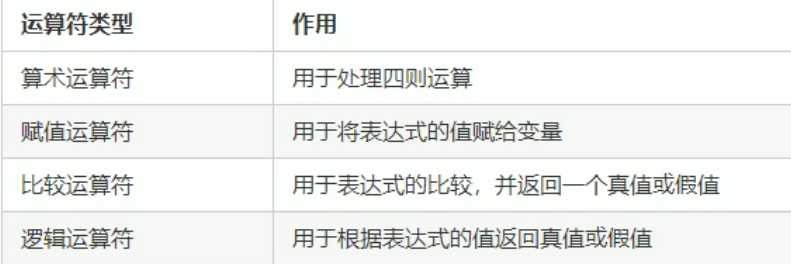
用于处理四则运算
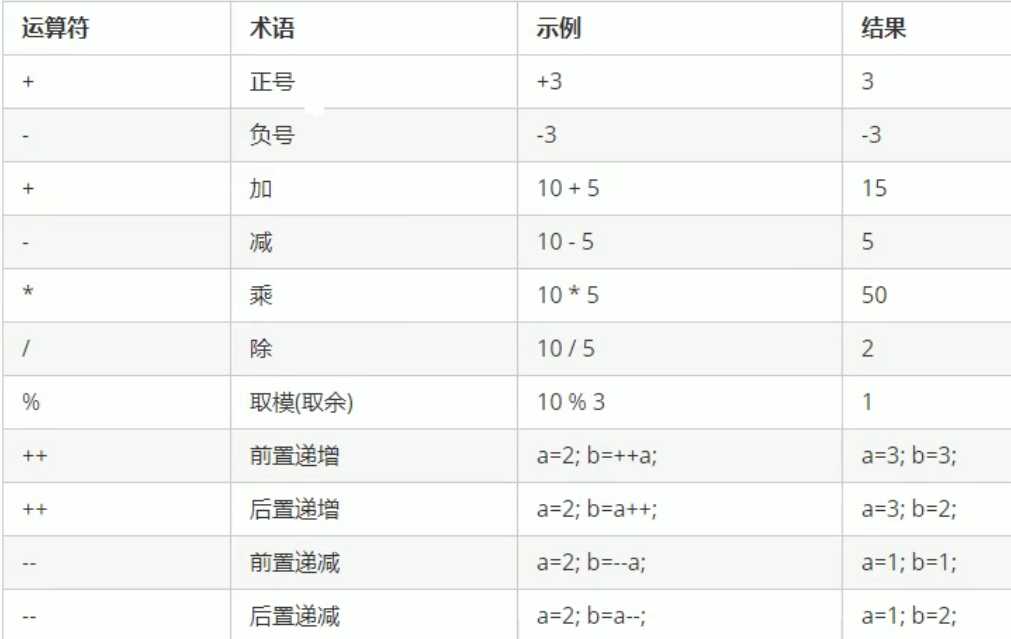
对于前置递增:将递增运算前置,使变量先加一,再进行表达式运算。
对于后置递增:将递增运算后置,使变量先进行表达式运算,再加一。
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
//1.前置递增:先加一,再进行表达式运算
int a = 10;
int b = ++a * 10;
cout << "a = " << a << endl;
cout << "b = " << b << endl;
//2.后置递增:先进行表达式运算,再加一
int c = 10;
int d = c++ * 10;
cout << "c = " << c << endl;
cout << "d = " << d << endl;
system("pause");
return 0;
}
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main1()
{
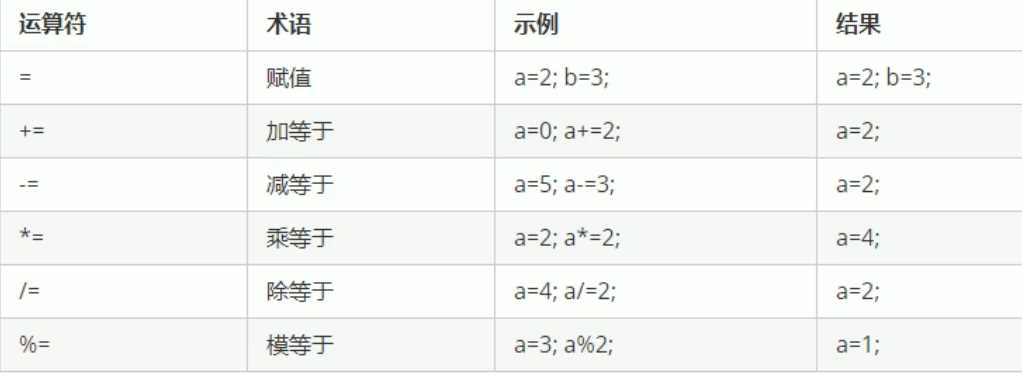
//赋值运算符
int a = 10;
int b = 2;
cout << "a = " << a << endl;
//+=
a = 10;
a += b;
cout << "a = " << a << endl;
//-=
a = 10;
a -= b;
cout << "a = " << a << endl;
//*=
a = 10;
a *= b;
cout << "a = " << a << endl;
// /=
a = 10;
a /= b;
cout << "a = " << a << endl;
// %=
a = 10;
a %= b;
cout << "a = " << a << endl;
system("pause");
return 0;
}
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
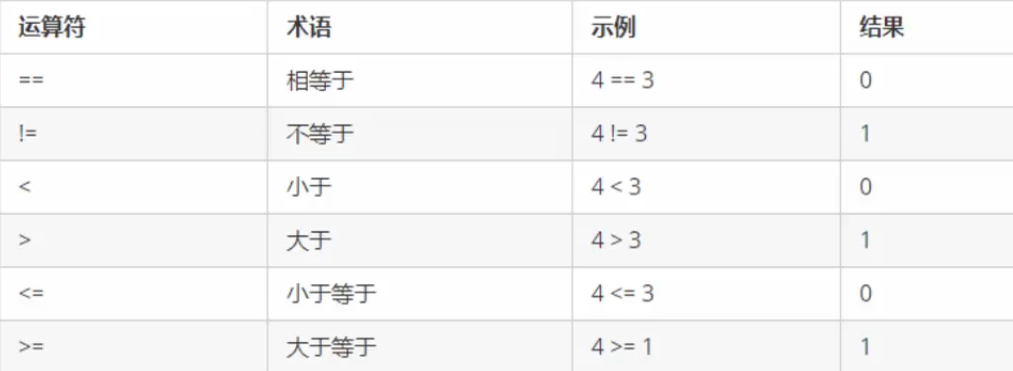
cout << (4 == 3) << endl;
cout << (4 != 3) << endl;
cout << (4 < 3) << endl;
cout << (4 > 3) << endl;
cout << (4 >= 3) << endl;
cout << (4 <= 3) << endl;
system("pause");
return 0;
}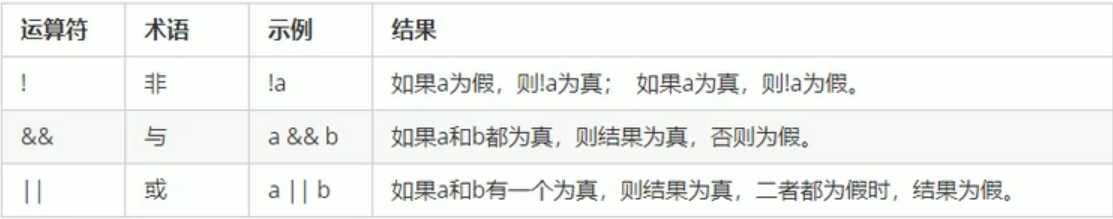
#include<iostream>using namespace std;int main(){int a = 5;// 逻辑运算符 非cout << !a << endl;cout << !!a << endl;// 逻辑运算符 与int b = 0;int c = 3;cout << (a && b) << endl;cout << (a && c) << endl;//逻辑运算符 或cout << (!a || b) << endl;cout << (a || c) << endl;system("pause");return 0;}#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int a = 5;
// 逻辑运算符 非
cout << !a << endl;
cout << !!a << endl;
// 逻辑运算符 与
int b = 0;
int c = 3;
cout << (a && b) << endl;
cout << (a && c) << endl;
//逻辑运算符 或
cout << (!a || b) << endl;
cout << (a || c) << endl;
system("pause");
return 0;
}以上就是“C++的运算符怎么正确使用”这篇文章的所有内容,感谢各位的阅读!相信大家阅读完这篇文章都有很大的收获,小编每天都会为大家更新不同的知识,如果还想学习更多的知识,请关注亿速云行业资讯频道。
亿速云「云服务器」,即开即用、新一代英特尔至强铂金CPU、三副本存储NVMe SSD云盘,价格低至29元/月。点击查看>>
免责声明:本站发布的内容(图片、视频和文字)以原创、转载和分享为主,文章观点不代表本网站立场,如果涉及侵权请联系站长邮箱:is@yisu.com进行举报,并提供相关证据,一经查实,将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容。