本篇内容介绍了“C语言顺序表如何使用”的有关知识,在实际案例的操作过程中,不少人都会遇到这样的困境,接下来就让小编带领大家学习一下如何处理这些情况吧!希望大家仔细阅读,能够学有所成!
编程环境为 ubuntu 18.04。
顺序表需要连续一片存储空间,存储任意类型的元素,这里以存储 int 类型数据为例。
size 为容量,length 为当前已知数据表元素的个数
typedef struct Vector{
int *data; //该顺序表这片连续空间的首地址
int size, length;
} Vec;Vec *init(int n){ //该顺序表具有n个存储单元
Vec *v = (Vec *)malloc(sizeof(Vec)); //在内存栈上开辟一个空间 malloc在内存的堆区,在函数外面也能访问
v->data = (int *)malloc(sizeof(int) * n);
v->size = n;
v->length = 0;
return v;
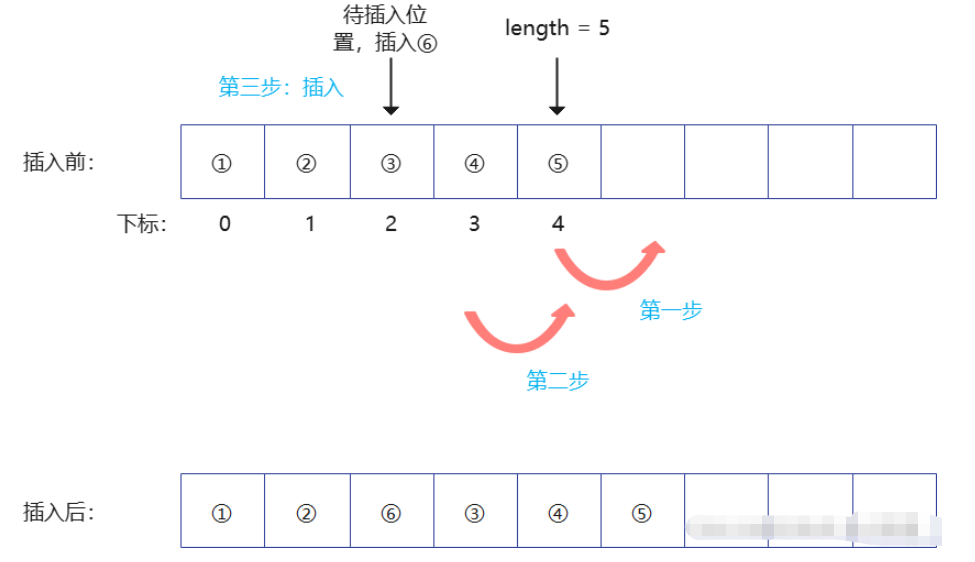
}int insert(Vec *v, int ind, int val) { //ind为插入元素的位置,val为插入元素的值
if(v == NULL) return 0;
if(ind < 0 || ind > v->length) return 0; //判断要插入的位置是否合法
if(v->length == v->size) {
if(!expand(v)){ //扩容失败
printf(RED("fail to expand!\n"));
}
printf(GREEN("success to expand! the size = %d\n"),v->size);
}
for(int i = v->length; i > ind; i--){
v->data[i] = v->data[i-1];
}
v->data[ind] = val;
v->length += 1;
return 1;
}为什么需要判断插入的位置是否合法呢?这是因为顺序表是连续一片存储空间,所以内存是连续的。
下图以 length = 5,size = 9 为例,我们只能在下标为 0 到 4 之间的数中插入数据。
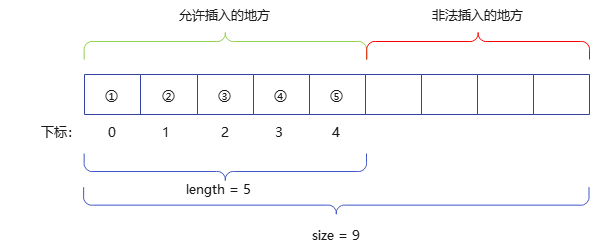
插入一个元素示意图
int erase(Vec *v, int ind){ //把下标为ind的元素删除
if(v == NULL) return 0;
if(ind < 0 || ind >= v->length) return 0;
for(int i = ind + 1; i < v->length; i++){
v->data[i - 1] = v->data[i];
}
v->length -= 1;
return 1;
}判断需要删除元素的下标是否合法,与插入元素类似
删除一个元素示意图

int expand(Vec *v){
//顺序表的扩容
//malloc 动态申请空间,空间不一定干净 calloc 动态申请空间,并且清空 realloc 重新申请空间
int extr_size = v->size;
int *p;
while(extr_size) {
p = (int *)realloc(v->data, sizeof(int) * (v->size + extr_size));
if(p != NULL) break; //p不为空,说明扩容成功,这个时候直接跳出循环
extr_size >>= 1; //否则就把额外扩容的空间除以2,降低要求
}
if(p == NULL) return 0; //判断跳出循环究竟是扩容成功还是扩容失败,如果扩容失败,那就是p为空地址,找不到符合条件的内存区域
v->size += extr_size;
v->data = p;
return 1;
}注意扩容这里写的比较巧妙,首先 int extr_size = v->size;表示先将需要扩容的大小设置成原本的大小,然后就判断能不能找到那么大的空间。 p = (int *)realloc(v->data, sizeof(int) * (v->size + extr_size)); 如果在系统中能找到这么大的容量,那么就返回找到的内存地址的首地址,然后就可以结束跳出循环;要是找不到的话那只能降低要求,把 extr_size 除以 2,看看能不能知道,如果实在找不到,extr_size 为 0,就会跳出循环。然后可以通过判断 p 是不是空指针来判断程序是找到能够扩容的空间退出的还是找不到退出的。
要是对 malloc、calloc 和 realloc 不熟悉的,可以看我这篇博文:C语言深入探索动态内存分配的使用
void clear(Vec *v){ //释放空间
if(v == NULL) return;
free(v->data);
free(v);
return;
}先释放数据,再释放整个顺序表。
void output(Vec *v){
if(v == NULL) return ;
printf("[");
for(int i = 0; i < v->length; i++){
i && printf(", ");
printf("%d", v->data[i]);
}
printf("]\n");
return ;
}#include <stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<time.h>
//#include<windows.h>
#define COLOR(a, b) "\033[" #b "m" a "\033[0m"
#define GREEN(a) COLOR(a, 32)
#define RED(a) COLOR(a, 31)
typedef struct Vector{
int *data; //该顺序表这片连续空间的首地址
int size, length;
} Vec;
Vec *init(int n){ //该顺序表具有n个存储单元
Vec *v = (Vec *)malloc(sizeof(Vec)); //在内存栈上开辟一个空间 malloc在内存的堆区,在函数外面也能访问
v->data = (int *)malloc(sizeof(int) * n);
v->size = n;
v->length = 0;
return v;
}
int expand(Vec *v){
//顺序表的扩容
//malloc 动态申请空间,空间不一定干净 calloc 动态申请空间,并且清空 realloc 重新申请空间
int extr_size = v->size;
int *p;
while(extr_size) {
p = (int *)realloc(v->data, sizeof(int) * (v->size + extr_size));
if(p != NULL) break; //p不为空,说明扩容成功,这个时候直接跳出循环
extr_size >>= 1; //否则就把额外扩容的空间除以2,降低要求
}
if(p == NULL) return 0; //判断跳出循环究竟是扩容成功还是扩容失败,如果扩容失败,那就是p为空地址,找不到符合条件的内存区域
v->size += extr_size;
v->data = p;
return 1;
}
int insert(Vec *v, int ind, int val) { //ind为插入元素的位置,val为插入元素的值
if(v == NULL) return 0;
if(ind < 0 || ind > v->length) return 0;
if(v->length == v->size) {
if(!expand(v)){
printf(RED("fail to expand!\n"));
}
printf(GREEN("success to expand! the size = %d\n"),v->size);
}
for(int i = v->length; i > ind; i--){
v->data[i] = v->data[i-1];
}
v->data[ind] = val;
v->length += 1;
return 1;
}
int erase(Vec *v, int ind){ //把下标为ind的元素删除
if(v == NULL) return 0;
if(ind < 0 || ind >= v->length) return 0;
for(int i = ind + 1; i < v->length; i++){
v->data[i - 1] = v->data[i];
}
v->length -= 1;
return 1;
}
void output(Vec *v){
if(v == NULL) return ;
printf("[");
for(int i = 0; i < v->length; i++){
i && printf(", ");
printf("%d", v->data[i]);
}
printf("]\n");
return ;
}
void clear(Vec *v){ //释放空间
if(v == NULL) return;
free(v->data);
free(v);
return;
}
int main(){
#define MAX_N 20
Vec *v = init(1);
srand(time(0)); //设置种子
for (int i = 0; i < MAX_N; i++){
int op = rand() % 4;
int ind = rand() % (v->length + 3) - 1; //取值范围[-1, v->length + 1]
int val = rand() % 100; //val为1到99之间的数
switch(op){
case 0:
case 1:
case 2: {
printf("insert %d at %d to the Vector = %d\n", val, ind, insert(v, ind, val));
}break;
case 3:{
printf("erase a item at %d = %d\n",ind,erase(v, ind));
}break;
}
output(v);
printf("\n");
}
#undef MAX_N
clear(v);
return 0;
}输出结果如下:
insert 82 at 0 to the Vector = 1
[82]
insert 38 at 2 to the Vector = 0
[82]
success to expand! the size = 2
insert 7 at 1 to the Vector = 1
[82, 7]
success to expand! the size = 4
insert 86 at 2 to the Vector = 1
[82, 7, 86]
erase a item at 4 = 0
[82, 7, 86]
erase a item at 4 = 0
[82, 7, 86]
insert 48 at 0 to the Vector = 1
[48, 82, 7, 86]
insert 65 at 5 to the Vector = 0
[48, 82, 7, 86]
success to expand! the size = 8
insert 92 at 4 to the Vector = 1
[48, 82, 7, 86, 92]
erase a item at 2 = 1
[48, 82, 86, 92]
insert 81 at 2 to the Vector = 1
[48, 82, 81, 86, 92]
insert 9 at 0 to the Vector = 1
[9, 48, 82, 81, 86, 92]
insert 99 at 1 to the Vector = 1
[9, 99, 48, 82, 81, 86, 92]
insert 29 at 7 to the Vector = 1
[9, 99, 48, 82, 81, 86, 92, 29]
success to expand! the size = 16
insert 38 at 0 to the Vector = 1
[38, 9, 99, 48, 82, 81, 86, 92, 29]
erase a item at 0 = 1
[9, 99, 48, 82, 81, 86, 92, 29]
erase a item at 8 = 0
[9, 99, 48, 82, 81, 86, 92, 29]
erase a item at 6 = 1
[9, 99, 48, 82, 81, 86, 29]
insert 57 at -1 to the Vector = 0
[9, 99, 48, 82, 81, 86, 29]
insert 32 at 4 to the Vector = 1
[9, 99, 48, 82, 32, 81, 86, 29]
“C语言顺序表如何使用”的内容就介绍到这里了,感谢大家的阅读。如果想了解更多行业相关的知识可以关注亿速云网站,小编将为大家输出更多高质量的实用文章!
亿速云「云服务器」,即开即用、新一代英特尔至强铂金CPU、三副本存储NVMe SSD云盘,价格低至29元/月。点击查看>>
免责声明:本站发布的内容(图片、视频和文字)以原创、转载和分享为主,文章观点不代表本网站立场,如果涉及侵权请联系站长邮箱:is@yisu.com进行举报,并提供相关证据,一经查实,将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容。