本文小编为大家详细介绍“C++怎么实现一个简单的线程池”,内容详细,步骤清晰,细节处理妥当,希望这篇“C++怎么实现一个简单的线程池”文章能帮助大家解决疑惑,下面跟着小编的思路慢慢深入,一起来学习新知识吧。
线程池应该包括
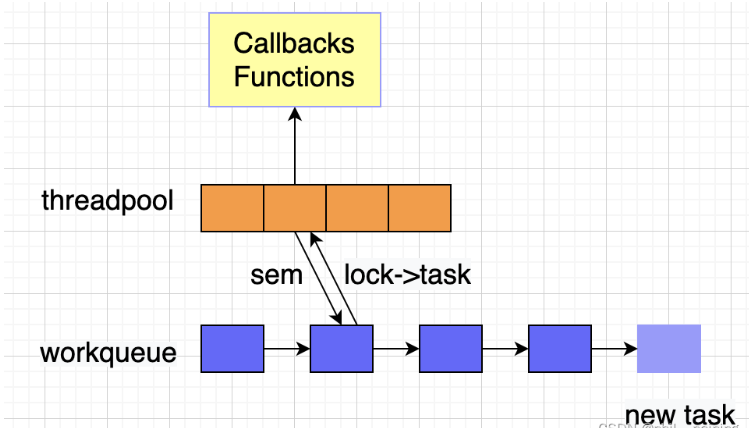
保存线程的容器,保存任务的容器。
为了能保证避免线程对任务的竞态获取,需要对任务队列进行加锁。
为了使得工作线程感知任务的到来,需要使用条件变量来唤醒工作线程。
任务容器中的任务管理。
任务的处理API。
使用数组存放线程,链表存放任务。
线程池类
template<typename T>
class threadpool
{
public:
threadpool(int thread_num,int max_request);
~threadpool();
bool append(T* request); // 在任务队列中添加任务
private:
static void worker(void* arg);
void run();
private:
int m_thread_num; // 线程池中的线程数
int m_max_request; // 任务队列最大保存的任务数
pthread_t *m_threads; // 保存线程的容器
std::list<T*>m_queuework; // 保存任务的链表
sem m_sem; // 通知工作线程任务到来
lock m_locker; // 互斥访问任务队列
};构造函数
template<typename T>
threadpool<T>::threadpool(int thread_num,int max_request):m_thread_num(thread_num),m_max_request(max_request)
{
if(thread_num <=0 || max_request <= 0) throw std::exception();
m_threads = new pthread_t[thread_num];
if(!m_threads) throw std::exception();
for(int i = 0;i < thread_num;++i)
{
// 创建线程
if(pthread_create(m_threads + i, NULL,worker,this)!=0)
{
delete[] m_threads;
throw std::exception();
}
// 分离线程
if(pthread_detach(m_threads[i]))
{
delete[] m_threads;
throw std::exception();
}
}
}析构函数
template<typename T>
threadpool<T>::~threadpool()
{
delete[] m_trheads;
}添加任务函数
template<typename T>
bool threadpool<T>::append(T* request)
{
m_locker.lock();
if(m_queuework.size() > m_max_request)
{
m_locker.unlock();
return false;
}
m_queuework.push_back(request);
m_locker.unlock();
m_sem.post();
return true;
}任务处理函数
template<typename T>
void* threadpool<T>::worker(void*arg)
{
threadpool* pool = (threadpool*)arg;
pool->run();
return pool;
}
template<typename T>
void threadpool<T>::run()
{
while(true)
{
m_sem.wait();
m_locker.lock();
if(m_queuework.empty())
{
m_locker.unlock();
continue;
}
T* request = m_queuework.front();
m_queuework.pop_front();
m_locker.unlock();
request.process(); // 具体任务的处理业务
}
}读到这里,这篇“C++怎么实现一个简单的线程池”文章已经介绍完毕,想要掌握这篇文章的知识点还需要大家自己动手实践使用过才能领会,如果想了解更多相关内容的文章,欢迎关注亿速云行业资讯频道。
免责声明:本站发布的内容(图片、视频和文字)以原创、转载和分享为主,文章观点不代表本网站立场,如果涉及侵权请联系站长邮箱:is@yisu.com进行举报,并提供相关证据,一经查实,将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容。