本篇内容主要讲解“C++逻辑操作符怎么使用”,感兴趣的朋友不妨来看看。本文介绍的方法操作简单快捷,实用性强。下面就让小编来带大家学习“C++逻辑操作符怎么使用”吧!
操作数只有两种值( true和 false )逻
辑表达式不用完全计算就能确定最终值
最终结果只能是 true 或者 false
下面看一个逻辑表达式的代码:
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
int func(int i)
{
cout << "int func(int i): i = " << i << endl;
return i;
}
int main()
{
if (func(0) && func(1))
{
cout << "Result is true!" << endl;
}
else
{
cout << "Result is False!" << endl;
}
cout << endl;
if (func(0) || func(1))
{
cout << "Result is true!" << endl;
}
else
{
cout << "Result is False!" << endl;
}
return 0;
}输出结果如下:
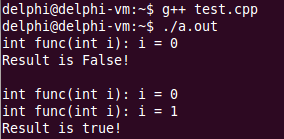
这就是逻辑操作符的短路规则,可以参照我之前写的详细讲解逻辑运算符的使用
逻辑操作符可以重载吗?重载逻辑操作符有什么意义?
下面看一个重载逻辑操作符示例:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Test
{
int mValue;
public:
Test(int v)
{
mValue = v;
}
int value() const
{
return mValue;
}
};
bool operator &&(const Test& l, const Test& r)
{
return l.value() && r.value();
}
bool operator ||(const Test& l, const Test& r)
{
return l.value() || r.value();
}
Test func(Test i)
{
cout << "Test func(Test i): i.value() = " << i.value() << endl;
return i;
}
int main()
{
Test t0(0);
Test t1(1);
if (func(t0) && func(t1))
{
cout << "Result is true!" << endl;
}
else
{
cout << "Result is false!" << endl;
}
cout << endl;
if (func(t0) || func(t1))
{
cout << "Result is true!" << endl;
}
else
{
cout << "Result is false!" << endl;
}
}输出结果如下:
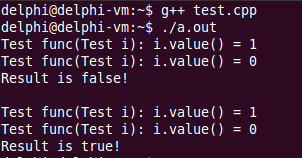
按照短路法则,func(t0) && func(t1) 应该只执行 func(t0),这里却输出了func(t0) 和 func(t1) 运行后的值,这是为什么呢?且看下面解析。
问题的本质分析
C++ 通过函数调用扩展操作符的功能
进入函数体前必须完成所有参数的计算
函数参数的计算次序是不定的
短路法则完全失效
逻辑操作符重载后无法完全实现原生的语义。
上述代码等效写法如下:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Test
{
int mValue;
public:
Test(int v)
{
mValue = v;
}
int value() const
{
return mValue;
}
};
bool operator &&(const Test& l, const Test& r)
{
return l.value() && r.value();
}
bool operator ||(const Test& l, const Test& r)
{
return l.value() || r.value();
}
Test func(Test i)
{
cout << "Test func(Test i): i.value() = " << i.value() << endl;
return i;
}
int main()
{
Test t0(0);
Test t1(1);
if (operator && (func(t0), func(t1)))
{
cout << "Result is true!" << endl;
}
else
{
cout << "Result is false!" << endl;
}
cout << endl;
if (operator || (func(t0), func(t1)))
{
cout << "Result is true!" << endl;
}
else
{
cout << "Result is false!" << endl;
}
}输出结果和上面一样:
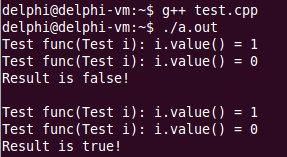
将func(t0) && func(t1) 改写成operator && (func(t0), func(t1)),就不难理解为什么了。核心就两点:
1.进入函数体前必须完成所有参数的计算
2.函数参数的计算次序是不定的
一些有用的建议
实际工程开发中避免重载逻辑操作符
通过重载比较操作符代替逻辑操作符重载
直接使用成员函数代替逻辑操作符重载
使用全局函数对逻辑操作符进行重载
到此,相信大家对“C++逻辑操作符怎么使用”有了更深的了解,不妨来实际操作一番吧!这里是亿速云网站,更多相关内容可以进入相关频道进行查询,关注我们,继续学习!
免责声明:本站发布的内容(图片、视频和文字)以原创、转载和分享为主,文章观点不代表本网站立场,如果涉及侵权请联系站长邮箱:is@yisu.com进行举报,并提供相关证据,一经查实,将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容。