жӮЁеҘҪпјҢзҷ»еҪ•еҗҺжүҚиғҪдёӢи®ўеҚ•е“ҰпјҒ
жӮЁеҘҪпјҢзҷ»еҪ•еҗҺжүҚиғҪдёӢи®ўеҚ•е“ҰпјҒ
жң¬зҜҮеҶ…е®№д»Ӣз»ҚдәҶвҖңжҖҺд№ҲдҪҝз”ЁC++е®һзҺ°Dijkstraз®—жі•вҖқзҡ„жңүе…ізҹҘиҜҶпјҢеңЁе®һйҷ…жЎҲдҫӢзҡ„ж“ҚдҪңиҝҮзЁӢдёӯпјҢдёҚе°‘дәәйғҪдјҡйҒҮеҲ°иҝҷж ·зҡ„еӣ°еўғпјҢжҺҘдёӢжқҘе°ұи®©е°Ҹзј–еёҰйўҶеӨ§е®¶еӯҰд№ дёҖдёӢеҰӮдҪ•еӨ„зҗҶиҝҷдәӣжғ…еҶөеҗ§пјҒеёҢжңӣеӨ§е®¶д»”з»Ҷйҳ…иҜ»пјҢиғҪеӨҹеӯҰжңүжүҖжҲҗпјҒ
graphзұ»з”ЁдәҺйӮ»жҺҘиЎЁе»әз«Ӣе’Ңдҝқеӯҳжңүеҗ‘еӣҫгҖӮ
graph.hпјҡ
#ifndef GRAPH_H
#define GRAPH_H
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <vector>
#include <stdlib.h>
using namespace std;
// е®ҡд№үйЎ¶зӮ№
typedef struct EdgeNode {
int adjvex; // йЎ¶зӮ№дёӢж Ү
struct EdgeNode *next; // дёӢдёҖжқЎиҫ№зҡ„жҢҮй’Ҳ
double cost; // еҪ“еүҚиҫ№зҡ„д»Јд»·
EdgeNode();
~EdgeNode();
} EdgeNode;
// е®ҡд№үйЎ¶зӮ№иЎЁ
typedef struct VexList
{
string Vexs; //з”ЁжқҘеӯҳеӮЁйЎ¶зӮ№дҝЎжҒҜ
EdgeNode *firstedge; //з”ЁжқҘеӯҳеӮЁеҪ“еүҚйЎ¶зӮ№зҡ„дёӢдёҖдёӘйЎ¶зӮ№
VexList();
~VexList();
} VertexList;
// е®ҡд№үеӣҫ
typedef class GraphList {
public:
GraphList();
~GraphList();
void PrintGraph(); // жү“еҚ°еӣҫ
void CreateGraph(); // жһ„е»әеӣҫ
vector<VexList> VexList;
int Vertexs, Edges;
} GraphList;
typedef GraphList* GraphListPtr;
#endifgraph.cpp
#include <graph.h>
EdgeNode::EdgeNode() {
cost = 0;
next = nullptr;
}
EdgeNode::~EdgeNode() {
//cout << "delete Node" << endl;
}
VexList::VexList() {
firstedge = nullptr;
}
VexList::~VexList() {
//cout << "delete VexList" << endl;
}
GraphList::GraphList() {
VexList.clear();
}
GraphList::~GraphList() {
//cout << "delete GraphList" << endl;
}
void GraphList::PrintGraph() {
cout << "жүҖе»әз«Ӣзҡ„ең°еӣҫеҰӮд»ҘдёӢжүҖзӨәпјҡ" << endl;
for (int i = 0; i< Vertexs; i++) {
cout << VexList[i].Vexs; //е…Ҳиҫ“еҮәйЎ¶зӮ№дҝЎжҒҜ
EdgeNode * e = VexList[i].firstedge;
while (e) { //然еҗҺе°ұејҖе§ӢйҒҚеҺҶиҫ“еҮәжҜҸдёӘиҫ№иЎЁжүҖеӯҳеӮЁзҡ„йӮ»жҺҘзӮ№зҡ„дёӢж Ү
if (e->cost == -1) {
cout << "---->" << e->adjvex;
}
else {
cout << "-- " << e->cost << " -->" << e->adjvex;
}
e = e->next;
}
cout << endl;
}
}
void GraphList::CreateGraph() {
EdgeNode *e = new EdgeNode();
cout << "иҜ·иҫ“е…ҘйЎ¶зӮ№ж•°е’Ңиҫ№ж•°пјҡ" << endl;
cin >> Vertexs >> Edges;
cout << "иҜ·иҫ“е…ҘйЎ¶зӮ№зҡ„дҝЎжҒҜпјҡ" << endl;
for (int i = 0; i <Vertexs; ++i) {
VertexList tmp;
cin >> tmp.Vexs;
tmp.firstedge = NULL;
VexList.push_back(tmp);
}
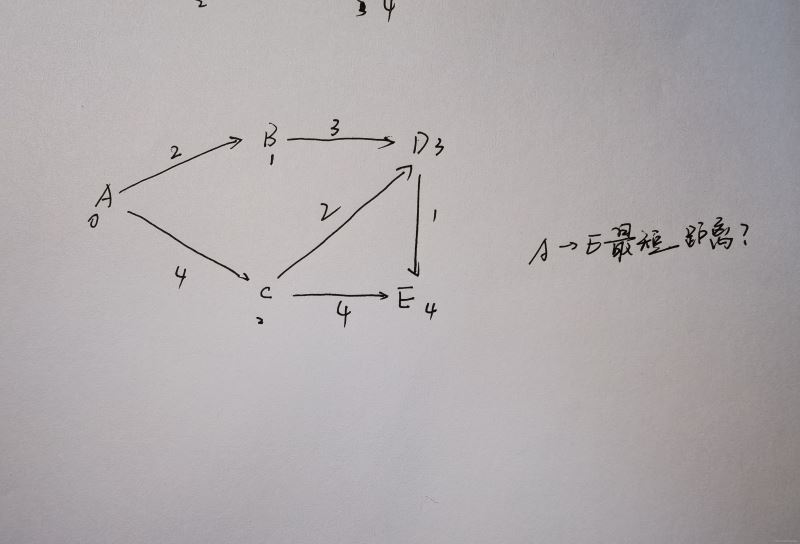
for (int k = 0; k < Edges; ++k) {
int i, j; //(ViпјҢVj)
double cost;
cout << "иҜ·иҫ“е…Ҙиҫ№пјҲVi,VjпјүдёҺ costпјҡ" << endl;
cin >> i >> j >> cost;
if (VexList[i].firstedge == NULL) {//еҪ“еүҚйЎ¶зӮ№iеҗҺйқўжІЎжңүйЎ¶зӮ№
e = new EdgeNode;
e->adjvex = j;
e->cost = cost;
e->next = NULL;
VexList[i].firstedge = e;
}
else { //еҪ“еүҚiеҗҺйқўжңүйЎ¶зӮ№
EdgeNode *p = VexList[i].firstedge;
while (p->next) {
p = p->next;
}
e = new EdgeNode;
e->adjvex = j;
e->cost = cost;
e->next = NULL;
p->next = e;
}
}
}PathFinderзұ»з”ЁдәҺжҗңзҙўжңҖзҹӯи·Ҝеҫ„
pathFinder.h
#ifndef PATH_FINDER_H
#define PATH_FINDER_H
#include <iostream>
#include <graph.h>
#include <queue>
enum State{OPEN = 0, CLOSED, UNFIND};
// е®ҡд№үdijkstraжұӮи§ЈеҷЁ
class DijNode {
public:
DijNode();
DijNode(double _val);
~DijNode() {};
double getCost() { return m_cost; }
State getState() { return m_state; }
void setCost(double _val) { m_cost = _val; }
void setState(State _state) { m_state = _state; }
int getIndex() { return m_index; }
void setIndex(int _idx) { m_index = _idx; }
void setPred(DijNode* _ptr) { preNode = _ptr; }
DijNode* getPred() { return preNode; }
VertexList Vertex;
private:
int m_index;
double m_cost; // иө·зӮ№еҲ°еҪ“еүҚзӮ№зҡ„д»Јд»·
State m_state;
DijNode* preNode; // дҝқеӯҳзҲ¶иҠӮзӮ№
};
typedef DijNode* DijNodePtr;
// жһ„йҖ дјҳе…ҲйҳҹеҲ—з”Ёзҡ„
struct cmp {
bool operator() (DijNodePtr &a, DijNodePtr &b) {
return a->getCost() > b->getCost();
}
};
class PathFinder {
public:
priority_queue<DijNodePtr, vector<DijNodePtr>, cmp > openList;//з”Ёдјҳе…ҲйҳҹеҲ—еҒҡopenListпјҢйҳҹйҰ–е…ғзҙ дёәжңҖе°ҸеҖј
vector<DijNodePtr> m_path; // еӯҳж”ҫжңҖз»Ҳи·Ҝеҫ„
PathFinder() {
openList.empty();
m_path.clear();
}
~PathFinder() {};
void StoreGraph(GraphListPtr _graph);
void Search(int start, int end);
void retrievePath(DijNodePtr _ptr);
vector<DijNodePtr> NodeList;
private:
GraphListPtr m_graph;
/*vector<DijNodePtr> NodeList;*/
};
typedef PathFinder* PathFinderPtr;
#endifPathFinder.cpp
#include <PathFinder.h>
DijNode::DijNode() {
m_cost = -1; // -1иЎЁзӨәжңӘиў«жҺўзҙўиҝҮпјҢи·қзҰ»дёәж— з©·пјҢйқһиҙҹж•°иЎЁзӨәе·Із»Ҹиў«жҺўзҙўиҝҮ
m_index = -1;
m_state = UNFIND; // OPENиЎЁзӨәopenlistпјҢ CLOSEDиЎЁзӨәеңЁcloseListдёӯпјҢUNFINDиЎЁзӨәжңӘжҺўзҙўиҝҮ
preNode = nullptr;
}
DijNode::DijNode(double _val) {
m_cost = _val; // -1иЎЁзӨәжңӘиў«жҺўзҙўиҝҮпјҢйқһиҙҹж•°иЎЁзӨәе·Із»Ҹиў«жҺўзҙўиҝҮ
m_index = -1;
m_state = UNFIND; // OPENиЎЁзӨәopenlistпјҢ CLOSEDиЎЁзӨәеңЁcloseListдёӯпјҢUNFINDиЎЁзӨәжңӘжҺўзҙўиҝҮ
preNode = nullptr;
}
void PathFinder::StoreGraph(GraphListPtr _graph) {
for (int i = 0; i < _graph->VexList.size(); ++i) {
DijNodePtr node = new DijNode();
node->Vertex = _graph->VexList[i];
node->setIndex(i);
NodeList.push_back(node);
}
}
void PathFinder::Search(int start, int end) {
// жҗңзҙўиө·зӮ№
DijNodePtr m_start = NodeList[start];
m_start->setCost(0);
m_start->setIndex(start);
m_start->setState(OPEN);
openList.push(m_start);
int count = 0;
while (!openList.empty()) {
// еј№еҮәopenListдёӯзҡ„йҳҹйҰ–е…ғзҙ
DijNodePtr cur = openList.top();
cur->setState(CLOSED); // еҠ е…Ҙcloselistдёӯ
openList.pop();
// йҒҚеҺҶйҳҹйҰ–е…ғзҙ жүҖжңүзҡ„иҫ№
EdgeNode *e = cur->Vertex.firstedge;
while (e != nullptr) {
int _index = e->adjvex;
double _cost = e->cost;
//cout << "_cost = " << _cost << endl;
// еҰӮжһңиҠӮзӮ№еңЁclose listдёӯпјҢзӣҙжҺҘи·іиҝҮ
if (NodeList[_index]->getState() == CLOSED) {
continue;
}
if (NodeList[_index]->getCost() == -1) {
NodeList[_index]->setCost(cur->getCost() + _cost); // жӣҙж–°д»Јд»·
NodeList[_index]->setPred(cur); // жӣҙж–°зҲ¶иҠӮзӮ№
NodeList[_index]->setState(OPEN); // еҠ е…Ҙopen listдёӯ
openList.push(NodeList[_index]);
}
else if (cur->getCost() + _cost < NodeList[_index]->getCost()) {
// еҰӮжһңд»ҺеҪ“еүҚиҠӮзӮ№еҲ°з¬¬_indexдёӘиҠӮзӮ№зҡ„и·қзҰ»жӣҙзҹӯпјҢжӣҙж–°и·қзҰ»е’ҢзҲ¶иҠӮзӮ№
NodeList[_index]->setCost(cur->getCost() + _cost); // жӣҙж–°д»Јд»·
NodeList[_index]->setPred(cur); // жӣҙж–°зҲ¶иҠӮзӮ№
NodeList[_index]->setState(OPEN); // еҠ е…Ҙopen listдёӯ
}
e = e->next;
}
}
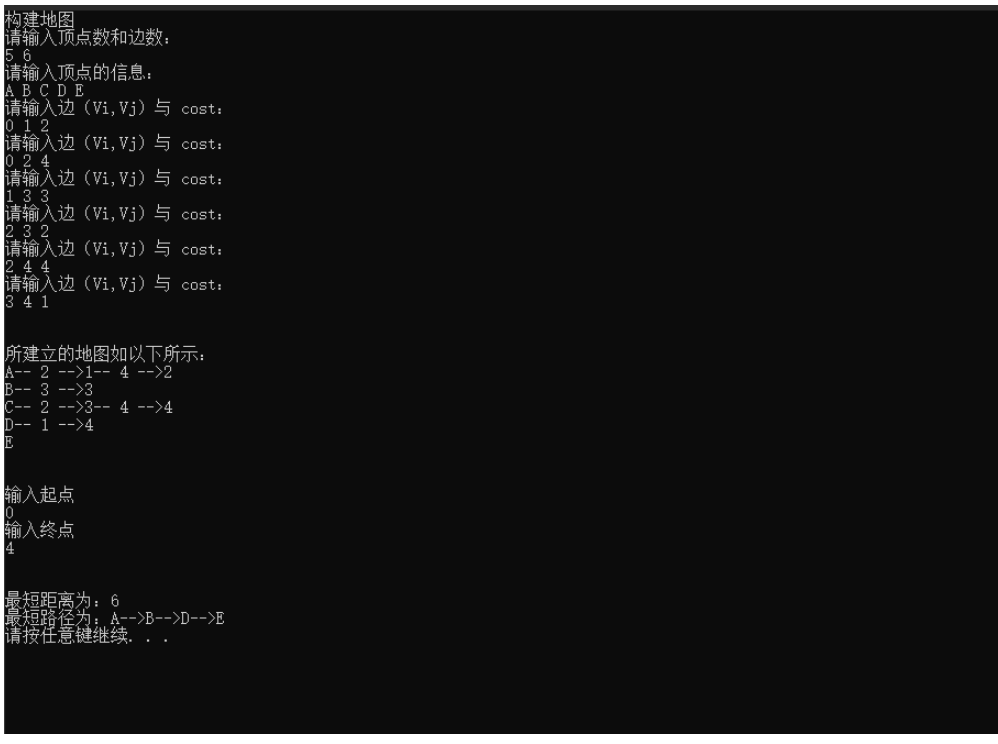
cout << "жңҖзҹӯи·қзҰ»дёәпјҡ" << NodeList[end]->getCost() << endl;
retrievePath(NodeList[end]);
}
void PathFinder::retrievePath(DijNodePtr ptr) {
while (ptr != nullptr) {
m_path.push_back(ptr);
ptr = ptr->getPred();
}
reverse(m_path.begin(),m_path.end());
}дё»еҮҪж•°
#include <graph.h>
#include <PathFinder.h>
int main() {
cout << "жһ„е»әең°еӣҫ" << endl;
GraphListPtr graph = new GraphList();
graph->CreateGraph();
cout << "\n \n";
graph->PrintGraph();
PathFinderPtr _solver = new PathFinder();
_solver->StoreGraph(graph);
cout << "\n \n";
int start, end;
cout << "иҫ“е…Ҙиө·зӮ№" << endl;
cin >> start;
cout << "иҫ“е…Ҙз»ҲзӮ№" << endl;
cin >> end;
cout << "\n \n";
_solver->Search(start, end);
cout << "жңҖзҹӯи·Ҝеҫ„дёәпјҡ";
for (int i = 0; i < _solver->m_path.size(); ++i) {
cout << _solver->m_path[i]->Vertex.Vexs ;
if (i < _solver->m_path.size() - 1)
cout << "-->";
}
cout << endl;
system("pause");
return 0;
}
вҖңжҖҺд№ҲдҪҝз”ЁC++е®һзҺ°Dijkstraз®—жі•вҖқзҡ„еҶ…е®№е°ұд»Ӣз»ҚеҲ°иҝҷйҮҢдәҶпјҢж„ҹи°ўеӨ§е®¶зҡ„йҳ…иҜ»гҖӮеҰӮжһңжғідәҶи§ЈжӣҙеӨҡиЎҢдёҡзӣёе…ізҡ„зҹҘиҜҶеҸҜд»Ҙе…іжіЁдәҝйҖҹдә‘зҪ‘з«ҷпјҢе°Ҹзј–е°ҶдёәеӨ§е®¶иҫ“еҮәжӣҙеӨҡй«ҳиҙЁйҮҸзҡ„е®һз”Ёж–Үз« пјҒ
е…ҚиҙЈеЈ°жҳҺпјҡжң¬з«ҷеҸ‘еёғзҡ„еҶ…е®№пјҲеӣҫзүҮгҖҒи§Ҷйў‘е’Ңж–Үеӯ—пјүд»ҘеҺҹеҲӣгҖҒиҪ¬иҪҪе’ҢеҲҶдә«дёәдё»пјҢж–Үз« и§ӮзӮ№дёҚд»ЈиЎЁжң¬зҪ‘з«ҷз«ӢеңәпјҢеҰӮжһңж¶үеҸҠдҫөжқғиҜ·иҒ”зі»з«ҷй•ҝйӮ®з®ұпјҡis@yisu.comиҝӣиЎҢдёҫжҠҘпјҢ并жҸҗдҫӣзӣёе…іиҜҒжҚ®пјҢдёҖз»ҸжҹҘе®һпјҢе°Ҷз«ӢеҲ»еҲ йҷӨж¶үе«ҢдҫөжқғеҶ…е®№гҖӮ