本文小编为大家详细介绍“Go gorilla securecookie库怎么安装使用”,内容详细,步骤清晰,细节处理妥当,希望这篇“Go gorilla securecookie库怎么安装使用”文章能帮助大家解决疑惑,下面跟着小编的思路慢慢深入,一起来学习新知识吧。
cookie 是用于在 Web 客户端(一般是浏览器)和服务器之间传输少量数据的一种机制。由服务器生成,发送到客户端保存,客户端后续的每次请求都会将 cookie 带上。cookie 现在已经被多多少少地滥用了。很多公司使用 cookie 来收集用户信息、投放广告等。
cookie 有两大缺点:
每次请求都需要传输,故不能用来存放大量数据;
安全性较低,通过浏览器工具,很容易看到由网站服务器设置的 cookie。
gorilla/securecookie提供了一种安全的 cookie,通过在服务端给 cookie 加密,让其内容不可读,也不可伪造。当然,敏感信息还是强烈建议不要放在 cookie 中。
本文代码使用 Go Modules。
创建目录并初始化:
$ mkdir gorilla/securecookie && cd gorilla/securecookie $ go mod init github.com/darjun/go-daily-lib/gorilla/securecookie
安装gorilla/securecookie库:
$ go get github.com/gorilla/securecookie
package main
import (
"fmt"
"github.com/gorilla/mux"
"github.com/gorilla/securecookie"
"log"
"net/http"
)
type User struct {
Name string
Age int
}
var (
hashKey = securecookie.GenerateRandomKey(16)
blockKey = securecookie.GenerateRandomKey(16)
s = securecookie.New(hashKey, blockKey)
)
func SetCookieHandler(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) {
u := &User {
Name: "dj",
Age: 18,
}
if encoded, err := s.Encode("user", u); err == nil {
cookie := &http.Cookie{
Name: "user",
Value: encoded,
Path: "/",
Secure: true,
HttpOnly: true,
}
http.SetCookie(w, cookie)
}
fmt.Fprintln(w, "Hello World")
}
func ReadCookieHandler(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) {
if cookie, err := r.Cookie("user"); err == nil {
u := &User{}
if err = s.Decode("user", cookie.Value, u); err == nil {
fmt.Fprintf(w, "name:%s age:%d", u.Name, u.Age)
}
}
}
func main() {
r := mux.NewRouter()
r.HandleFunc("/set_cookie", SetCookieHandler)
r.HandleFunc("/read_cookie", ReadCookieHandler)
http.Handle("/", r)
log.Fatal(http.ListenAndServe(":8080", nil))
}首先需要创建一个SecureCookie对象:
var s = securecookie.New(hashKey, blockKey)
其中hashKey是必填的,它用来验证 cookie 是否是伪造的,底层使用 HMAC(Hash-based message authentication code)算法。推荐hashKey使用 32/64 字节的 Key。
blockKey是可选的,它用来加密 cookie,如不需要加密,可以传nil。如果设置了,它的长度必须与对应的加密算法的块大小(block size)一致。例如对于 AES 系列算法,AES-128/AES-192/AES-256 对应的块大小分别为 16/24/32 字节。
为了方便也可以使用GenerateRandomKey()函数生成一个安全性足够强的随机 key。每次调用该函数都会返回不同的 key。上面代码就是通过这种方式创建 key 的。
调用s.Encode("user", u)将对象u编码成字符串,内部实际上使用了标准库encoding/gob。所以gob支持的类型都可以编码。
调用s.Decode("user", cookie.Value, u)将 cookie 值解码到对应的u对象中。
运行:
$ go run main.go
首先使用浏览器访问localhost:8080/set_cookie,这时可以在 Chrome 开发者工具的 Application 页签中看到 cookie 内容:
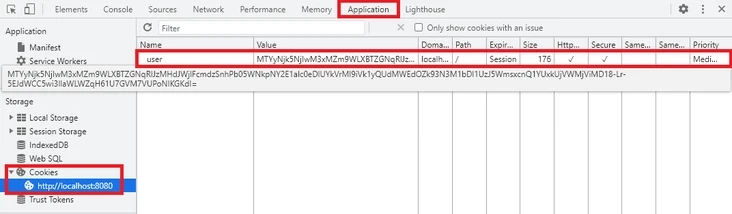
访问localhost:8080/read_cookie,页面显示name: dj age: 18。
securecookie默认使用encoding/gob编码 cookie 值,我们也可以改用encoding/json。securecookie将编解码器封装成一个Serializer接口:
type Serializer interface {
Serialize(src interface{}) ([]byte, error)
Deserialize(src []byte, dst interface{}) error
}securecookie提供了GobEncoder和JSONEncoder的实现:
func (e GobEncoder) Serialize(src interface{}) ([]byte, error) {
buf := new(bytes.Buffer)
enc := gob.NewEncoder(buf)
if err := enc.Encode(src); err != nil {
return nil, cookieError{cause: err, typ: usageError}
}
return buf.Bytes(), nil
}
func (e GobEncoder) Deserialize(src []byte, dst interface{}) error {
dec := gob.NewDecoder(bytes.NewBuffer(src))
if err := dec.Decode(dst); err != nil {
return cookieError{cause: err, typ: decodeError}
}
return nil
}
func (e JSONEncoder) Serialize(src interface{}) ([]byte, error) {
buf := new(bytes.Buffer)
enc := json.NewEncoder(buf)
if err := enc.Encode(src); err != nil {
return nil, cookieError{cause: err, typ: usageError}
}
return buf.Bytes(), nil
}
func (e JSONEncoder) Deserialize(src []byte, dst interface{}) error {
dec := json.NewDecoder(bytes.NewReader(src))
if err := dec.Decode(dst); err != nil {
return cookieError{cause: err, typ: decodeError}
}
return nil
}我们可以调用securecookie.SetSerializer(JSONEncoder{})设置使用 JSON 编码:
var (
hashKey = securecookie.GenerateRandomKey(16)
blockKey = securecookie.GenerateRandomKey(16)
s = securecookie.New(hashKey, blockKey)
)
func init() {
s.SetSerializer(securecookie.JSONEncoder{})
}我们可以定义一个类型实现Serializer接口,那么该类型的对象可以用作securecookie的编解码器。我们实现一个简单的 XML 编解码器:
package main
type XMLEncoder struct{}
func (x XMLEncoder) Serialize(src interface{}) ([]byte, error) {
buf := &bytes.Buffer{}
encoder := xml.NewEncoder(buf)
if err := encoder.Encode(buf); err != nil {
return nil, err
}
return buf.Bytes(), nil
}
func (x XMLEncoder) Deserialize(src []byte, dst interface{}) error {
dec := xml.NewDecoder(bytes.NewBuffer(src))
if err := dec.Decode(dst); err != nil {
return err
}
return nil
}
func init() {
s.SetSerializer(XMLEncoder{})
}由于securecookie.cookieError未导出,XMLEncoder与GobEncoder/JSONEncoder返回的错误有些不一致,不过不影响使用。
securecookie默认使用sha256.New作为 Hash 函数(用于 HMAC 算法),使用aes.NewCipher作为 Block 函数(用于加解密):
// securecookie.go
func New(hashKey, blockKey []byte) *SecureCookie {
s := &SecureCookie{
hashKey: hashKey,
blockKey: blockKey,
// 这里设置 Hash 函数
hashFunc: sha256.New,
maxAge: 86400 * 30,
maxLength: 4096,
sz: GobEncoder{},
}
if hashKey == nil {
s.err = errHashKeyNotSet
}
if blockKey != nil {
// 这里设置 Block 函数
s.BlockFunc(aes.NewCipher)
}
return s
}可以通过securecookie.HashFunc()修改 Hash 函数,传入一个func () hash.Hash类型:
func (s *SecureCookie) HashFunc(f func() hash.Hash) *SecureCookie {
s.hashFunc = f
return s
}通过securecookie.BlockFunc()修改 Block 函数,传入一个f func([]byte) (cipher.Block, error):
func (s *SecureCookie) BlockFunc(f func([]byte) (cipher.Block, error)) *SecureCookie {
if s.blockKey == nil {
s.err = errBlockKeyNotSet
} else if block, err := f(s.blockKey); err == nil {
s.block = block
} else {
s.err = cookieError{cause: err, typ: usageError}
}
return s
}更换这两个函数更多的是处于安全性的考虑,例如选用更安全的sha512算法:
s.HashFunc(sha512.New512_256)
为了防止 cookie 泄露造成安全风险,有个常用的安全策略:定期更换 Key。更换 Key,让之前获得的 cookie 失效。对应securecookie库,就是更换SecureCookie对象:
var (
prevCookie unsafe.Pointer
currentCookie unsafe.Pointer
)
func init() {
prevCookie = unsafe.Pointer(securecookie.New(
securecookie.GenerateRandomKey(64),
securecookie.GenerateRandomKey(32),
))
currentCookie = unsafe.Pointer(securecookie.New(
securecookie.GenerateRandomKey(64),
securecookie.GenerateRandomKey(32),
))
}程序启动时,我们先生成两个SecureCookie对象,然后每隔一段时间就生成一个新的对象替换旧的。
由于每个请求都是在一个独立的 goroutine 中处理的(读),更换 key 也是在一个单独的 goroutine(写)。为了并发安全,我们必须增加同步措施。但是这种情况下使用锁又太重了,毕竟这里更新的频率很低。
我这里将securecookie.SecureCookie对象存储为unsafe.Pointer类型,然后就可以使用atomic原子操作来同步读取和更新了:
func rotateKey() {
newcookie := securecookie.New(
securecookie.GenerateRandomKey(64),
securecookie.GenerateRandomKey(32),
)
atomic.StorePointer(&prevCookie, currentCookie)
atomic.StorePointer(&currentCookie, unsafe.Pointer(newcookie))
}rotateKey()需要在一个新的 goroutine 中定期调用,我们在main函数中启动这个 goroutine
func main() {
ctx, cancel := context.WithCancel(context.Background())
defer cancel()
go RotateKey(ctx)
}
func RotateKey(ctx context.Context) {
ticker := time.NewTicker(30 * time.Second)
defer ticker.Stop()
for {
select {
case <-ctx.Done():
break
case <-ticker.C:
}
rotateKey()
}
}这里为了方便测试,我设置每隔 30s 就轮换一次。同时为了防止 goroutine 泄漏,我们传入了一个可取消的Context。还需要注意time.NewTicker()创建的*time.Ticker对象不使用时需要手动调用Stop()关闭,否则会造成资源泄漏。
使用两个SecureCookie对象之后,我们编解码可以调用EncodeMulti/DecodeMulti这组方法,它们可以接受多个SecureCookie对象:
func SetCookieHandler(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) {
u := &User{
Name: "dj",
Age: 18,
}
if encoded, err := securecookie.EncodeMulti(
"user", u,
// 看这里 ????
(*securecookie.SecureCookie)(atomic.LoadPointer(¤tCookie)),
); err == nil {
cookie := &http.Cookie{
Name: "user",
Value: encoded,
Path: "/",
Secure: true,
HttpOnly: true,
}
http.SetCookie(w, cookie)
}
fmt.Fprintln(w, "Hello World")
}使用unsafe.Pointer保存SecureCookie对象后,使用时需要类型转换。并且由于并发问题,需要使用atomic.LoadPointer()访问。
解码时调用DecodeMulti依次传入currentCookie和prevCookie,让prevCookie不会立刻失效:
func ReadCookieHandler(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) {
if cookie, err := r.Cookie("user"); err == nil {
u := &User{}
if err = securecookie.DecodeMulti(
"user", cookie.Value, u,
// 看这里 ????
(*securecookie.SecureCookie)(atomic.LoadPointer(¤tCookie)),
(*securecookie.SecureCookie)(atomic.LoadPointer(&prevCookie)),
); err == nil {
fmt.Fprintf(w, "name:%s age:%d", u.Name, u.Age)
} else {
fmt.Fprintf(w, "read cookie error:%v", err)
}
}
}运行程序:
$ go run main.go
先请求localhost:8080/set_cookie,然后请求localhost:8080/read_cookie读取 cookie。等待 1 分钟后,再次请求,发现之前的 cookie 失效了:
read cookie error:securecookie: the value is not valid (and 1 other error)
读到这里,这篇“Go gorilla securecookie库怎么安装使用”文章已经介绍完毕,想要掌握这篇文章的知识点还需要大家自己动手实践使用过才能领会,如果想了解更多相关内容的文章,欢迎关注亿速云行业资讯频道。
免责声明:本站发布的内容(图片、视频和文字)以原创、转载和分享为主,文章观点不代表本网站立场,如果涉及侵权请联系站长邮箱:is@yisu.com进行举报,并提供相关证据,一经查实,将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容。