本篇文章和大家了解一下react用g6的方法。有一定的参考价值,有需要的朋友可以参考一下,希望对大家有所帮助。
react用g6使用方法:1、通过“npm install --save @antv/g6”命令在项目引入AntV G6;2、使用“yarn install”重新载入依赖;3、在需要使用到G6的js文件中引入G6即可。
react能用g6吗?
能用。
React中使用AntV G6
AntV G6:G6 是一个简单、易用、完备的图可视化引擎,它在高定制能力的基础上,提供了一系列设计优雅、便于使用的图可视化解决方案。能帮助开发者搭建属于自己的图可视化、图分析、或图编辑器应用。官网
AntV G6的引入
项目中使用npm对包引入
npm install --save @antv/g6
重新载入依赖
yarn install
在需要使用到G6的js文件中引入G6
import G6 from '@antv/g6';
自此,准备工作结束,下面开始使用G6绘制需要的关系图,以力导向图为例描述一对多、一对一的关系。
AntV G6的使用
创建容器:在 HTML 中创建一个用于容纳 G6 绘制的图的容器,通常为 div 标签。G6 在绘制时会在该容器下追加 canvas 标签,然后将图绘制在其中。
ref:在 React 中,可以通过ref.current获取到真实的 DOM 元素。Forwarding Refs(官方文档)
<div ref={ref} id="test"/>创建关系图:创建关系图(实例化)时,至少需要为图设置容器、宽和高。其余请参考图例对应的API以及官方API文档,按需配置。
graph = new G6.Graph({
container: ref.current,
width: width < 1000 ? 387 : width,
height: width < 1000 ? 220 : 550,
layout: {
type: 'force',
preventOverlap: true,
linkDistance: (d) => {
if (d.source.id === 'node0') {
return 10;
}
return 80;
},
nodeStrength: (d) => {
if (d.isLeaf) {
return 200;
}
return -500;
},
edgeStrength: (d) => {
if (d.source.edgeStrength) {
return 0.1;
}
return 0.8;
},
},
defaultNode: {
color: '#5B8FF9',
},
edgeStateStyles: {
highlight: {
stroke: '#5B8FF9' // 这个颜色可以根据个人喜好进行修改
}
},
modes: {
default: ['drag-canvas', 'zoom-canvas'],
},
});数据处理及准备:根据所需图表的数据格式,对数据进行处理。
配置数据源并渲染:
graph.data(data); // 读取 Step 2 中的数据源到图上 graph.render(); // 渲染图
AntV G6的基本使用阐述完后,需要注意在React中,G6与AntV L7及AntV G2,BizCharts有所不同,AntV G6在使用过程中需要访问节点,将其图形作为组件使用时,如果忽略这一点,则会出现问题。 React中使用G6(官网文档)
AntV G6在React中注意
将渲染G6图形的Demo作为匿名函数返回,同时函数return的应为上文创建的容器,在其他js文件中调用Demo时作为组件,同时传入的参数为匿名函数的形参。
上文中第二步:“创建关系图”中生成的实例应在副作用useEffect中定义。
由于在CompotentDidMount中获取数据,当渲染Demo时可能会存在数据并未得到响应便渲染Demo导致报错,解决办法如下:
{deviceData.length ? <G6Picture g6Data={deviceData}/> : <></>}实现效果
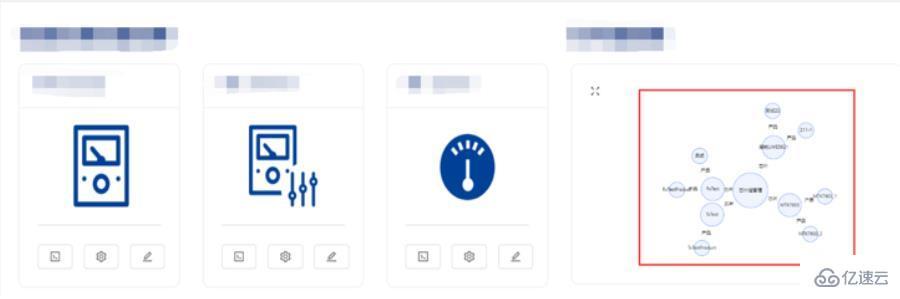
完整代码及部分解释如下:
Demo.js
import G6 from '@antv/g6';
import React, {useEffect} from "react";
import groupBy from 'lodash/groupBy'
import router from "umi/router";
function dealData(data) {//数据处理函数
const dataGroup = groupBy(data, (item) => [item.chipGroupName])
const nodes = [];
const edges = [];
let index = 0;
nodes.push({id: `node${index}`, size: 90, label: "芯片组管理", edgeStrength: true})
for (const key in dataGroup) {
index += 1;
nodes.push({id: `node${index}`, size: 60, label: key, edgeStrength: false, isLeaf: true})
edges.push({source: `node0`, target: `node${index}`, label: '芯片', routerFlag: 0})
if (dataGroup[key]) {
const indexTemp = index;
dataGroup[key].map((item) => {
index += 1;
nodes.push({id: `node${index}`, size: 40, label: item.name, edgeStrength: false})
edges.push({source: `node${indexTemp}`, target: `node${index}`, label: "产品", routerFlag: 1})
})
}
}
const returnData = {
nodes: [...nodes],
edges: [...edges],
}
return returnData;
}
export default function (props) {//props为传入的参数
const ref = React.useRef(null)
let graph = null;
useEffect(() => {
const {g6Data} = props;
const data = dealData(g6Data);
const width = document.getElementById('test').clientWidth;//获取当前宽度
if (!graph) {
graph = new G6.Graph({//生成关系图实例
container: ref.current,//获取真实的DOM节点
width: width < 1000 ? 387 : width,//根据所需大小定义高度、宽度
height: width < 1000 ? 220 : 550,
layout: {//根据要求所需及官方API文档配置
type: 'force',
preventOverlap: true,
linkDistance: (d) => {
if (d.source.id === 'node0') {
return 10;
}
return 80;
},
nodeStrength: (d) => {//根据要求所需及官方API文档配置
if (d.isLeaf) {
return 200;
}
return -500;
},
edgeStrength: (d) => {//根据要求所需及官方API文档配置
if (d.source.edgeStrength) {
return 0.1;
}
return 0.8;
},
},
defaultNode: {//根据要求所需及官方API文档配置
color: '#5B8FF9',
},
edgeStateStyles: {//根据要求所需及官方API文档配置
highlight: {
stroke: '#5B8FF9' // 这个颜色可以根据个人喜好进行修改
}
},
modes: {//根据要求所需及官方API文档配置
default: ['drag-canvas', 'zoom-canvas'],
},
});
}
const {nodes} = data;
graph.data({//绑定数据
nodes,
edges: data.edges.map((edge, i) => {
edge.id = `edge${i}`;
return Object.assign({}, edge);
}),
});
graph.render();//渲染图形
//下面为交互事件配置及操作函数
graph.on('node:dragstart', (e) => {
graph.layout();
refreshDragedNodePosition(e);
});
graph.on('node:drag', (e) => {
refreshDragedNodePosition(e);
});
graph.on('node:dragend', (e) => {
e.item.get('model').fx = null;
e.item.get('model').fy = null;
});
graph.zoom(width < 1000 ? 0.7 : 1, {x: 300, y: 300});
graph.on('node:mouseenter', (ev) => {
const node = ev.item;
const edges = node.getEdges();
const model = node.getModel();
const size = model.size * 1.2;
graph.updateItem(node, {
size,
});
edges.forEach((edge) => {
graph.setItemState(edge, 'highlight', true)
});
});
graph.on('node:click', (e) => {
router.push({pathname: `/DeviceSetting/ChipsetManagement`})
});
graph.on('node:mouseleave', (ev) => {
const node = ev.item;
const edges = node.getEdges();
const model = node.getModel();
const size = model.size / 1.2;
graph.updateItem(node, {
size,
});
edges.forEach((edge) => graph.setItemState(edge, 'highlight', false));
});
function refreshDragedNodePosition(e) {
const model = e.item.get('model');
model.fx = e.x;
model.fy = e.y;
}
}, []);
return <>
<div ref={ref} id="test"/>
</>;
};具体使用Demo的js文件:
import G6Picture from './Demo'
render(
return(
<>
{deviceData.length ? <G6Picture g6Data={deviceData}/> : <></>}
</>
)
)以上就是react用g6的方法的简略介绍,当然详细使用上面的不同还得要大家自己使用过才领会。如果想了解更多,欢迎关注亿速云行业资讯频道哦!
免责声明:本站发布的内容(图片、视频和文字)以原创、转载和分享为主,文章观点不代表本网站立场,如果涉及侵权请联系站长邮箱:is@yisu.com进行举报,并提供相关证据,一经查实,将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容。