жӮЁеҘҪпјҢзҷ»еҪ•еҗҺжүҚиғҪдёӢи®ўеҚ•е“ҰпјҒ
жӮЁеҘҪпјҢзҷ»еҪ•еҗҺжүҚиғҪдёӢи®ўеҚ•е“ҰпјҒ
д»ҠеӨ©е°Ҹзј–з»ҷеӨ§е®¶еҲҶдә«дёҖдёӢSpring refresh()жәҗз ҒеҲҶжһҗзҡ„зӣёе…ізҹҘиҜҶзӮ№пјҢеҶ…е®№иҜҰз»ҶпјҢйҖ»иҫ‘жё…жҷ°пјҢзӣёдҝЎеӨ§йғЁеҲҶдәәйғҪиҝҳеӨӘдәҶи§Јиҝҷж–№йқўзҡ„зҹҘиҜҶпјҢжүҖд»ҘеҲҶдә«иҝҷзҜҮж–Үз« з»ҷеӨ§е®¶еҸӮиҖғдёҖдёӢпјҢеёҢжңӣеӨ§е®¶йҳ…иҜ»е®ҢиҝҷзҜҮж–Үз« еҗҺжңүжүҖ收иҺ·пјҢдёӢйқўжҲ‘们дёҖиө·жқҘдәҶи§ЈдёҖдёӢеҗ§гҖӮ
public void refresh() throws BeansException, IllegalStateException {
synchronized(this.startupShutdownMonitor) {
// 1. еҲқе§ӢеҢ–еүҚзҡ„йў„еӨ„зҗҶ
this.prepareRefresh();
// 2. еҲ·ж–°Beanе·ҘеҺӮ
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = this.obtainFreshBeanFactory();
// 3. BeanFactoryзҡ„йў„еӨ„зҗҶй…ҚзҪ®
this.prepareBeanFactory(beanFactory);
try {
// 4. BeanFactoryзҡ„еҗҺзҪ®еӨ„зҗҶ
this.postProcessBeanFactory(beanFactory);
// 5. жү§иЎҢBeanFactoryеҗҺзҪ®еӨ„зҗҶеҷЁ
this.invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory);
// 6. жіЁеҶҢBeanзҡ„еҗҺзҪ®еӨ„зҗҶеҷЁ
this.registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory);
// 7. еҲқе§ӢеҢ–MessageSource
this.initMessageSource();
// 8. еҲқе§ӢеҢ–дәӢ件жҙҫеҸ‘еҷЁ
this.initApplicationEventMulticaster();
// 9. еӯҗзұ»зҡ„еӨҡжҖҒonRefresh
this.onRefresh();
// 10. жіЁеҶҢзӣ‘еҗ¬еҷЁ
this.registerListeners();
// 11. еҲқе§ӢеҢ–жүҖжңүеү©дёӢзҡ„еҚ•дҫӢBean
this.finishBeanFactoryInitialization(beanFactory);
// 12. е®ҢжҲҗе®№еҷЁзҡ„еҲӣе»әе·ҘдҪң
this.finishRefresh();
} catch (BeansException var9) {
if (this.logger.isWarnEnabled()) {
this.logger.warn("Exception encountered during context initialization - cancelling refresh attempt: " + var9);
}
this.destroyBeans();
this.cancelRefresh(var9);
throw var9;
} finally {
// 13. жё…йҷӨзј“еӯҳ
this.resetCommonCaches();
}
}
}protected void prepareRefresh() {
//и®ҫзҪ®е®№еҷЁеҗҜеҠЁж—¶й—ҙ
this.startupDate = System.currentTimeMillis();
//и®ҫзҪ®е®№еҷЁе…ій—ӯзҠ¶жҖҒдёәfalse
this.closed.set(false);
//и®ҫзҪ®е®№еҷЁжҝҖжҙ»зҠ¶жҖҒдёәtrue
this.active.set(true);
if (this.logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
if (this.logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
this.logger.trace("Refreshing " + this);
} else {
this.logger.debug("Refreshing " + this.getDisplayName());
}
}
//1.1еҲқе§ӢеҢ–еұһжҖ§иө„жәҗ
this.initPropertySources();
//1.2ж ЎйӘҢ
this.getEnvironment().validateRequiredProperties();
this.earlyApplicationEvents = new LinkedHashSet();
}еҲқе§ӢеҢ–ж–№жі•жҳҜдёӘжЁЎеҺӢж–№жі•пјҢз”ұеӯҗзұ»йҮҚеҶҷ
protected void initPropertySources() {
}Webе®№еҷЁGenericWebApplicationContextйҮҚеҶҷдәҶжӯӨж–№жі•
protected void initPropertySources() {
//иҺ·еҸ–зҺҜеўғдҝЎжҒҜ
ConfigurableEnvironment env = getEnvironment();
//еҲӨж–ӯжҳҜеҗҰжҳҜwebй…ҚзҪ®зҺҜеўғ
if (env instanceof ConfigurableWebEnvironment) {
((ConfigurableWebEnvironment) env).initPropertySources(this.servletContext, null);
}
}жңҖз»Ҳз”ұStandardServletEnvironmentиҝӣиЎҢеҲқе§ӢеҢ–
public void initPropertySources(@Nullable ServletContext servletContext, @Nullable ServletConfig servletConfig) {
//дҪҝз”Ёwebе®№еҷЁе·Ҙе…·еҲқе§ӢеҢ–
WebApplicationContextUtils.initServletPropertySources(getPropertySources(), servletContext, servletConfig);
}жҠҠ Servlet зҡ„дёҖдәӣеҲқе§ӢеҢ–еҸӮж•°ж”ҫе…ҘIOCе®№еҷЁдёӯ
public static void initServletPropertySources(MutablePropertySources sources, @Nullable ServletContext servletContext, @Nullable ServletConfig servletConfig) {
Assert.notNull(sources, "'propertySources' must not be null");
String name = "servletContextInitParams";
if (servletContext != null && sources.contains(name) && sources.get(name) instanceof StubPropertySource) {
sources.replace(name, new ServletContextPropertySource(name, servletContext));
}
name = "servletConfigInitParams";
if (servletConfig != null && sources.contains(name) && sources.get(name) instanceof StubPropertySource) {
sources.replace(name, new ServletConfigPropertySource(name, servletConfig));
}
}йҖҡиҝҮеҚ дҪҚз¬Ұи§ЈжһҗеҷЁж ЎйӘҢиө„жәҗйӣҶеҗҲ
public void validateRequiredProperties() throws MissingRequiredPropertiesException {
this.propertyResolver.validateRequiredProperties();
}иҝҷйҮҢзҡ„и§ЈжһҗеҷЁдҪңдёәеёёйҮҸеңЁзҺҜеўғиў«е®һдҫӢеҢ–ж—¶е°ұиў«еҲӣе»әеҮәжқҘзҡ„пјҢPropertySourcesPropertyResolverжҳҜеҚ дҪҚз¬Ұи§ЈжһҗеҷЁпјҢе°Ҷж•°жҚ®жәҗдёӯеҚ дҪҚз¬ҰжӣҝжҚўжҲҗзӣ®ж ҮеҖј
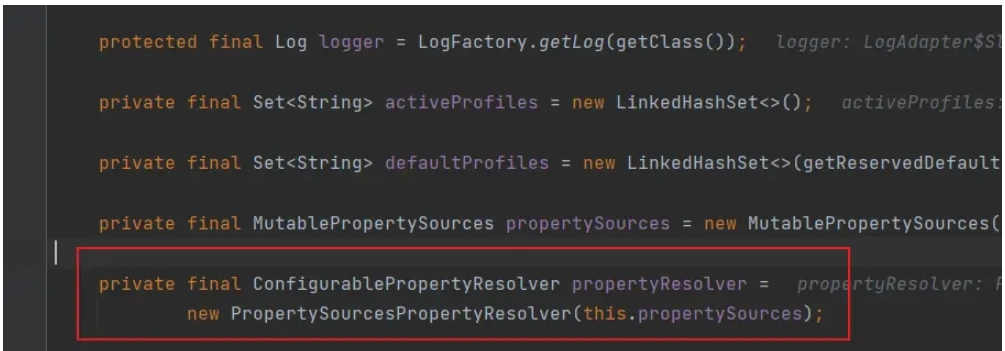
ж ЎйӘҢжҳҜеҗҰжңүйңҖиҰҒиў«еҚ дҪҚз¬Ұдҝ®йҘ°зҡ„еұһжҖ§пјҢеҰӮжһңжңүдҪҶжҳҜиө„жәҗдёӯжүҫдёҚеҲ°еҜ№еә”еұһжҖ§зҡ„keyе°ұдјҡжҠӣеҮәејӮеёё
public void validateRequiredProperties() {
MissingRequiredPropertiesException ex = new MissingRequiredPropertiesException();
for (String key : this.requiredProperties) {
if (this.getProperty(key) == null) {
ex.addMissingRequiredProperty(key);
}
}
if (!ex.getMissingRequiredProperties().isEmpty()) {
throw ex;
}
}жЎҲдҫӢпјҡ иө„жәҗж–Ү件
name=zhansan
age=${name},10
encoding=utf-8
name2=${name}жөӢиҜ•д»Јз Ғ
@Test
public void test1() throws Exception {
//зңҒз•ҘpropertySources
PropertyResolver propertyResolver = new PropertySourcesPropertyResolver(getPropertySources());
System.out.println(propertyResolver.getProperty("age"));
System.out.println(propertyResolver.getProperty("encoding"));
System.out.println(propertyResolver.resolvePlaceholders("must be encoding ${encoding}")); //иҫ“еҮәmust be encoding gbk
}иҫ“еҮәз»“жһң
10,zhansan
utf-8
must be encoding utf-8
protected ConfigurableListableBeanFactory obtainFreshBeanFactory() {
//2.1еҲ·ж–°Beanе·ҘеҺӮ
refreshBeanFactory();
return getBeanFactory();
}е°Ҷе®№еҷЁеҲ·ж–°ж ҮиҜҶж”№дёәtrueпјҢ并且и®ҫзҪ®дәҶе·ҘеҺӮеәҸеҲ—еҢ–id
protected final void refreshBeanFactory() throws IllegalStateException {
if (!this.refreshed.compareAndSet(false, true)) {
throw new IllegalStateException(
"GenericApplicationContext does not support multiple refresh attempts: just call 'refresh' once");
}
this.beanFactory.setSerializationId(getId());
}protected void prepareBeanFactory(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) {
// и®ҫзҪ®BeanFactoryзҡ„зұ»еҠ иҪҪеҷЁгҖҒиЎЁиҫҫејҸи§ЈжһҗеҷЁзӯү
beanFactory.setBeanClassLoader(getClassLoader());
beanFactory.setBeanExpressionResolver(new StandardBeanExpressionResolver(beanFactory.getBeanClassLoader()));
beanFactory.addPropertyEditorRegistrar(new ResourceEditorRegistrar(this, getEnvironment()));
// 3.1 ж·»еҠ Awareжү§иЎҢеҷЁ
beanFactory.addBeanPostProcessor(new ApplicationContextDProcessor(this));
beanFactory.ignoreDependencyInterface(EnvironmentAware.class);
beanFactory.ignoreDependencyInterface(EmbeddedValueResolverAware.class);
beanFactory.ignoreDependencyInterface(ResourceLoaderAware.class);
beanFactory.ignoreDependencyInterface(ApplicationEventPublisherAware.class);
beanFactory.ignoreDependencyInterface(MessageSourceAware.class);
beanFactory.ignoreDependencyInterface(ApplicationContextAware.class);
// 3.2 иҮӘеҠЁжіЁе…Ҙзҡ„ж”ҜжҢҒ
beanFactory.registerResolvableDependency(BeanFactory.class, beanFactory);
beanFactory.registerResolvableDependency(ResourceLoader.class, this);
beanFactory.registerResolvableDependency(ApplicationEventPublisher.class, this);
beanFactory.registerResolvableDependency(ApplicationContext.class, this);
// 3.3 ж·»еҠ зӣ‘еҗ¬еҷЁжү§иЎҢеҷЁ
beanFactory.addBeanPostProcessor(new ApplicationListenerDetector(this));
// Detect a LoadTimeWeaver and prepare for weaving, if found.
if (beanFactory.containsBean(LOAD_TIME_WEAVER_BEAN_NAME)) {
beanFactory.addBeanPostProcessor(new LoadTimeWeaverAwareProcessor(beanFactory));
// Set a temporary ClassLoader for type matching.
beanFactory.setTempClassLoader(new ContextTypeMatchClassLoader(beanFactory.getBeanClassLoader()));
}
// Register default environment beans.
if (!beanFactory.containsLocalBean(ENVIRONMENT_BEAN_NAME)) {
beanFactory.registerSingleton(ENVIRONMENT_BEAN_NAME, getEnvironment());
}
if (!beanFactory.containsLocalBean(SYSTEM_PROPERTIES_BEAN_NAME)) {
beanFactory.registerSingleton(SYSTEM_PROPERTIES_BEAN_NAME, getEnvironment().getSystemProperties());
}
if (!beanFactory.containsLocalBean(SYSTEM_ENVIRONMENT_BEAN_NAME)) {
beanFactory.registerSingleton(SYSTEM_ENVIRONMENT_BEAN_NAME, getEnvironment().getSystemEnvironment());
}
}ApplicationContextDProcessorе®һзҺ°дәҶBeanPostProcessorзҡ„postProcessBeforeInitializationжҺҘеҸЈпјҢеңЁжүҖжңүBeanеҲқе§ӢеҢ–еүҚдјҡжү§иЎҢеҪ“еүҚж–№жі•
public Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
//еҲӨж–ӯBeanжҳҜAwareзҡ„еӯҗзұ»
if (!(bean instanceof EnvironmentAware || bean instanceof EmbeddedValueResolverAware ||
bean instanceof ResourceLoaderAware || bean instanceof ApplicationEventPublisherAware ||
bean instanceof MessageSourceAware || bean instanceof ApplicationContextAware)){
return bean;
}
AccessControlContext acc = null;
if (System.getSecurityManager() != null) {
acc = this.applicationContext.getBeanFactory().getAccessControlContext();
}
if (acc != null) {
AccessController.doPrivileged((PrivilegedAction<Object>) () -> {
invokeAwareInterfaces(bean);
return null;
}, acc);
}
else {
//еӣһи°ғжү§иЎҢAwareжҺҘеҸЈ
invokeAwareInterfaces(bean);
}
return bean;
}еҰӮжһңеҪ“еүҚBeanжҳҜAwareзҡ„еӯҗзұ»пјҢйӮЈд№Ҳе°ҶBeanејәиҪ¬жҲҗAwareзұ»еһӢпјҢйҖҡиҝҮеӣһи°ғе°ҶдҝЎжҒҜи®ҫзҪ®еҲ°Beanдёӯ
private void invokeAwareInterfaces(Object bean) {
if (bean instanceof EnvironmentAware) {
((EnvironmentAware) bean).setEnvironment(this.applicationContext.getEnvironment());
}
if (bean instanceof EmbeddedValueResolverAware) {
((EmbeddedValueResolverAware) bean).setEmbeddedValueResolver(this.embeddedValueResolver);
}
if (bean instanceof ResourceLoaderAware) {
((ResourceLoaderAware) bean).setResourceLoader(this.applicationContext);
}
if (bean instanceof ApplicationEventPublisherAware) {
((ApplicationEventPublisherAware) bean).setApplicationEventPublisher(this.applicationContext);
}
if (bean instanceof MessageSourceAware) {
((MessageSourceAware) bean).setMessageSource(this.applicationContext);
}
if (bean instanceof ApplicationContextAware) {
((ApplicationContextAware) bean).setApplicationContext(this.applicationContext);
}
}еҰӮжһңиҝҮе®№еҷЁдёӯжңүеӨҡдёӘзӣёеҗҢжҺҘеҸЈзҡ„е®һзҺ°зұ»пјҢйӮЈд№ҲеңЁиҮӘеҠЁжіЁе…Ҙзҡ„ж—¶еҖҷдјҡжіЁе…ҘжіЁеҶҢзҡ„е®һзҺ°зұ»
beanFactory.registerResolvableDependency(BeanFactory.class, beanFactory); beanFactory.registerResolvableDependency(ResourceLoader.class, this); beanFactory.registerResolvableDependency(ApplicationEventPublisher.class, this); beanFactory.registerResolvableDependency(ApplicationContext.class, this);
ApplicationListenerDetectorдё»иҰҒдҪңз”ЁжҳҜж·»еҠ е’Ңй”ҖжҜҒзӣ‘еҗ¬еҷЁ,е®һзҺ°дәҶBeanPostProcessorзҡ„postProcessAfterInitializationпјҲBeanе®һдҫӢеҢ–д№ӢеҗҺпјүж–№жі•е’ҢDestructionAwareBeanPostProcessorзҡ„postProcessBeforeDestructionпјҲBeanй”ҖжҜҒд№ӢеүҚпјүж–№жі•
иҝҷжҳҜдёӘжЁЎеҺӢж–№жі•,з”ұеӯҗзұ»AnnotationConfigServletWebServerApplicationContextе®һзҺ°
protected void postProcessBeanFactory(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) {
}AnnotationConfigServletWebServerApplicationContextйҰ–е…Ҳи°ғдәҶзҲ¶зұ» ServletWebServerApplicationContext зҡ„ postProcessBeanFactory ж–№жі•
protected void postProcessBeanFactory(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) {
//4.1еҗҺзҪ®еӨ„зҗҶBeanе·ҘеҺӮ
super.postProcessBeanFactory(beanFactory);
if (this.basePackages != null && this.basePackages.length > 0) {
//basePackagesдёәз©әдёҚдјҡжү§иЎҢ
this.scanner.scan(this.basePackages);
}
if (!this.annotatedClasses.isEmpty()) {
this.reader.register(ClassUtils.toClassArray(this.annotatedClasses));
}
}зҲ¶зұ»ServletWebServerApplicationContextйҰ–е…Ҳеҗ‘Beanе·ҘеҺӮдёӯжіЁе…ҘдәҶдёҖдёӘжү§иЎҢеҷЁ
protected void postProcessBeanFactory(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) {
//4.1.1жіЁе…Ҙжү§иЎҢеҷЁ
beanFactory.addBeanPostProcessor(new WebApplicationContextServletContextAwareProcessor(this));
beanFactory.ignoreDependencyInterface(ServletContextAware.class);
//4.1.2жіЁеҶҢдҪңз”Ёеҹҹ
registerWebApplicationScopes();
}WebApplicationContextServletContextAwareProcessor继жүҝдәҶServletContextAwareProcessor
ServletContextAwareProcessor继жүҝдәҶBeanPostProcessorе®һзҺ°дәҶpostProcessBeforeInitializationпјҲBeanеҲқе§ӢеҢ–еүҚжү§иЎҢпјү
public Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
//жіЁе…ҘServletContext
if (getServletContext() != null && bean instanceof ServletContextAware) {
((ServletContextAware) bean).setServletContext(getServletContext());
}
//жіЁе…ҘServletConfig
if (getServletConfig() != null && bean instanceof ServletConfigAware) {
((ServletConfigAware) bean).setServletConfig(getServletConfig());
}
return bean;
}// жүҖеңЁзұ»еҸҠж–№жі•пјҡServletWebServerApplicationContext#registerWebApplicationScopes
private void registerWebApplicationScopes() {
ExistingWebApplicationScopes existingScopes = new ExistingWebApplicationScopes(getBeanFactory());
WebApplicationContextUtils.registerWebApplicationScopes(getBeanFactory());
existingScopes.restore();
}ExistingWebApplicationScopesжҳҜServletWebServerApplicationContextзұ»дёӯзҡ„дёҖдёӘйқҷжҖҒзұ»
жәҗз ҒеҰӮдёӢпјҡ
public static class ExistingWebApplicationScopes {
static {
Set<String> scopes = new LinkedHashSet<>();
scopes.add(WebApplicationContext.SCOPE_REQUEST);
scopes.add(WebApplicationContext.SCOPE_SESSION);
SCOPES = Collections.unmodifiableSet(scopes);
}
// иҝҷжҳҜжһ„йҖ ж–№жі•пјҢеӨ§жҰӮе°ұжҳҜж №жҚ®SCOPESиҺ·еҸ–beanFactoryдёӯе·Із»ҸжіЁеҶҢзҡ„scopeпјҢ然еҗҺж”ҫе…Ҙscopes
// йңҖиҰҒжіЁж„Ҹзҡ„жҳҜпјҢеңЁдёҠйқўзҡ„ж–№жі•дёӯпјҢ第дәҢиЎҢжүҚеңЁеҗ‘beanFactoryдёӯжіЁеҶҢпјҢд№ҹе°ұжҳҜиҝҷж—¶зҡ„beanFactoryйҮҢйқўжІЎжңүrequestе’ҢsessionиҝҷдёӨдёӘscop
// жүҖд»ҘиҝҷйҮҢе°ұе®ҢжҲҗдәҶbeanFactoryзҡ„иөӢеҖјгҖӮе»әи®®жү“ж–ӯзӮ№иҝӣеҺ»зңӢзңӢ
public ExistingWebApplicationScopes(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) {
this.beanFactory = beanFactory;
for (String scopeName : SCOPES) {
Scope scope = beanFactory.getRegisteredScope(scopeName);
if (scope != null) {
this.scopes.put(scopeName, scope);
}
}
}
// з”ұдәҺдёҠйқўзҡ„方法并没жңүеҖјеӯҳе…ҘscopesпјҢжүҖд»ҘиҝҷйҮҢд№ҹе°ұжІЎжү§иЎҢйҮҢйқўзҡ„еҶ…е®№
public void restore() {
this.scopes.forEach((key, value) -> {
if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
logger.info("Restoring user defined scope " + key);
}
this.beanFactory.registerScope(key, value);
});
}
}WebApplicationContextUtils.registerWebApplicationScopes()пјҢиҝҷдёӘж–№жі•е°ұжҳҜеҗ‘beanFactoryжіЁеҶҢwebзҡ„scopeдәҶпјҢжәҗз ҒеҰӮдёӢ
public static void registerWebApplicationScopes(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) {
registerWebApplicationScopes(beanFactory, null);
}
public static void registerWebApplicationScopes(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory,
@Nullable ServletContext sc) {
// жіЁеҶҢдҪңз”Ёеҹҹ
beanFactory.registerScope(WebApplicationContext.SCOPE_REQUEST, new RequestScope());// жіЁеҶҢrequest SCOP
beanFactory.registerScope(WebApplicationContext.SCOPE_SESSION, new SessionScope());// жіЁеҶҢsession SCOP
if (sc != null) {
ServletContextScope appScope = new ServletContextScope(sc);
beanFactory.registerScope(WebApplicationContext.SCOPE_APPLICATION, appScope); // жіЁеҶҢapplication SCOP
// Register as ServletContext attribute, for ContextCleanupListener to detect it.
sc.setAttribute(ServletContextScope.class.getName(), appScope);
}
// ж·»еҠ дҫқиө–йЎ№
beanFactory.registerResolvableDependency(ServletRequest.class, new RequestObjectFactory());
beanFactory.registerResolvableDependency(ServletResponse.class, new ResponseObjectFactory());
beanFactory.registerResolvableDependency(HttpSession.class, new SessionObjectFactory());
beanFactory.registerResolvableDependency(WebRequest.class, new WebRequestObjectFactory());
if (jsfPresent) {
FacesDependencyRegistrar.registerFacesDependencies(beanFactory);
}
}д»ҘдёҠе°ұжҳҜвҖңSpring refresh()жәҗз ҒеҲҶжһҗвҖқиҝҷзҜҮж–Үз« зҡ„жүҖжңүеҶ…е®№пјҢж„ҹи°ўеҗ„дҪҚзҡ„йҳ…иҜ»пјҒзӣёдҝЎеӨ§е®¶йҳ…иҜ»е®ҢиҝҷзҜҮж–Үз« йғҪжңүеҫҲеӨ§зҡ„收иҺ·пјҢе°Ҹзј–жҜҸеӨ©йғҪдјҡдёәеӨ§е®¶жӣҙж–°дёҚеҗҢзҡ„зҹҘиҜҶпјҢеҰӮжһңиҝҳжғіеӯҰд№ жӣҙеӨҡзҡ„зҹҘиҜҶпјҢиҜ·е…іжіЁдәҝйҖҹдә‘иЎҢдёҡиө„и®Ҝйў‘йҒ“гҖӮ
е…ҚиҙЈеЈ°жҳҺпјҡжң¬з«ҷеҸ‘еёғзҡ„еҶ…е®№пјҲеӣҫзүҮгҖҒи§Ҷйў‘е’Ңж–Үеӯ—пјүд»ҘеҺҹеҲӣгҖҒиҪ¬иҪҪе’ҢеҲҶдә«дёәдё»пјҢж–Үз« и§ӮзӮ№дёҚд»ЈиЎЁжң¬зҪ‘з«ҷз«ӢеңәпјҢеҰӮжһңж¶үеҸҠдҫөжқғиҜ·иҒ”зі»з«ҷй•ҝйӮ®з®ұпјҡis@yisu.comиҝӣиЎҢдёҫжҠҘпјҢ并жҸҗдҫӣзӣёе…іиҜҒжҚ®пјҢдёҖз»ҸжҹҘе®һпјҢе°Ҷз«ӢеҲ»еҲ йҷӨж¶үе«ҢдҫөжқғеҶ…е®№гҖӮ