本篇内容介绍了“c++怎么使用单例模式实现命名空间函数”的有关知识,在实际案例的操作过程中,不少人都会遇到这样的困境,接下来就让小编带领大家学习一下如何处理这些情况吧!希望大家仔细阅读,能够学有所成!
本案例实现一个test命名空间,此命名空间内有两个函数,分别为getName()和getNameSpace();
声明命名空间及函数
namespace test{
const std::string& getName()和();
const std::string& getNameSpace();
}命名空间内实现单例类
实现一个单例类,构造函数要为private,自身对象为private
静态成员函数(才可以调用静态成员变量)
namespace test{
// 实现一个单例类,构造函数要为private,自身对象为private
class ThisNode{
private:
std::string name_;
std::string namespace_;
static ThisNode *thisNode;
ThisNode():name_("empty"),namespace_("namespace"){};
public:
// 静态成员函数(才可以调用静态成员变量)
/**
* 函数:实例化类
* 返回值:ThisNode&
*/
static ThisNode& instance(){
if(thisNode==nullptr){
std::cout << "没有" <<std::endl;
thisNode = new ThisNode();
return *thisNode;
}else{
std::cout << "有" <<std::endl;
return *thisNode;
}
}
// 普通成员函数
const std::string& getName() const{
std::cout <<"get name:"<<name_<<std::endl;
return name_;
}
const std::string& getNameSpace() const{
std::cout <<"getNameSpace:" << namespace_ << std::endl;
return namespace_;
}
};
// 初始化静态成员
ThisNode *ThisNode::thisNode = nullptr;
// 实现命名空间内的函数,实例化一个类,并调用函数
const std::string& getNameSpace(){
return ThisNode::instance().getNameSpace();
}
const std::string& getName(){
return ThisNode::instance().getName();
}
};实现命名空间函数
首先调用的是类的静态成员函数实例化唯一对象,然后调用对象中的方法;
// 实现命名空间内的函数,实例化一个类,并调用函数
const std::string& getNameSpace(){
return ThisNode::instance().getNameSpace();
}
const std::string& getName(){
return ThisNode::instance().getName();
}调用
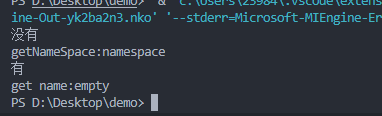
int main(){
// 使用
test::getNameSpace();
test::getName();
return 0;
}
全部代码
#include<string>
#include<iostream>
// 声明命名空间内的两个函数
namespace test{
const std::string& getName()和();
const std::string& getNameSpace();
}
namespace test{
// 实现一个单例类,构造函数要为private,自身对象为private
class ThisNode{
private:
std::string name_;
std::string namespace_;
static ThisNode *thisNode;
ThisNode():name_("empty"),namespace_("namespace"){};
public:
// 静态成员函数(才可以调用静态成员变量)
/**
* 函数:实例化类
* 返回值:ThisNode&
*/
static ThisNode& instance(){
if(thisNode==nullptr){
std::cout << "没有" <<std::endl;
thisNode = new ThisNode();
return *thisNode;
}else{
std::cout << "有" <<std::endl;
return *thisNode;
}
}
// 普通成员函数
const std::string& getName() const{
std::cout <<"get name:"<<name_<<std::endl;
return name_;
}
const std::string& getNameSpace() const{
std::cout <<"getNameSpace:" << namespace_ << std::endl;
return namespace_;
}
};
// 初始化静态成员
ThisNode *ThisNode::thisNode = nullptr;
// 实现命名空间内的函数,实例化一个类,并调用函数
const std::string& getNameSpace(){
return ThisNode::instance().getNameSpace();
}
const std::string& getName(){
return ThisNode::instance().getName();
}
};
int main(){
// 使用
test::getNameSpace();
test::getName();
return 0;
}“c++怎么使用单例模式实现命名空间函数”的内容就介绍到这里了,感谢大家的阅读。如果想了解更多行业相关的知识可以关注亿速云网站,小编将为大家输出更多高质量的实用文章!
免责声明:本站发布的内容(图片、视频和文字)以原创、转载和分享为主,文章观点不代表本网站立场,如果涉及侵权请联系站长邮箱:is@yisu.com进行举报,并提供相关证据,一经查实,将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容。