今天制作一期人机互动的例子带给大家:用按钮控制LED。将开关作为延时开关来使用,按下开关后1秒钟,灯才会亮,灯亮5秒后才熄灭,这样大家就能依据这个例子,自己延伸出很多好玩的玩法出来。通过案例学习变量、运算符、条件语句三种语法知识。
| 名称 | 数量 | 规格 |
|---|---|---|
| Arduino uno控制板 | 1 | R3 |
| 按钮开关 | 1 | |
| 蓝色LED | 1 |
开关:有按键式、滑动式、微动型,除了尺寸和外型不同,开关可分成:
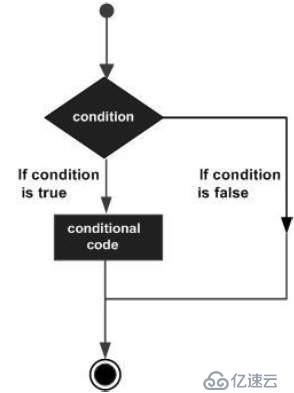
if (expression)
statement;
如果你有一个语句,你可以使用没有大括号{}的if语句。
if (expression) {
Block of statements;
}
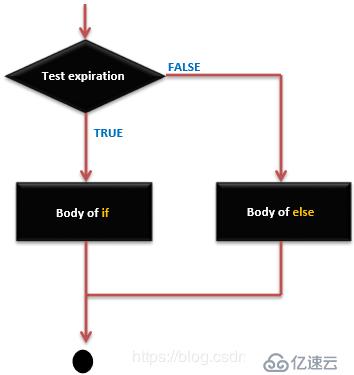
if ... else语句语法
if (expression) { Block of statements; }
else { Block of statements; }
| 比较运算符 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| == | 如果两者相等则成立,请注意,这要写成两个连续等号,中间不能有空格 |
| != | 如果不相等则成立 |
| < | 如果左边小于右边则成立 |
| > | 如果左边大于右边则成立 |
| <= | 如果左边小于或等于右边则成立 |
| >= | 如果左边大于或等于右边则成立 |
比较运算符参与运算后,会返回一个布尔值(true或false)。
| 名称 | 运算符号 | 表达式 | 说明 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 与(and) | && | A && B | 只有A和B两个值都成立时,整个条件才算成立。 |
| 或(OR) | || | A || B | 只要A或B任何一方成立,整个条件就算成立 |
| 非(NOT) | ! | !A | 把成立的变为不成立;不成立的变为成立 |
| 运算符 | 意义 | 说明 |
|---|---|---|
| ++ | 递增 | 将变量值增加1 |
| -- | 递减 | 将变量值减1 |
| += | 指定增加 | 将变量加上某数 |
| -= | 指定减少 | 将变量减去某数 |
| *= | 指定相乘 | 将变量乘上某数 |
| /= | 指定相除 | 将变量除以某数 |
处理器有D、B两个数位输出/输入接口,以及一个类比接口C。
DDRB = B00110100; //DDRB包含8、13接口,DDRD包含07接口
PORTB= B00100100;
利用按钮控制LED
/*
作用:当你按下按钮后1秒钟,灯会亮,然后维持5秒钟,熄灭
*/
void setup () {
pinMode(4,INPUT); //将4号数字口设置为输入状态,13号数字口设置为输出状态
pinMode(13,OUTPUT);
}
void loop(){
int n =digitalRead(4); //创建一个变量n,将4号数字口的状态采集出来赋值给他。
if (n==HIGH) //判断n是否为高电平,如果是执行下面的语句,不是则跳过。
{
delay(1000);
digitalWrite(13,HIGH);
delay(5000);
digitalWrite(13,LOW);
}
}编译并上传代码之后,按着、放开几次微动开关试试,理论上,LED将在按着开关时被点亮,放开开关时熄灭。但实际上,LED可能在你放开开光之后,仍然点亮着,这是机械式开关的弹跳(bouncing)现象。
在arduino控制板上的3、4、5引脚上连接3个LED,通过程序依次控制3个LED灯的亮灭
const byte LED1 = 3;
const byte LED2 = 4;
const byte LED3 = 5;
void setup() {
// put your setup code here, to run once:
pinMode(LED1, OUTPUT);
pinMode(LED2, OUTPUT);
pinMode(LED3, OUTPUT);
}
void loop() {
// put your main code here, to run repeatedly:
digitalWrite(LED1,HIGH);
digitalWrite(LED2,LOW);
digitalWrite(LED3,LOW);
delay(1000);
digitalWrite(LED1,LOW);
digitalWrite(LED2,HIGH);
digitalWrite(LED3,LOW);
delay(1000);
digitalWrite(LED1,LOW);
digitalWrite(LED2,LOW);
digitalWrite(LED3,HIGH);
delay(1000);
}上例中连接在13引脚的led闪烁,如果把led接在10脚,代码需要修改2次,利用变量可简化代码的修改。
byte led = 13;
void setup(){
pinMode(led, OUTPUT);
}
void loop(){
digitalWrite(led, HIGH);
}数据类型 变量名
例如:
int age = 18; //预留16位的存储空间,并存入数字18;
int older = age +10; //先取出age的值,加上10之后,再赋值给older。
• 变量名称只能包含英文字母、数字和底线(_)。
• 第一个字符不能是数字。
• 变量的名称大小写有别,因此LED和led是两个不同的变量!
• 变量名称应该使用有意义的文字,如LED和pin,。让代码变得容易理解。
• 若要用两个单字来命名变量,可以用“驼峰式”记法,
• 避免用特殊意义的保留字来命名。
数据类型用于设置“数据容器”的格式和容量。在声明变量的同时,必须设置该变量所能保存的数据类型。
| 类型 | 中文名 | 占用内存大小 | 数值范围 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| boolean | 布尔 | 8位 | 1或0 | true或false) |
| byte | 字节 | 8位 | 0~255 | |
| char | 字符 | 8位 | -127~127 | |
| int | 整型 | 16位 | -32768~32767 | |
| long | 长整数 | 32位 | -2147483648~2147483647 | |
| float | 浮点数 | 32位 | ±3.4028235E+38 | |
| double | 双精度浮点数 | ±3.4028235E+38 |
| 类型 | 中文名称 | 数值范围 |
|---|---|---|
| unsigned char | 正字符 | 0~255 |
| unsigned int | 正整数 | 0~65535 |
| unsigned long | 正长整数 | 0~4294967295 |
| 格式字符 | 说明 | 示例 |
|---|---|---|
| L或l | 强制转换成长整数 | 4000L |
| U或u | 转化成无正负号(unsigned)整数 | 32800U |
| UL或ul | 强制转换成无正负号的长整数(unsigned long) | 7295UL |
ATmega微处理器内部没有浮点运算处理单元,因此,执行浮点数值运算,不仅耗时且精确度不高,请避免在程序中执行大量的浮点数运算。附带一提,浮点数值可以用科学记号E或e表示,例如:
1.8E3 = 1800
在数字系统中,用四个二进制数来代表十进制的编码,又称为BCD码(Binary Coded Decimal, 二进编码十进数)
常量: 存放固定、不变量值的容器。
若要让常量仅仅保存在程序内存,需要在常量声明代码中加入PROGMEM关键字。
计算机内存分为RAM和ROM两大类型
| C中的数据类型是指用于声明不同类型的变量或函数的扩展系统。变量的类型确定它在存储器中占用多少空间以及如何解释存储的位模式。 下表提供了你将在Arduino编程期间使用的所有数据类型。 |
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| void | Boolean | char | Unsigned char | |
| byte | int | Unsigned int | word | |
| long | Unsigned long | short | float | |
| double | array | String-chararray | String-object |
Void Loop ( ) {
// rest of the code
}boolean val = false ; // declaration of variable with type boolean and initialize it with false
boolean state = true ; // declaration of variable with type boolean and initialize it with falseChar chr_a = ‘a’ ;//declaration of variable with type char and initialize it with character a
Char chr_c = 97 ;//declaration of variable with type char and initialize it with character 97 ASCII Char TableUnsigned Char chr_y = 121 ; // declaration of variable with type Unsigned char and initialize it with character ybyte m = 25 ;//declaration of variable with type byte and initialize it with 25int counter = 32 ;// declaration of variable with type int and initialize it with 32Unsigned int counter = 60 ; // declaration of variable with type unsigned int and initialize it with 60word w = 1000 ;//declaration of variable with type word and initialize it with 1000Long velocity = 102346 ;//declaration of variable with type Long and initialize it with 102346Unsigned Long velocity = 101006 ;// declaration of variable with type Unsigned Long and initialize it with 101006short val = 13 ;//declaration of variable with type short and initialize it with 13float num = 1.352;//declaration of variable with type float and initialize it with 1.352double num = 45.352 ;// declaration of variable with type double and initialize it with 45.352亿速云「云服务器」,即开即用、新一代英特尔至强铂金CPU、三副本存储NVMe SSD云盘,价格低至29元/月。点击查看>>
免责声明:本站发布的内容(图片、视频和文字)以原创、转载和分享为主,文章观点不代表本网站立场,如果涉及侵权请联系站长邮箱:is@yisu.com进行举报,并提供相关证据,一经查实,将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容。