构造函数存在的问题:
A、构造函数只提供自动初始化成员变量的机会
B、不能保证初始化逻辑一定成功,如申请系统资源可能失败
C、执行return语句后构造函数立即结束
构造函数创建的对象可能是半成品对象,半成品对象是合法的对象,但是程序bug的来源之一。因此实际工程开发过程中使用二阶构造模式。
由于构造函数存在的潜在问题,实际工程开发中类对象的构造过程如下:
A、资源无关的初始化操作
资源无关的初始化操作一般不会出现异常的情况
B、系统资源相关的操作
与系统资源有关的操作如堆空间申请,文件访问可能会失败。
二阶构造模式的流程如下: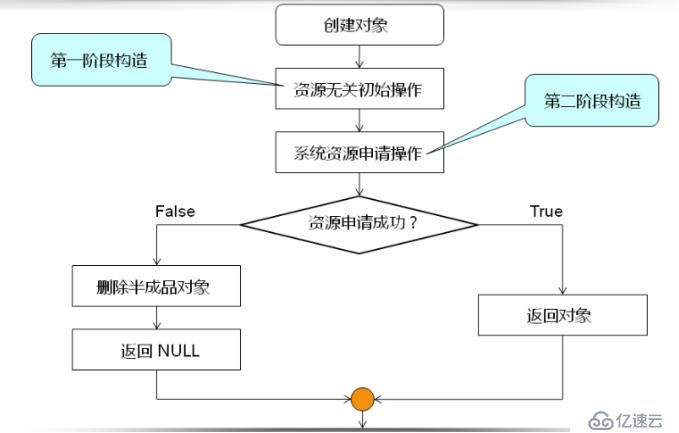
二阶构造模式能够确保创建的对象都是完整初始化的。由于工程实践中类对象占用的存储空间比较大,一般需要分配在堆空间,因此二阶构造模式构造对象的方式舍弃了构造函数中将对象分配在栈和全局数据区的情况,只保留创建在堆空间的对象的构造。
二阶构造模式示例代码:
#include <stdio.h>
class TwoPhaseCons
{
private:
TwoPhaseCons() // 第一阶段构造函数
{
}
bool construct() // 第二阶段构造函数
{
return true;
}
public:
static TwoPhaseCons* NewInstance(); // 对象创建函数
};
TwoPhaseCons* TwoPhaseCons::NewInstance()
{
TwoPhaseCons* ret = new TwoPhaseCons();
// 若第二阶段构造失败,返回 NULL
if( !(ret && ret->construct()) )
{
delete ret;
ret = NULL;
}
return ret;
}
int main()
{
TwoPhaseCons* obj = TwoPhaseCons::NewInstance();
printf("obj = %p\n", obj);
delete obj;
return 0;
}#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class IntArray
{
private:
IntArray(int len)
{
m_length = len;
}
IntArray(const IntArray& obj);
bool construct()
{
bool ret = true;
m_pointer = new int[m_length];
if( m_pointer )
{
for(int i=0; i<m_length; i++)
{
m_pointer[i] = 0;
}
}
else
{
ret = false;
}
return ret;
}
public:
static IntArray* NewInstance(int length)
{
IntArray* ret = new IntArray(length);
//如果资源申请失败
if( !(ret && ret->construct()) )
{
delete ret;
ret = 0;
}
return ret;
}
int length()
{
return m_length;
}
bool get(int index, int& value)
{
bool ret = (0 <= index) && (index < length());
if( ret )
{
value = m_pointer[index];
}
return ret;
}
bool set(int index ,int value)
{
bool ret = (0 <= index) && (index < length());
if( ret )
{
m_pointer[index] = value;
}
return ret;
}
~IntArray()
{
delete [] m_pointer;
}
private:
int m_length;
int* m_pointer;
};
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
IntArray* array = IntArray::NewInstance(5);
cout << array->length() << endl;
return 0;
}亿速云「云服务器」,即开即用、新一代英特尔至强铂金CPU、三副本存储NVMe SSD云盘,价格低至29元/月。点击查看>>
免责声明:本站发布的内容(图片、视频和文字)以原创、转载和分享为主,文章观点不代表本网站立场,如果涉及侵权请联系站长邮箱:is@yisu.com进行举报,并提供相关证据,一经查实,将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容。