准备把原来上学时候写的数据结构、算法相关的代码再重新写一遍,温习下。首先从链表说起,链表可能是我们平时用的较多的一种结构,链表操作对于删除、添加的算法时间复杂度为O(1)。
说到链表就不得不提到他的表哥数组,通过下图来看下一数据和链表在内存中的区别(此处所说的内存都是虚拟内存)。

数组在内存中的存放
注:这里addr + 1 并不是一个字节或者一个字,是一个数据单位的大小。
由上图可以看出数组是在内存中连续存放的,这就成在数据删除或者插入的时候可能要移动很多的数据,其可扩展性也不好。
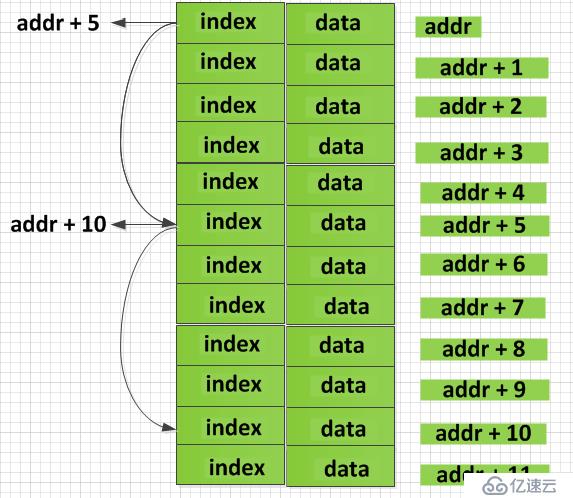
链表在内存中的表示
上图中一个数据单元中除了放本单元的数据,还存放了下一个单元的地址,上图可以简化一下:
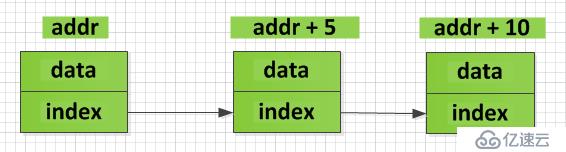
从上图可以看出,链表中的数据在内存中并不是连续存放的,而是通过index将两个数据单元关联起来,这样可以方便我们在不同的数据单元之间插入数据,例如在数据单元1和数据单元2之间插入数据如下:
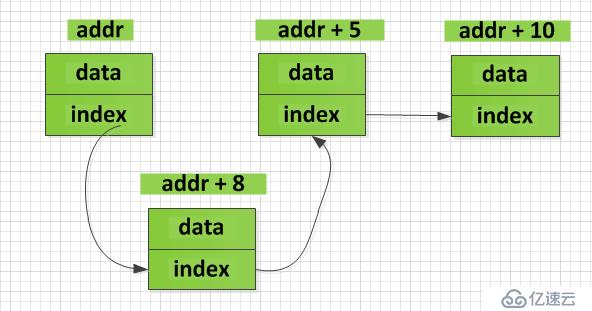
数据插入
链表还可以分为单链表、双链表、循环链表,不过其原理都是大同小异,下面以单链表为例练练手,以面向对象的思路进行编程,可能在这里不是太合适,不过训练对事物进行抽象能力绝对对编程大有好处。
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <string.h>
typedef struct list {
char name[32];
int age;
struct list *next; /* 指向下一个节点 */
/* 在头节点之后插入新节点 */
void (* insert)(struct list *head, struct list *node);
int (* delete)(struct list *head, struct list *node); /* 删除指定的节点 */
/* 查找是否存在指定节点 */
struct list *(* find_node)(struct list *head, struct list *node, int *ret);
void (* print_list)(struct list *head); /* 打印节点内容 */
void (* destroy_list)(struct list *head); /* 销毁整个链表 */
}list_t;
struct info {
char *name;
int age;
}person[] = {
{"zhangsan", 18},
{"lisi", 20},
{"xiaohong", 30},
{"end",0},
};
/*
*fun : 头结点之后插入新节点
*head :头结点指针
*node : 待插入节点指针
*/
void list_insert_node(struct list *head, struct list *node)
{
if (head == NULL || node == NULL) {
printf("insert node failed ! \n");
return;
}
node->next = head->next;
head->next = node;
}
/*
*fun : 查找指定的节点是否存在
*head :头结点指针
*node : 待查找节点指针
*ret : 查找成功失败的标志,0 成功,-1 失败
*return : 删除节点的前一个节点指针
*/
struct list *list_find_node(struct list *head, struct list *node, int *ret)
{
struct list *tmp;
if (head == NULL || node == NULL) {
printf("find node failed ! \n");
*ret = -1;
return NULL;
}
while (head->next) {
tmp = head->next;
if ((tmp->age == node->age) && (strcmp(tmp->name, node->name) == 0)){
return head;
}
head = head->next;
}
*ret = -1;
return NULL;
}
/*
*fun : 删除指定节点
*head :头结点指针
*node : 待删除节点指针
*return : 0 成功,-1 失败
*/
int list_del_node(struct list *head, struct list *node)
{
int ret;
struct list *pre_del_node;
struct list *tmp;
if (head == NULL || node == NULL) {
printf("del node failed ! \n");
return -1;
}
ret = 0;
pre_del_node = head->find_node(head, node ,&ret);
if (ret == -1) {
return ret;
}
tmp = pre_del_node->next;
pre_del_node->next = tmp->next;
free(tmp);
return 0;
}
/*
*fun : 显示链表内容
*head :头结点指针
*/
void print_list(struct list *head)
{
struct list *tmp;
tmp = head->next;
while (tmp) {
printf("name = %s, age = %d \n", tmp->name, tmp->age);
tmp = tmp->next;
}
}
/*
*fun : 删除成个链表
*head :头结点指针
*/
void destroy_list(struct list *head)
{
struct list *tmp;
struct list *assit;
assit = head->next;
while (assit) {
tmp = assit;
assit = assit->next;
free(tmp);
}
free(head); /* 释放头节点指针 */
}
void init_head(struct list *head)
{
head->next = NULL;
head->insert = list_insert_node;
head->delete = list_del_node;
head->find_node = list_find_node;
head->print_list = print_list;
head->destroy_list = destroy_list;
}
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
int i;
struct list *head, *tmp;
head = (struct list *)malloc(sizeof(struct list));
if (head == NULL) {
printf("no memory \n");
exit(-1);
}
init_head(head);
i = 0;
while (person[i].age) {
tmp = (struct list *)malloc(sizeof(struct list));
if (tmp == NULL) {
/*此处应该释放掉已经分配的内存,防止内存泄漏,偷懒没有写*/
printf("no memory \n");
exit(-1);
}
strcpy(tmp->name, person[i].name);
tmp->age = person[i].age;
tmp->next = NULL;
head->insert(head, tmp);
i++;
}
head->print_list(head);
head->delete(head, tmp);
printf("删除最后插入的节点之后 \n");
head->print_list(head);
return 0;
}说明:次例子仅作练习用,真正用到项目中可以找一些开源的,简洁高效的链表代码,例如我们公司项目中的链表就是修改的LINUX内核链表来用的,没有必要重复造轮子,但作为练习还是要敲一下。
亿速云「云服务器」,即开即用、新一代英特尔至强铂金CPU、三副本存储NVMe SSD云盘,价格低至29元/月。点击查看>>
免责声明:本站发布的内容(图片、视频和文字)以原创、转载和分享为主,文章观点不代表本网站立场,如果涉及侵权请联系站长邮箱:is@yisu.com进行举报,并提供相关证据,一经查实,将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容。