如下所示:
import numpy as np
from torchvision.transforms import Compose, ToTensor
from torch import nn
import torch.nn.init as init
def transform():
return Compose([
ToTensor(),
# Normalize((12,12,12),std = (1,1,1)),
])
arr = range(1,26)
arr = np.reshape(arr,[5,5])
arr = np.expand_dims(arr,2)
arr = arr.astype(np.float32)
# arr = arr.repeat(3,2)
print(arr.shape)
arr = transform()(arr)
arr = arr.unsqueeze(0)
print(arr)
conv1 = nn.Conv2d(1, 1, 3, stride=1, bias=False, dilation=1) # 普通卷积
conv2 = nn.Conv2d(1, 1, 3, stride=1, bias=False, dilation=2) # dilation就是空洞率,即间隔
init.constant_(conv1.weight, 1)
init.constant_(conv2.weight, 1)
out1 = conv1(arr)
out2 = conv2(arr)
print('standare conv:\n', out1.detach().numpy())
print('dilated conv:\n', out2.detach().numpy())
输出:
(5, 5, 1)
tensor([[[[ 1., 2., 3., 4., 5.],
[ 6., 7., 8., 9., 10.],
[11., 12., 13., 14., 15.],
[16., 17., 18., 19., 20.],
[21., 22., 23., 24., 25.]]]])
standare conv:
[[[[ 63. 72. 81.]
[108. 117. 126.]
[153. 162. 171.]]]]
dilated conv:
[[[[117.]]]]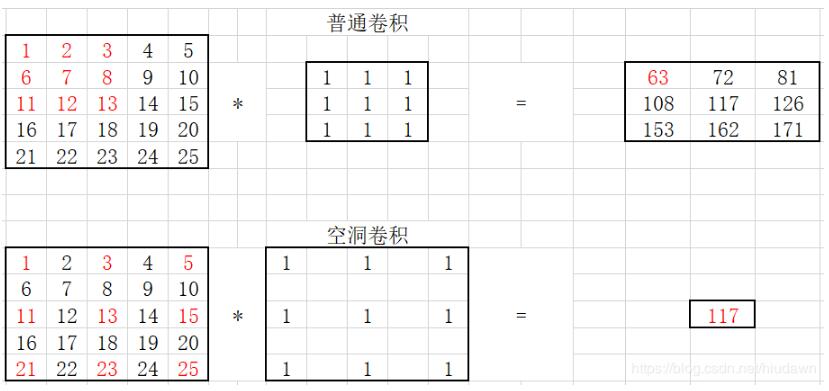
以上这篇PyTorch 普通卷积和空洞卷积实例就是小编分享给大家的全部内容了,希望能给大家一个参考,也希望大家多多支持亿速云。
亿速云「云服务器」,即开即用、新一代英特尔至强铂金CPU、三副本存储NVMe SSD云盘,价格低至29元/月。点击查看>>
免责声明:本站发布的内容(图片、视频和文字)以原创、转载和分享为主,文章观点不代表本网站立场,如果涉及侵权请联系站长邮箱:is@yisu.com进行举报,并提供相关证据,一经查实,将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容。