这篇文章将为大家详细讲解有关Spring Cloud Ribbon原理的示例分析,小编觉得挺实用的,因此分享给大家做个参考,希望大家阅读完这篇文章后可以有所收获。
简介
Spring Cloud Ribbon 是一个基于Http和TCP的客服端负载均衡工具,它是基于Netflix Ribbon实现的。它不像服务注册中心、配置中心、API网关那样独立部署,但是它几乎存在于每个微服务的基础设施中。包括前面的提供的声明式服务调用也是基于该Ribbon实现的。理解Ribbon对于我们使用Spring Cloud来讲非常的重要,因为负载均衡是对系统的高可用、网络压力的缓解和处理能力扩容的重要手段之一。在上节的例子中,我们采用了声明式的方式来实现负载均衡。实际上,内部调用维护了一个RestTemplate对象,该对象会使用Ribbon的自动化配置,同时通过@LoadBalanced开启客户端负载均衡。其实RestTemplate是Spring自己提供的对象,不是新的内容。读者不知道RestTemplate可以查看相关的文档。
现象
前两天碰到一个ribbon相关的问题,觉得值得记录一下。表象是对外的接口返回内部异常,这个是封装的统
一错误信息,Spring的异常处理器catch到未捕获异常统一返回的信息。因此到日志平台查看实际的异常:
org.springframework.web.client.HttpClientErrorException: 404 null
这里介绍一下背景,出现问题的开放网关,做点事情说白了就是转发对应的请求给后端的服务。这里用到了ribbon去做服务负载均衡、eureka负责服务发现。
这里出现404,首先看了下请求的url以及对应的参数,都没有发现问题,对应的后端服务也没有收到请求。这就比较诡异了,开始怀疑是ribbon或者Eureka的缓存导致请求到了错误的ip或端口,但由于日志中打印的是Eureka的serviceId而不是实际的ip:port,因此先加了个日志:
@Slf4j
public class CustomHttpRequestInterceptor implements ClientHttpRequestInterceptor {
@Override
public ClientHttpResponse intercept(HttpRequest request, byte[] body, ClientHttpRequestExecution execution) throws IOException {
log.info("Request , url:{},method:{}.", request.getURI(), request.getMethod());
return execution.execute(request, body);
}
}这里是通过给RestTemplate添加拦截器的方式,但要注意,ribbon也是通过给RestTemplate添加拦截器实现的解析serviceId到实际的ip:port,因此需要注意下优先级添加到ribbon的 LoadBalancerInterceptor 之后,我这里是通过Spring的初始化完成事件的回调中添加的,另外也添加了另一条日志,在catch到这个异常的时候,利用Eureka的 DiscoveryClient#getInstances 获取到当前的实例信息。
之后在测试环境中复现了这个问题,看了下日志,eurek中缓存的实例信息是对的,但是实际调用的确实另外一个服务的地址,从而导致了接口404。
源码解析
从上述的信息中可以知道,问题出在ribbon中,具体的原因后面会说,这里先讲一下Spring Cloud Ribbon的初始化流程。
@Configuration
@ConditionalOnClass({ IClient.class, RestTemplate.class, AsyncRestTemplate.class, Ribbon.class})
@RibbonClients
@AutoConfigureAfter(name = "org.springframework.cloud.netflix.eureka.EurekaClientAutoConfiguration")
@AutoConfigureBefore({LoadBalancerAutoConfiguration.class, AsyncLoadBalancerAutoConfiguration.class})
@EnableConfigurationProperties({RibbonEagerLoadProperties.class, ServerIntrospectorProperties.class})
public class RibbonAutoConfiguration {
}注意这个注解 @RibbonClients , 如果想要覆盖Spring Cloud提供的默认Ribbon配置就可以使用这个注解,最终的解析类是:
public class RibbonClientConfigurationRegistrar implements ImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar {
@Override
public void registerBeanDefinitions(AnnotationMetadata metadata,
BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) {
Map<String, Object> attrs = metadata.getAnnotationAttributes(
RibbonClients.class.getName(), true);
if (attrs != null && attrs.containsKey("value")) {
AnnotationAttributes[] clients = (AnnotationAttributes[]) attrs.get("value");
for (AnnotationAttributes client : clients) {
registerClientConfiguration(registry, getClientName(client),
client.get("configuration"));
}
}
if (attrs != null && attrs.containsKey("defaultConfiguration")) {
String name;
if (metadata.hasEnclosingClass()) {
name = "default." + metadata.getEnclosingClassName();
} else {
name = "default." + metadata.getClassName();
}
registerClientConfiguration(registry, name,
attrs.get("defaultConfiguration"));
}
Map<String, Object> client = metadata.getAnnotationAttributes(
RibbonClient.class.getName(), true);
String name = getClientName(client);
if (name != null) {
registerClientConfiguration(registry, name, client.get("configuration"));
}
}
private String getClientName(Map<String, Object> client) {
if (client == null) {
return null;
}
String value = (String) client.get("value");
if (!StringUtils.hasText(value)) {
value = (String) client.get("name");
}
if (StringUtils.hasText(value)) {
return value;
}
throw new IllegalStateException(
"Either 'name' or 'value' must be provided in @RibbonClient");
}
private void registerClientConfiguration(BeanDefinitionRegistry registry,
Object name, Object configuration) {
BeanDefinitionBuilder builder = BeanDefinitionBuilder
.genericBeanDefinition(RibbonClientSpecification.class);
builder.addConstructorArgValue(name);
builder.addConstructorArgValue(configuration);
registry.registerBeanDefinition(name + ".RibbonClientSpecification",
builder.getBeanDefinition());
}
}atrrs包含defaultConfiguration,因此会注册RibbonClientSpecification类型的bean,注意名称以 default. 开头,类型是RibbonAutoConfiguration,注意上面说的RibbonAutoConfiguration被@RibbonClients修饰。
然后再回到上面的源码:
public class RibbonAutoConfiguration {
//上文中会解析被@RibbonClients注解修饰的类,然后注册类型为RibbonClientSpecification的bean。
//主要有两个: RibbonAutoConfiguration、RibbonEurekaAutoConfiguration
@Autowired(required = false)
private List<RibbonClientSpecification> configurations = new ArrayList<>();
@Bean
public SpringClientFactory springClientFactory() {
//初始化SpringClientFactory,并将上面的配置注入进去,这段很重要。
SpringClientFactory factory = new SpringClientFactory();
factory.setConfigurations(this.configurations);
return factory;
}
//其他的都是提供一些默认的bean配置
@Bean
@ConditionalOnMissingBean(LoadBalancerClient.class)
public LoadBalancerClient loadBalancerClient() {
return new RibbonLoadBalancerClient(springClientFactory());
}
@Bean
@ConditionalOnClass(name = "org.springframework.retry.support.RetryTemplate")
@ConditionalOnMissingBean
public LoadBalancedRetryPolicyFactory loadBalancedRetryPolicyFactory(SpringClientFactory clientFactory) {
return new RibbonLoadBalancedRetryPolicyFactory(clientFactory);
}
@Bean
@ConditionalOnMissingClass(value = "org.springframework.retry.support.RetryTemplate")
@ConditionalOnMissingBean
public LoadBalancedRetryPolicyFactory neverRetryPolicyFactory() {
return new LoadBalancedRetryPolicyFactory.NeverRetryFactory();
}
@Bean
@ConditionalOnClass(name = "org.springframework.retry.support.RetryTemplate")
@ConditionalOnMissingBean
public LoadBalancedBackOffPolicyFactory loadBalancedBackoffPolicyFactory() {
return new LoadBalancedBackOffPolicyFactory.NoBackOffPolicyFactory();
}
@Bean
@ConditionalOnClass(name = "org.springframework.retry.support.RetryTemplate")
@ConditionalOnMissingBean
public LoadBalancedRetryListenerFactory loadBalancedRetryListenerFactory() {
return new LoadBalancedRetryListenerFactory.DefaultRetryListenerFactory();
}
@Bean
@ConditionalOnMissingBean
public PropertiesFactory propertiesFactory() {
return new PropertiesFactory();
}
@Bean
@ConditionalOnProperty(value = "ribbon.eager-load.enabled", matchIfMissing = false)
public RibbonApplicationContextInitializer ribbonApplicationContextInitializer() {
return new RibbonApplicationContextInitializer(springClientFactory(),
ribbonEagerLoadProperties.getClients());
}
@Configuration
@ConditionalOnClass(HttpRequest.class)
@ConditionalOnRibbonRestClient
protected static class RibbonClientConfig {
@Autowired
private SpringClientFactory springClientFactory;
@Bean
public RestTemplateCustomizer restTemplateCustomizer(
final RibbonClientHttpRequestFactory ribbonClientHttpRequestFactory) {
return new RestTemplateCustomizer() {
@Override
public void customize(RestTemplate restTemplate) {
restTemplate.setRequestFactory(ribbonClientHttpRequestFactory);
}
};
}
@Bean
public RibbonClientHttpRequestFactory ribbonClientHttpRequestFactory() {
return new RibbonClientHttpRequestFactory(this.springClientFactory);
}
}
//TODO: support for autoconfiguring restemplate to use apache http client or okhttp
@Target({ ElementType.TYPE, ElementType.METHOD })
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@Conditional(OnRibbonRestClientCondition.class)
@interface ConditionalOnRibbonRestClient { }
private static class OnRibbonRestClientCondition extends AnyNestedCondition {
public OnRibbonRestClientCondition() {
super(ConfigurationPhase.REGISTER_BEAN);
}
@Deprecated //remove in Edgware"
@ConditionalOnProperty("ribbon.http.client.enabled")
static class ZuulProperty {}
@ConditionalOnProperty("ribbon.restclient.enabled")
static class RibbonProperty {}
}
}注意这里的SpringClientFactory, ribbon默认情况下,每个eureka的serviceId(服务),都会分配自己独立的Spring的上下文,即ApplicationContext, 然后这个上下文中包含了必要的一些bean,比如: ILoadBalancer 、 ServerListFilter 等。而Spring Cloud默认是使用RestTemplate封装了ribbon的调用,核心是通过一个拦截器:
@Bean
@ConditionalOnMissingBean
public RestTemplateCustomizer restTemplateCustomizer(
final LoadBalancerInterceptor loadBalancerInterceptor) {
return new RestTemplateCustomizer() {
@Override
public void customize(RestTemplate restTemplate) {
List<ClientHttpRequestInterceptor> list = new ArrayList<>(
restTemplate.getInterceptors());
list.add(loadBalancerInterceptor);
restTemplate.setInterceptors(list);
}
};
}因此核心是通过这个拦截器实现的负载均衡:
public class LoadBalancerInterceptor implements ClientHttpRequestInterceptor {
private LoadBalancerClient loadBalancer;
private LoadBalancerRequestFactory requestFactory;
@Override
public ClientHttpResponse intercept(final HttpRequest request, final byte[] body,
final ClientHttpRequestExecution execution) throws IOException {
final URI originalUri = request.getURI(); //这里传入的url是解析之前的,即http://serviceId/服务地址的形式
String serviceName = originalUri.getHost(); //解析拿到对应的serviceId
Assert.state(serviceName != null, "Request URI does not contain a valid hostname: " + originalUri);
return this.loadBalancer.execute(serviceName, requestFactory.createRequest(request, body, execution));
}
}然后将请求转发给LoadBalancerClient:
public class RibbonLoadBalancerClient implements LoadBalancerClient {
@Override
public <T> T execute(String serviceId, LoadBalancerRequest<T> request) throws IOException {
ILoadBalancer loadBalancer = getLoadBalancer(serviceId); //获取对应的LoadBalancer
Server server = getServer(loadBalancer); //获取服务器,这里会执行对应的分流策略,比如轮训
//、随机等
if (server == null) {
throw new IllegalStateException("No instances available for " + serviceId);
}
RibbonServer ribbonServer = new RibbonServer(serviceId, server, isSecure(server,
serviceId), serverIntrospector(serviceId).getMetadata(server));
return execute(serviceId, ribbonServer, request);
}
}而这里的LoadBalancer是通过上文中提到的SpringClientFactory获取到的,这里会初始化一个新的Spring上下文,然后将Ribbon默认的配置类,比如说: RibbonAutoConfiguration 、 RibbonEurekaAutoConfiguration 等添加进去, 然后将当前spring的上下文设置为parent,再调用refresh方法进行初始化。
public class SpringClientFactory extends NamedContextFactory<RibbonClientSpecification> {
protected AnnotationConfigApplicationContext createContext(String name) {
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext();
if (this.configurations.containsKey(name)) {
for (Class<?> configuration : this.configurations.get(name)
.getConfiguration()) {
context.register(configuration);
}
}
for (Map.Entry<String, C> entry : this.configurations.entrySet()) {
if (entry.getKey().startsWith("default.")) {
for (Class<?> configuration : entry.getValue().getConfiguration()) {
context.register(configuration);
}
}
}
context.register(PropertyPlaceholderAutoConfiguration.class,
this.defaultConfigType);
context.getEnvironment().getPropertySources().addFirst(new MapPropertySource(
this.propertySourceName,
Collections.<String, Object> singletonMap(this.propertyName, name)));
if (this.parent != null) {
// Uses Environment from parent as well as beans
context.setParent(this.parent);
}
context.refresh();
return context;
}
}最核心的就在这一段,也就是说对于每一个不同的serviceId来说,都拥有一个独立的spring上下文,并且在第一次调用这个服务的时候,会初始化ribbon相关的所有bean, 如果不存在 才回去父context中去找。
再回到上文中根据分流策略获取实际的ip:port的代码段:
public class RibbonLoadBalancerClient implements LoadBalancerClient {
@Override
public <T> T execute(String serviceId, LoadBalancerRequest<T> request) throws IOException {
ILoadBalancer loadBalancer = getLoadBalancer(serviceId); //获取对应的LoadBalancer
Server server = getServer(loadBalancer); //获取服务器,这里会执行对应的分流策略,比如轮训
//、随机等
if (server == null) {
throw new IllegalStateException("No instances available for " + serviceId);
}
RibbonServer ribbonServer = new RibbonServer(serviceId, server, isSecure(server,
serviceId), serverIntrospector(serviceId).getMetadata(server));
return execute(serviceId, ribbonServer, request);
}
} protected Server getServer(ILoadBalancer loadBalancer) {
if (loadBalancer == null) {
return null;
}
// 选择对应的服务器
return loadBalancer.chooseServer("default"); // TODO: better handling of key
}
public class ZoneAwareLoadBalancer<T extends Server> extends DynamicServerListLoadBalancer<T> {
@Override
public Server chooseServer(Object key) {
if (!ENABLED.get() || getLoadBalancerStats().getAvailableZones().size() <= 1) {
logger.debug("Zone aware logic disabled or there is only one zone");
return super.chooseServer(key); //默认不配置可用区,走的是这段
}
Server server = null;
try {
LoadBalancerStats lbStats = getLoadBalancerStats();
Map<String, ZoneSnapshot> zoneSnapshot = ZoneAvoidanceRule.createSnapshot(lbStats);
logger.debug("Zone snapshots: {}", zoneSnapshot);
if (triggeringLoad == null) {
triggeringLoad = DynamicPropertyFactory.getInstance().getDoubleProperty(
"ZoneAwareNIWSDiscoveryLoadBalancer." + this.getName() + ".triggeringLoadPerServerThreshold", 0.2d);
}
if (triggeringBlackoutPercentage == null) {
triggeringBlackoutPercentage = DynamicPropertyFactory.getInstance().getDoubleProperty(
"ZoneAwareNIWSDiscoveryLoadBalancer." + this.getName() + ".avoidZoneWithBlackoutPercetage", 0.99999d);
}
Set<String> availableZones = ZoneAvoidanceRule.getAvailableZones(zoneSnapshot, triggeringLoad.get(), triggeringBlackoutPercentage.get());
logger.debug("Available zones: {}", availableZones);
if (availableZones != null && availableZones.size() < zoneSnapshot.keySet().size()) {
String zone = ZoneAvoidanceRule.randomChooseZone(zoneSnapshot, availableZones);
logger.debug("Zone chosen: {}", zone);
if (zone != null) {
BaseLoadBalancer zoneLoadBalancer = getLoadBalancer(zone);
server = zoneLoadBalancer.chooseServer(key);
}
}
} catch (Exception e) {
logger.error("Error choosing server using zone aware logic for load balancer={}", name, e);
}
if (server != null) {
return server;
} else {
logger.debug("Zone avoidance logic is not invoked.");
return super.chooseServer(key);
}
}
//实际走到的方法
public Server chooseServer(Object key) {
if (counter == null) {
counter = createCounter();
}
counter.increment();
if (rule == null) {
return null;
} else {
try {
return rule.choose(key);
} catch (Exception e) {
logger.warn("LoadBalancer [{}]: Error choosing server for key {}", name, key, e);
return null;
}
}
}
}也就是说最终会调用 IRule 选择到一个节点,这里支持很多策略,比如随机、轮训、响应时间权重等:
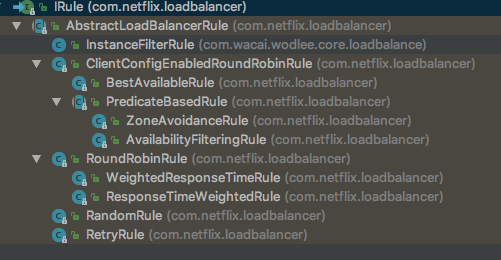
public interface IRule{
public Server choose(Object key);
public void setLoadBalancer(ILoadBalancer lb);
public ILoadBalancer getLoadBalancer();
}这里的LoadBalancer是在BaseLoadBalancer的构造器中设置的,上文说过,对于每一个serviceId服务来说,当第一次调用的时候会初始化对应的spring上下文,而这个上下文中包含了所有ribbon相关的bean,其中就包括ILoadBalancer、IRule。
原因
通过跟踪堆栈,发现不同的serviceId,IRule是同一个, 而上文说过,每个serviceId都拥有自己独立的上下文,包括独立的loadBalancer、IRule,而IRule是同一个,因此怀疑是这个bean是通过parent context获取到的,换句话说应用自己定义了一个这样的bean。查看代码果然如此。
这样就会导致一个问题,IRule是共享的,而其他bean是隔离开的,因此后面的serviceId初始化的时候,会修改这个IRule的LoadBalancer, 导致之前的服务获取到的实例信息是错误的,从而导致接口404。
public class BaseLoadBalancer extends AbstractLoadBalancer implements
PrimeConnections.PrimeConnectionListener, IClientConfigAware {
public BaseLoadBalancer() {
this.name = DEFAULT_NAME;
this.ping = null;
setRule(DEFAULT_RULE); // 这里会设置IRule的loadbalancer
setupPingTask();
lbStats = new LoadBalancerStats(DEFAULT_NAME);
}
}
解决方案
解决方法也很简单,最简单就将这个自定义的IRule的bean干掉,另外更标准的做法是使用RibbonClients注解,具体做法可以参考文档。
关于“Spring Cloud Ribbon原理的示例分析”这篇文章就分享到这里了,希望以上内容可以对大家有一定的帮助,使各位可以学到更多知识,如果觉得文章不错,请把它分享出去让更多的人看到。
亿速云「云服务器」,即开即用、新一代英特尔至强铂金CPU、三副本存储NVMe SSD云盘,价格低至29元/月。点击查看>>
免责声明:本站发布的内容(图片、视频和文字)以原创、转载和分享为主,文章观点不代表本网站立场,如果涉及侵权请联系站长邮箱:is@yisu.com进行举报,并提供相关证据,一经查实,将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容。