这篇文章主要讲解了IO中如何使用flush()函数,内容清晰明了,对此有兴趣的小伙伴可以学习一下,相信大家阅读完之后会有帮助。
The java.io.Writer.flush() method flushes the stream. If the stream has saved any characters from the various write() methods in a buffer, write them immediately to their intended destination. Then, if that destination is another character or byte stream, flush it. Thus one flush() invocation will flush all the buffers in a chain of Writers and OutputStreams.
public class Demo {
public static void main(String[] ars) throws Exception {
System.out.println("hello");
PrintWriter writer = new PrintWriter(System.out);
writer.println("writer start");
// writer.flush();
try {
Thread.sleep(3000);
}
catch (InterruptedException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
writer.println("writer close");
writer.close();
}
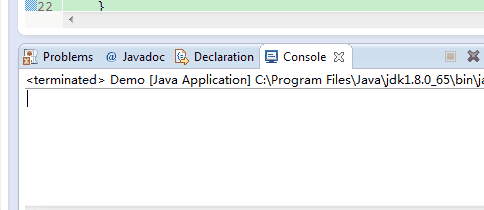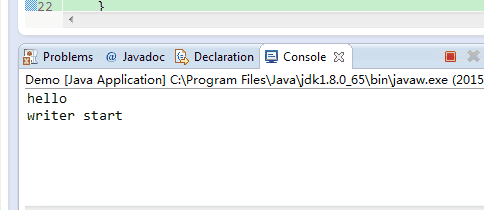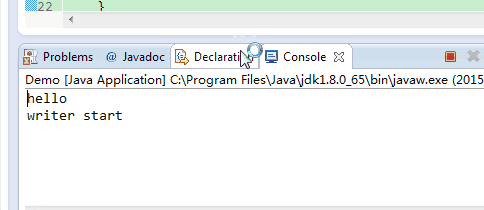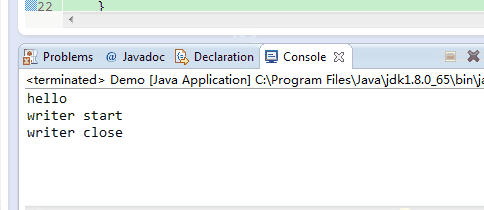
}如上面代码,如果flush()被注释掉,则打印完“hello”之后3秒才会打印”writer start”,”writer close”,因为writer.close()在关闭输出流前会调用一次flush()。效果如下:
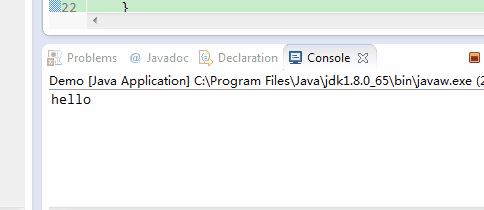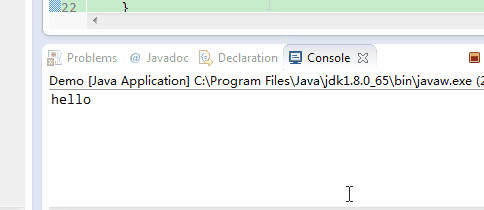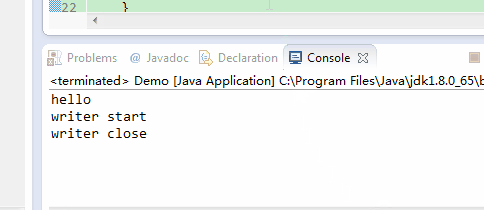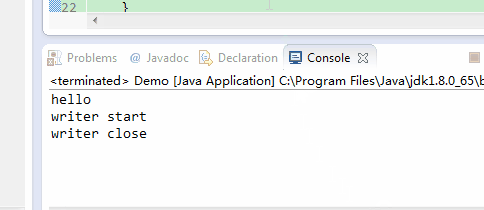
如果flush()没有被注释掉,则则打印完“hello”之后会立即打印”writer start”。
看完上述内容,是不是对IO中如何使用flush()函数有进一步的了解,如果还想学习更多内容,欢迎关注亿速云行业资讯频道。
亿速云「云服务器」,即开即用、新一代英特尔至强铂金CPU、三副本存储NVMe SSD云盘,价格低至29元/月。点击查看>>
免责声明:本站发布的内容(图片、视频和文字)以原创、转载和分享为主,文章观点不代表本网站立场,如果涉及侵权请联系站长邮箱:is@yisu.com进行举报,并提供相关证据,一经查实,将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容。