这篇文章主要讲解了“Spring bean生命周期知识点讲解”,文中的讲解内容简单清晰,易于学习与理解,下面请大家跟着小编的思路慢慢深入,一起来研究和学习“Spring bean生命周期知识点讲解”吧!
前言
任何一个事物都有自己的生命周期,生命的开始、生命中、生命结束。大家最熟悉的应该是servlet 的生命周期吧。和 servlet 一样 spring bean 也有自己的生命周期。
在开发中生命周期是一个很常见的名词,基本每种编程语言都能找到与它关联的。关于bean的生命周期我在网上也找了好多,基本都差不多。这里我主要是想通过代码来验证,毕竟学的知识都是一样的,都是学的Java,最重要的是动手练习,这样印象更深。
下面是它生命周期的描述,我们通过demo来进行验证。
下图是它执行的顺序。
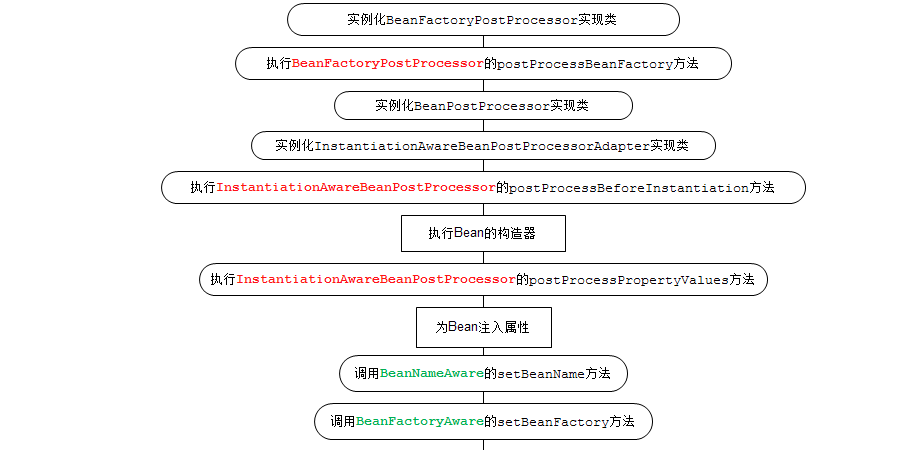

一、创建LiftCycle类实现BeanFactoryAware,BeanNameAware,InitializingBean,DisposableBean,ApplicationContextAware5个接口方法
package Cuiyw.Spring.Service;
import org.springframework.beans.BeansException;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanFactory;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanFactoryAware;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanNameAware;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.DisposableBean;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.InitializingBean;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContextAware;
public class LifeCycle implements BeanFactoryAware,BeanNameAware,InitializingBean,DisposableBean,ApplicationContextAware{
private String name;
public String getName() {
System.out.println("getName name="+name);
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
System.out.println("setName name="+name);
this.name = name;
}
public void afterPropertiesSet() throws Exception {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
System.out.println("InitializingBean.afterPropertiesSet()");
}
public void setBeanName(String arg0) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
System.out.println("BeanNameAware.setBeanName");
}
public void setBeanFactory(BeanFactory arg0) throws BeansException {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
System.out.println("BeanFactoryAware.setBeanFactory");
}
public void destroy() throws Exception {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
System.out.println("DisposableBean.destroy");
}
public void myInit() {
System.out.println("【init-method】调用<bean>的init-method属性指定的初始化方法");
}
public void myDestory() {
System.out.println("【destroy-method】调用<bean>的destroy-method属性指定的初始化方法");
}
public void setApplicationContext(ApplicationContext arg0) throws BeansException {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
System.out.println("ApplicationContextAware.setApplicationContext");
}
}二、注册InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor接口
package Cuiyw.Spring.Service;
import java.beans.PropertyDescriptor;
import org.springframework.beans.BeansException;
import org.springframework.beans.PropertyValues;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.config.InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor;
public class MyInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor implements InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor{
public Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
System.out.println("InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor.postProcessAfterInitialization");
return bean;
}
public Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
System.out.println("InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor.postProcessBeforeInitialization");
return bean;
}
public boolean postProcessAfterInstantiation(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
System.out.println("InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor.postProcessAfterInstantiation");
return true;
}
public Object postProcessBeforeInstantiation(Class<?> beanClass, String beanName) throws BeansException {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
System.out.println("InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor.postProcessBeforeInstantiation");
return null;
}
public PropertyValues postProcessPropertyValues(PropertyValues pvs, PropertyDescriptor[] pds, Object bean,
String beanName) throws BeansException {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
System.out.println("InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor.postProcessPropertyValues");
return pvs;
}
}三、注册BeanPostProcessor接口
其实InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor继承BeanPostProcessor,所以在上面我也实现了BeanPostProcessor接口的方法
package Cuiyw.Spring.Service;
import org.springframework.beans.BeansException;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.config.BeanPostProcessor;
public class MyBeanPostProcessor implements BeanPostProcessor {
public Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
System.out.println("BeanPostProcessor.postProcessAfterInitialization ");
return bean;
}
public Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
System.out.println("BeanPostProcessor.postProcessBeforeInitialization");
return bean;
}
}四、注册BeanFactoryPostProcessor接口
package Cuiyw.Spring.Service;
import org.springframework.beans.BeansException;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.config.BeanFactoryPostProcessor;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.config.ConfigurableListableBeanFactory;
public class MyBeanFactoryPostProcessor implements BeanFactoryPostProcessor {
public void postProcessBeanFactory(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory arg0) throws BeansException {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
System.out.println("BeanFactoryPostProcessor.postProcessBeanFactory");
}
}五、在上下文中配置
这里还是在上一个博客demo的基础上进行修改,为了有其他干扰,我先把service去掉了。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean id="beanPostProcessor" class="Cuiyw.Spring.Service.MyBeanPostProcessor"></bean>
<bean id="instantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor" class="Cuiyw.Spring.Service.MyInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor"></bean>
<bean id="beanFactoryPostProcessor" class="Cuiyw.Spring.Service.MyBeanFactoryPostProcessor"></bean>
<bean id="lifeCycle" class="Cuiyw.Spring.Service.LifeCycle" init-method="myInit" destroy-method="myDestory">
<property name="name" value="cuiyw1"></property>
</bean>
</beans>六、在main中使用bean
package Cuiyw.SpringAop;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanFactory;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
import Cuiyw.Spring.IService.IService;
import Cuiyw.Spring.Service.LifeCycle;
public class App
{
public static void main( String[] args )
{
ApplicationContext context=new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(new String[]{"ApplicationContext.xml"});
BeanFactory factory=context;
LifeCycle lifeCycle=factory.getBean("lifeCycle",LifeCycle.class);
lifeCycle.setName("cuiyw2");
System.out.println("lifeCycle.name="+lifeCycle.getName());
((ClassPathXmlApplicationContext)factory).registerShutdownHook();
/*service=(IService)factory.getBean("ServiceA");
service.service("Cuiyw ServiceA");
service=(IService)factory.getBean("ServiceImpl");
service.service("Cuiyw ServiceImpl"); */
}
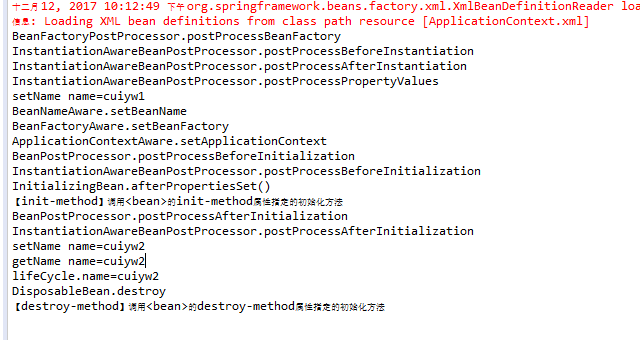
}七、输入打印结果
可以发现输出的顺序和上面图的顺序基本一致。
感谢各位的阅读,以上就是“Spring bean生命周期知识点讲解”的内容了,经过本文的学习后,相信大家对Spring bean生命周期知识点讲解这一问题有了更深刻的体会,具体使用情况还需要大家实践验证。这里是亿速云,小编将为大家推送更多相关知识点的文章,欢迎关注!
亿速云「云服务器」,即开即用、新一代英特尔至强铂金CPU、三副本存储NVMe SSD云盘,价格低至29元/月。点击查看>>
免责声明:本站发布的内容(图片、视频和文字)以原创、转载和分享为主,文章观点不代表本网站立场,如果涉及侵权请联系站长邮箱:is@yisu.com进行举报,并提供相关证据,一经查实,将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容。