Android开发中怎么实现一个底部菜单栏?针对这个问题,这篇文章详细介绍了相对应的分析和解答,希望可以帮助更多想解决这个问题的小伙伴找到更简单易行的方法。
在Android中实现菜单功能有多种方法。
Options Menu:用户按下menu Button时显示的菜单。
Context Menu:用户长时间按下屏幕,所显示出来的菜单也称为上下文菜单。
Submenu:子菜单。
但是有时候这些内置的菜单并不能满足我们功能,这就需要自己自定义一种菜单。接下来我说的这种就是通过TabHost与RadioGroup结合完成的菜单。这也是很常用的一种底部菜单做法。先上图:
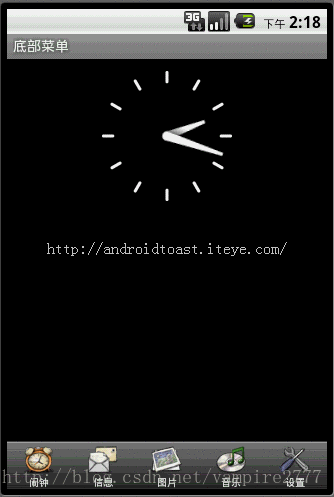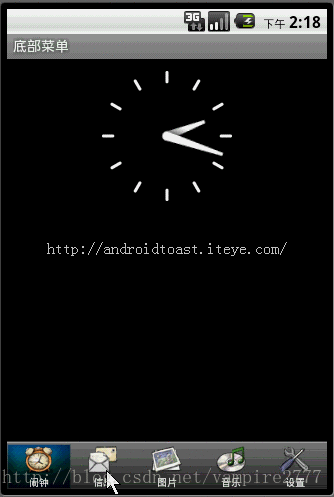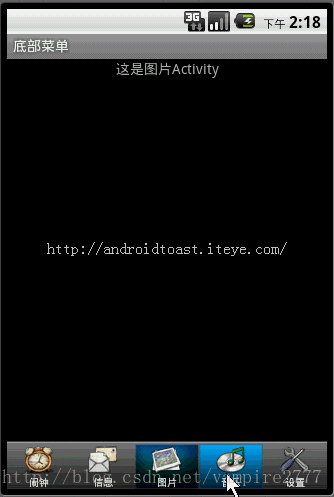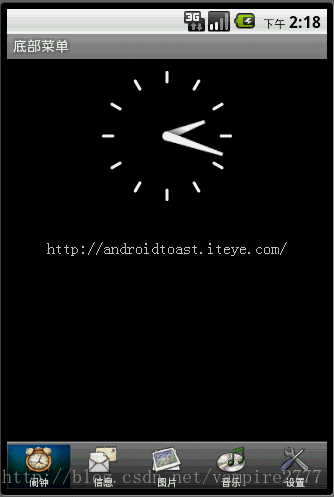
Xml代码
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<TabHost android:id="@android:id/tabhost" android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="fill_parent"
xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android">
<LinearLayout
android:orientation="vertical"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="fill_parent">
<FrameLayout
android:id="@android:id/tabcontent"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="0.0dip"
android:layout_weight="1.0" />
<TabWidget
android:id="@android:id/tabs"
android:visibility="gone"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_weight="0.0" />
<RadioGroup
android:gravity="center_vertical"
android:layout_gravity="bottom"
android:orientation="horizontal"
android:id="@+id/main_radio"
android:background="@drawable/maintab_toolbar_bg"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content">
<RadioButton
android:id="@+id/radio_button0"
android:tag="radio_button0"
android:layout_marginTop="2.0dip"
android:text="@string/alarm"
android:drawableTop="@drawable/icon_1"
/>
<RadioButton
android:id="@+id/radio_button1"
android:tag="radio_button1"
android:layout_marginTop="2.0dip"
android:text="@string/message"
android:drawableTop="@drawable/icon_2"
/>
<RadioButton
android:id="@+id/radio_button2"
android:tag="radio_button2"
android:layout_marginTop="2.0dip"
android:text="@string/photo"
android:drawableTop="@drawable/icon_3"
/>
<RadioButton
android:id="@+id/radio_button3"
android:tag="radio_button3"
android:layout_marginTop="2.0dip"
android:text="@string/music"
android:drawableTop="@drawable/icon_4"
/>
<RadioButton
android:id="@+id/radio_button4"
android:tag="radio_button4"
android:layout_marginTop="2.0dip"
android:text="@string/setting"
android:drawableTop="@drawable/icon_5"
/>
</RadioGroup>
</LinearLayout>
</TabHost> 需要注意的是,如果用TabHost这个控件,其中有几个ID是必须这么写的,android:id=”@android:id/tabhost ;android:id=”@android:id/tabcontent” ;android:id=”@android:id/tabs” ;之所以要这么写是因为在TabHost这个类中。需要实例化上述这个ID的控件。看源码:
在TabActivity中有么个方法:
@Override
public void onContentChanged() {
super.onContentChanged();
mTabHost = (TabHost) findViewById(com.android.internal.R.id.tabhost);
if (mTabHost == null) {
throw new RuntimeException(
"Your content must have a TabHost whose id attribute is " +
"'android.R.id.tabhost'");
}
mTabHost.setup(getLocalActivityManager());
}
private void ensureTabHost() {
if (mTabHost == null) {
this.setContentView(com.android.internal.R.layout.tab_content);
}
}
当内容发生改变时它会调用这个方法,来更新列表或者其他视图,而这个方法中需要实例化TabHost,所以必须通过ID为tabhost实例化。
再看看TabHost这个类中
public void setup() {
mTabWidget = (TabWidget) findViewById(com.android.internal.R.id.tabs);
if (mTabWidget == null) {
throw new RuntimeException(
"Your TabHost must have a TabWidget whose id attribute is 'android.R.id.tabs'");
}
// KeyListener to attach to all tabs. Detects non-navigation keys
// and relays them to the tab content.
mTabKeyListener = new OnKeyListener() {
public boolean onKey(View v, int keyCode, KeyEvent event) {
switch (keyCode) {
case KeyEvent.KEYCODE_DPAD_CENTER:
case KeyEvent.KEYCODE_DPAD_LEFT:
case KeyEvent.KEYCODE_DPAD_RIGHT:
case KeyEvent.KEYCODE_DPAD_UP:
case KeyEvent.KEYCODE_DPAD_DOWN:
case KeyEvent.KEYCODE_ENTER:
return false;
}
mTabContent.requestFocus(View.FOCUS_FORWARD);
return mTabContent.dispatchKeyEvent(event);
}
};
mTabWidget.setTabSelectionListener(new TabWidget.OnTabSelectionChanged() {
public void onTabSelectionChanged(int tabIndex, boolean clicked) {
setCurrentTab(tabIndex);
if (clicked) {
mTabContent.requestFocus(View.FOCUS_FORWARD);
}
}
});
mTabContent = (FrameLayout) findViewById(com.android.internal.R.id.tabcontent);
if (mTabContent == null) {
throw new RuntimeException(
"Your TabHost must have a FrameLayout whose id attribute is "
+ "'android.R.id.tabcontent'");
}
}
这个方法,是在增加选项卡之前由系统调用。在这个方法中需要通过tabs 这个ID实例化一个TabWidget,通过tabcontent这个ID实例化一个FrameLayout,用来放置选项卡内容。所以这两个ID也是固定的。
在上述布局文件中隐藏了系统默认的Widget,取而代之的是带有图片的Button。
看一下主要代码:
package com.iteye.androidtoast;
import android.app.TabActivity;
import android.content.Intent;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.widget.RadioGroup;
import android.widget.RadioGroup.OnCheckedChangeListener;
import android.widget.TabHost;
public class MainActivity extends TabActivity implements OnCheckedChangeListener{
/** Called when the activity is first created. */
private TabHost mHost;
private RadioGroup radioderGroup;
@Override
public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.maintabs);
//实例化TabHost
mHost=this.getTabHost();
//添加选项卡
mHost.addTab(mHost.newTabSpec("ONE").setIndicator("ONE")
.setContent(new Intent(this,OneActivity.class)));
mHost.addTab(mHost.newTabSpec("TWO").setIndicator("TWO")
.setContent(new Intent(this,TwoActivity.class)));
mHost.addTab(mHost.newTabSpec("THREE").setIndicator("THREE")
.setContent(new Intent(this,ThreeActivity.class)));
mHost.addTab(mHost.newTabSpec("FOUR").setIndicator("FOUR")
.setContent(new Intent(this,FourActivity.class)));
mHost.addTab(mHost.newTabSpec("FIVE").setIndicator("FIVE")
.setContent(new Intent(this,FiveActivity.class)));
radioderGroup = (RadioGroup) findViewById(R.id.main_radio);
radioderGroup.setOnCheckedChangeListener(this);
}
@Override
public void onCheckedChanged(RadioGroup group, int checkedId) {
switch(checkedId){
case R.id.radio_button0:
mHost.setCurrentTabByTag("ONE");
break;
case R.id.radio_button1:
mHost.setCurrentTabByTag("TWO");
break;
case R.id.radio_button2:
mHost.setCurrentTabByTag("THREE");
break;
case R.id.radio_button3:
mHost.setCurrentTabByTag("FOUR");
break;
case R.id.radio_button4:
mHost.setCurrentTabByTag("FIVE");
break;
}
}
}
关于Android开发中怎么实现一个底部菜单栏问题的解答就分享到这里了,希望以上内容可以对大家有一定的帮助,如果你还有很多疑惑没有解开,可以关注亿速云行业资讯频道了解更多相关知识。
亿速云「云服务器」,即开即用、新一代英特尔至强铂金CPU、三副本存储NVMe SSD云盘,价格低至29元/月。点击查看>>
免责声明:本站发布的内容(图片、视频和文字)以原创、转载和分享为主,文章观点不代表本网站立场,如果涉及侵权请联系站长邮箱:is@yisu.com进行举报,并提供相关证据,一经查实,将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容。