жӮЁеҘҪпјҢзҷ»еҪ•еҗҺжүҚиғҪдёӢи®ўеҚ•е“ҰпјҒ
жӮЁеҘҪпјҢзҷ»еҪ•еҗҺжүҚиғҪдёӢи®ўеҚ•е“ҰпјҒ
жң¬зҜҮж–Үз« з»ҷеӨ§е®¶еҲҶдә«зҡ„жҳҜжңүе…ідҪҝз”ЁSpring AopеҰӮдҪ•й…ҚзҪ®xmlпјҢе°Ҹзј–и§үеҫ—жҢәе®һз”Ёзҡ„пјҢеӣ жӯӨеҲҶдә«з»ҷеӨ§е®¶еӯҰд№ пјҢеёҢжңӣеӨ§е®¶йҳ…иҜ»е®ҢиҝҷзҜҮж–Үз« еҗҺеҸҜд»ҘжңүжүҖ收иҺ·пјҢиҜқдёҚеӨҡиҜҙпјҢи·ҹзқҖе°Ҹзј–дёҖиө·жқҘзңӢзңӢеҗ§гҖӮ
AOPзҡ„й…ҚзҪ®ж–№ејҸжңү2з§Қж–№ејҸпјҡxmlй…ҚзҪ®е’ҢAspectJжіЁи§Јж–№ејҸгҖӮд»ҠеӨ©жҲ‘们е°ұжқҘе®һи·өдёҖдёӢxmlй…ҚзҪ®ж–№ејҸгҖӮ
жҲ‘йҮҮз”Ёзҡ„jdkд»ЈзҗҶпјҢжүҖд»ҘйҰ–е…Ҳе°ҶжҺҘеҸЈе’Ңе®һзҺ°зұ»д»Јз Ғйҷ„дёҠ
package com.tgb.aop;
public interface UserManager {
public String findUserById(int userId);
}
package com.tgb.aop;
public class UserManagerImpl implements UserManager {
public String findUserById(int userId) {
System.out.println("---------UserManagerImpl.findUserById()--------");
if (userId <= 0) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("иҜҘз”ЁжҲ·дёҚеӯҳеңЁ!");
}
return "еј дёү";
}
}еҚ•зӢ¬еҶҷдёҖдёӘAdviceйҖҡзҹҘзұ»иҝӣиЎҢжөӢиҜ•гҖӮиҝҷдёӘйҖҡзҹҘзұ»еҸҜд»ҘжҚўжҲҗе®үе…ЁжҖ§жЈҖжөӢгҖҒж—Ҙеҝ—з®ЎзҗҶзӯүзӯүгҖӮ
package com.tgb.aop;
import org.aspectj.lang.JoinPoint;
import org.aspectj.lang.ProceedingJoinPoint;
/**
* AdviceйҖҡзҹҘзұ»
* жөӢиҜ•after,before,around,throwing,returning Advice.
* @author Admin
*
*/
public class XMLAdvice {
/**
* еңЁж ёеҝғдёҡеҠЎжү§иЎҢеүҚжү§иЎҢпјҢдёҚиғҪйҳ»жӯўж ёеҝғдёҡеҠЎзҡ„и°ғз”ЁгҖӮ
* @param joinPoint
*/
private void doBefore(JoinPoint joinPoint) {
System.out.println("-----doBefore().invoke-----");
System.out.println(" жӯӨеӨ„ж„ҸеңЁжү§иЎҢж ёеҝғдёҡеҠЎйҖ»иҫ‘еүҚпјҢеҒҡдёҖдәӣе®үе…ЁжҖ§зҡ„еҲӨж–ӯзӯүзӯү");
System.out.println(" еҸҜйҖҡиҝҮjoinPointжқҘиҺ·еҸ–жүҖйңҖиҰҒзҡ„еҶ…е®№");
System.out.println("-----End of doBefore()------");
}
/**
* жүӢеҠЁжҺ§еҲ¶и°ғз”Ёж ёеҝғдёҡеҠЎйҖ»иҫ‘пјҢд»ҘеҸҠи°ғз”ЁеүҚе’Ңи°ғз”ЁеҗҺзҡ„еӨ„зҗҶ,
*
* жіЁж„ҸпјҡеҪ“ж ёеҝғдёҡеҠЎжҠӣејӮеёёеҗҺпјҢз«ӢеҚійҖҖеҮәпјҢиҪ¬еҗ‘After Advice
* жү§иЎҢе®ҢжҜ•After AdviceпјҢеҶҚиҪ¬еҲ°Throwing Advice
* @param pjp
* @return
* @throws Throwable
*/
private Object doAround(ProceedingJoinPoint pjp) throws Throwable {
System.out.println("-----doAround().invoke-----");
System.out.println(" жӯӨеӨ„еҸҜд»ҘеҒҡзұ»дјјдәҺBefore Adviceзҡ„дәӢжғ…");
//и°ғз”Ёж ёеҝғйҖ»иҫ‘
Object retVal = pjp.proceed();
System.out.println(" жӯӨеӨ„еҸҜд»ҘеҒҡзұ»дјјдәҺAfter Adviceзҡ„дәӢжғ…");
System.out.println("-----End of doAround()------");
return retVal;
}
/**
* ж ёеҝғдёҡеҠЎйҖ»иҫ‘йҖҖеҮәеҗҺпјҲеҢ…жӢ¬жӯЈеёёжү§иЎҢз»“жқҹе’ҢејӮеёёйҖҖеҮәпјүпјҢжү§иЎҢжӯӨAdvice
* @param joinPoint
*/
private void doAfter(JoinPoint joinPoint) {
System.out.println("-----doAfter().invoke-----");
System.out.println(" жӯӨеӨ„ж„ҸеңЁжү§иЎҢж ёеҝғдёҡеҠЎйҖ»иҫ‘д№ӢеҗҺпјҢеҒҡдёҖдәӣж—Ҙеҝ—и®°еҪ•ж“ҚдҪңзӯүзӯү");
System.out.println(" еҸҜйҖҡиҝҮjoinPointжқҘиҺ·еҸ–жүҖйңҖиҰҒзҡ„еҶ…е®№");
System.out.println("-----End of doAfter()------");
}
/**
* ж ёеҝғдёҡеҠЎйҖ»иҫ‘и°ғз”ЁжӯЈеёёйҖҖеҮәеҗҺпјҢдёҚз®ЎжҳҜеҗҰжңүиҝ”еӣһеҖјпјҢжӯЈеёёйҖҖеҮәеҗҺпјҢеқҮжү§иЎҢжӯӨAdvice
* @param joinPoint
*/
private void doReturn(JoinPoint joinPoint) {
System.out.println("-----doReturn().invoke-----");
System.out.println(" жӯӨеӨ„еҸҜд»ҘеҜ№иҝ”еӣһеҖјеҒҡиҝӣдёҖжӯҘеӨ„зҗҶ");
System.out.println(" еҸҜйҖҡиҝҮjoinPointжқҘиҺ·еҸ–жүҖйңҖиҰҒзҡ„еҶ…е®№");
System.out.println("-----End of doReturn()------");
}
/**
* ж ёеҝғдёҡеҠЎйҖ»иҫ‘и°ғз”ЁејӮеёёйҖҖеҮәеҗҺпјҢжү§иЎҢжӯӨAdviceпјҢеӨ„зҗҶй”ҷиҜҜдҝЎжҒҜ
* @param joinPoint
* @param ex
*/
private void doThrowing(JoinPoint joinPoint,Throwable ex) {
System.out.println("-----doThrowing().invoke-----");
System.out.println(" й”ҷиҜҜдҝЎжҒҜпјҡ"+ex.getMessage());
System.out.println(" жӯӨеӨ„ж„ҸеңЁжү§иЎҢж ёеҝғдёҡеҠЎйҖ»иҫ‘еҮәй”ҷж—¶пјҢжҚ•иҺ·ејӮеёёпјҢ并еҸҜеҒҡдёҖдәӣж—Ҙеҝ—и®°еҪ•ж“ҚдҪңзӯүзӯү");
System.out.println(" еҸҜйҖҡиҝҮjoinPointжқҘиҺ·еҸ–жүҖйңҖиҰҒзҡ„еҶ…е®№");
System.out.println("-----End of doThrowing()------");
}
}
еҸӘжңүAdviceиҝҳдёҚиЎҢпјҢиҝҳйңҖиҰҒеңЁapplication-config.xmlдёӯиҝӣиЎҢй…ҚзҪ®пјҡ
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-2.0.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop-2.0.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx-2.0.xsd">
<bean id="userManager" class="com.tgb.aop.UserManagerImpl"/>
<!--<bean id="aspcejHandler" class="com.tgb.aop.AspceJAdvice"/>-->
<bean id="xmlHandler" class="com.tgb.aop.XMLAdvice" />
<aop:config>
<aop:aspect id="aspect" ref="xmlHandler">
<aop:pointcut id="pointUserMgr" expression="execution(* com.tgb.aop.*.find*(..))"/>
<aop:before method="doBefore" pointcut-ref="pointUserMgr"/>
<aop:after method="doAfter" pointcut-ref="pointUserMgr"/>
<aop:around method="doAround" pointcut-ref="pointUserMgr"/>
<aop:after-returning method="doReturn" pointcut-ref="pointUserMgr"/>
<aop:after-throwing method="doThrowing" throwing="ex" pointcut-ref="pointUserMgr"/>
</aop:aspect>
</aop:config>
</beans> зј–дёҖдёӘе®ўжҲ·з«Ҝзұ»иҝӣиЎҢжөӢиҜ•дёҖдёӢпјҡ
package com.tgb.aop;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanFactory;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
public class Client {
public static void main(String[] args) {
BeanFactory factory = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
UserManager userManager = (UserManager)factory.getBean("userManager");
//еҸҜд»ҘжҹҘжүҫеј дёү
userManager.findUserById(1);
System.out.println("=====жҲ‘==жҳҜ==еҲҶ==еүІ==зәҝ=====");
try {
// жҹҘдёҚеҲ°ж•°жҚ®пјҢдјҡжҠӣејӮеёёпјҢејӮеёёдјҡиў«AfterThrowingAdviceжҚ•иҺ·
userManager.findUserById(0);
} catch (IllegalArgumentException e) {
}
}
} з»“жһңеҰӮеӣҫпјҡ
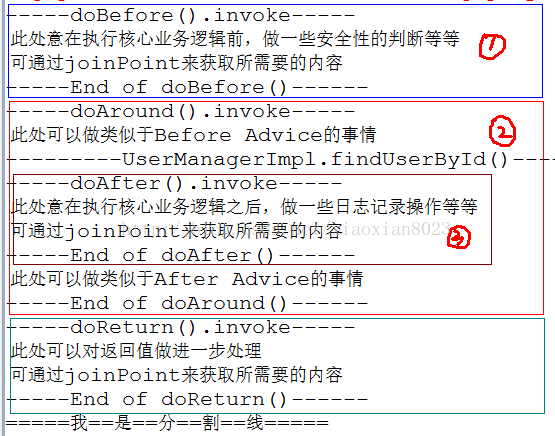
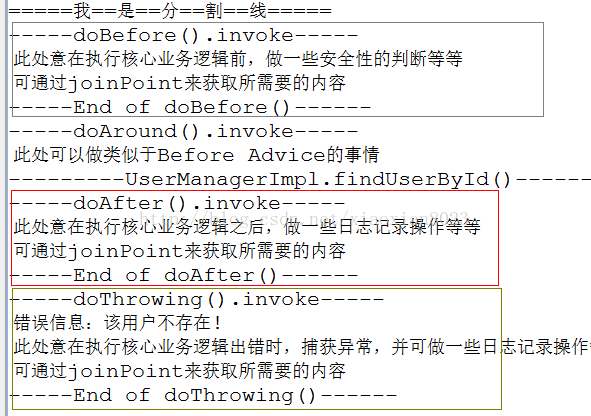
еҖјеҫ—жіЁж„Ҹзҡ„жҳҜAroundдёҺBeforeе’ҢAfterзҡ„жү§иЎҢйЎәеәҸгҖӮ3иҖ…зҡ„жү§иЎҢйЎәеәҸеҸ–еҶідәҺеңЁxmlдёӯзҡ„й…ҚзҪ®йЎәеәҸгҖӮеӣҫдёӯж Үи®°дәҶ3еқ—пјҢеҲҶеҲ«еҜ№еә”BeforeпјҢAroundпјҢAfterгҖӮе…¶дёӯв‘ЎдёӯеҢ…еҗ«жңүв‘ўгҖӮиҝҷжҳҜеӣ дёәaop:afterй…ҚзҪ®еҲ°дәҶaop:aroundзҡ„еүҚйқўпјҢеҰӮжһң2иҖ…и°ғжҚўдёҖдёӢдҪҚзҪ®пјҢиҝҷдёүеқ—е°ұдјҡеҲҶејҖзӢ¬з«ӢжҳҫзӨәгҖӮеҰӮжһңй…ҚзҪ®йЎәеәҸжҳҜaop:after -> aop:around ->aop:beforeпјҢйӮЈд№Ҳв‘ е’Ңв‘ўйғҪдјҡеҢ…еҗ«еңЁв‘ЎдёӯгҖӮиҝҷз§Қжғ…еҶөзҡ„дә§з”ҹжҳҜз”ұдәҺAroundзҡ„зү№ж®ҠжҖ§пјҢе®ғеҸҜд»ҘеҒҡзұ»дјјдәҺBeforeе’ҢAfterзҡ„ж“ҚдҪңгҖӮеҪ“е®үе…ЁжҖ§зҡ„еҲӨж–ӯдёҚйҖҡиҝҮж—¶пјҢеҸҜд»Ҙйҳ»жӯўж ёеҝғдёҡеҠЎйҖ»иҫ‘зҡ„и°ғз”ЁпјҢиҝҷжҳҜBeforeеҒҡдёҚеҲ°зҡ„гҖӮ


дҪҝз”ЁxmlеҸҜд»ҘеҜ№aopиҝӣиЎҢйӣҶдёӯй…ҚзҪ®гҖӮеҫҲж–№дҫҝиҖҢз®ҖеҚ•гҖӮеҸҜд»ҘеҜ№жүҖжңүзҡ„aopиҝӣиЎҢй…ҚзҪ®пјҢеҪ“然д№ҹеҸҜд»ҘеҲҶејҖеҲ°еҚ•зӢ¬зҡ„xmlдёӯиҝӣиЎҢй…ҚзҪ®гҖӮеҪ“йңҖжұӮеҸҳеҠЁж—¶пјҢдёҚз”Ёдҝ®ж”№д»Јз ҒпјҢеҸӘиҰҒйҮҚж–°й…ҚзҪ®aopпјҢе°ұеҸҜд»Ҙе®ҢжҲҗдҝ®ж”№ж“ҚдҪңгҖӮ
д»ҘдёҠе°ұжҳҜдҪҝз”ЁSpring AopеҰӮдҪ•й…ҚзҪ®xmlпјҢе°Ҹзј–зӣёдҝЎжңүйғЁеҲҶзҹҘиҜҶзӮ№еҸҜиғҪжҳҜжҲ‘们ж—Ҙеёёе·ҘдҪңдјҡи§ҒеҲ°жҲ–з”ЁеҲ°зҡ„гҖӮеёҢжңӣдҪ иғҪйҖҡиҝҮиҝҷзҜҮж–Үз« еӯҰеҲ°жӣҙеӨҡзҹҘиҜҶгҖӮжӣҙеӨҡиҜҰжғ…敬иҜ·е…іжіЁдәҝйҖҹдә‘иЎҢдёҡиө„и®Ҝйў‘йҒ“гҖӮ
е…ҚиҙЈеЈ°жҳҺпјҡжң¬з«ҷеҸ‘еёғзҡ„еҶ…е®№пјҲеӣҫзүҮгҖҒи§Ҷйў‘е’Ңж–Үеӯ—пјүд»ҘеҺҹеҲӣгҖҒиҪ¬иҪҪе’ҢеҲҶдә«дёәдё»пјҢж–Үз« и§ӮзӮ№дёҚд»ЈиЎЁжң¬зҪ‘з«ҷз«ӢеңәпјҢеҰӮжһңж¶үеҸҠдҫөжқғиҜ·иҒ”зі»з«ҷй•ҝйӮ®з®ұпјҡis@yisu.comиҝӣиЎҢдёҫжҠҘпјҢ并жҸҗдҫӣзӣёе…іиҜҒжҚ®пјҢдёҖз»ҸжҹҘе®һпјҢе°Ҷз«ӢеҲ»еҲ йҷӨж¶үе«ҢдҫөжқғеҶ…е®№гҖӮ