今天就跟大家聊聊有关python中怎么模拟感知机算法,可能很多人都不太了解,为了让大家更加了解,小编给大家总结了以下内容,希望大家根据这篇文章可以有所收获。
通过梯度下降模拟感知机算法。数据来源于sklearn.datasets中经典数据集。
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
# 导入数据集load_iris。
# 其中前四列为花萼长度,花萼宽度,花瓣长度,花瓣宽度等4个用于识别鸢尾花的属性,
from sklearn.datasets import load_iris
import matplotlib.pyplot as plot
# load data
iris = load_iris()
# 构造函数DataFrame(data,index,columns),data为数据,index为行索引,columns为列索引
# 构造数据结构
df = pd.DataFrame(data=iris.data, columns=iris.feature_names)
# 在df中加入了新的一列:列名label的数据是target,即类型
# 第5列为鸢尾花的类别(包括Setosa,Versicolour,Virginica三类)。
# 也即通过判定花萼长度,花萼宽度,花瓣长度,花瓣宽度的尺寸大小来识别鸢尾花的类别。
df['label'] = iris.target
df.columns = ['sepal length', 'sepal width', 'petal length', 'petal width', 'label']
# 打印出label列值对应的数量。以及列名称、类型
# print(df.label.value_counts())
# 创建数组,
# 第一个参数:100表示取0-99行,即前100行;但100:表示100以后的所有数据。
# 第二个参数,0,1表示第一列和第二列,-1表示最后一列
data = np.array(df.iloc[:100, [0, 1, -1]])
# 数组切割,X切除了最后一列;y仅切最后一列
X, y = data[:, :-1], data[:, -1]
# 数据整理,将y中非1的改为-1
y = np.array([1 if i == 1 else -1 for i in y])
# 数据线性可分,二分类数据
# 此处为一元一次线性方程
class Model:
def __init__(self):
# w初始为自变量个数相同的(1,1)阵
self.w = np.ones(len(data[0]) - 1, dtype=np.float32)
self.b = 0
# 学习率设置为0.1
self.l_rate = 0.1
def sign(self, x, w, b):
# dot函数为点乘,区别于*乘。
# dot对矩阵运算的时候为矩阵乘法,一行乘一列。
# *乘对矩阵运算的时候,是对应元素相乘
y = np.dot(x, w) + b
return y
# 随机梯度下降法
def fit(self, X_train, y_train):
is_wrong = False
while not is_wrong:
# 记录当前的分类错误的点数,当分类错误的点数归零的时候,即分类结束
wrong_count = 0
# d从0-49遍历
for d in range(len(X_train)):
# 这里的X为一行两列数组
X = X_train[d]
y = y_train[d]
if y * self.sign(X, self.w, self.b) <= 0:
self.w = self.w + self.l_rate * np.dot(y, X)
self.b = self.b + self.l_rate * y
wrong_count += 1
if wrong_count == 0:
is_wrong = True
return 'Perceptron Model!'
def score(self):
pass
perceptron = Model()
# 对perception进行梯度下降
perceptron.fit(X, y)
print(perceptron.w)
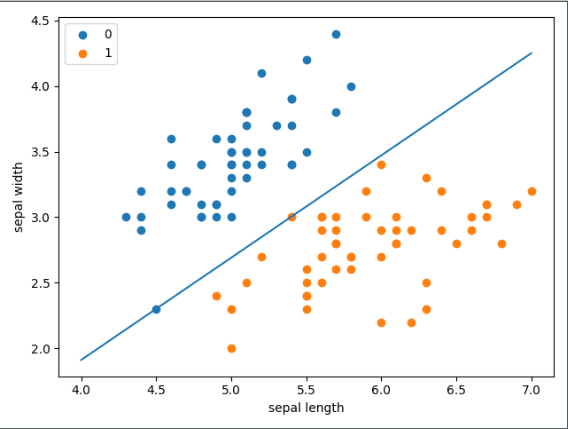
x_points = np.linspace(4, 7, 10)
# 最后拟合的函数瑞如下:
# w1*x1 + w2*x2 + b = 0
# 其中x1就是下边的x_points,x2就是y_
y_ = -(perceptron.w[0] * x_points + perceptron.b) / perceptron.w[1]
plot.plot(x_points, y_)
# scatter两个属性分别对应于x,y。
# 先画出了前50个点的花萼长度宽度,这时的花类型是0;
# 接着画50-100,这时花类型1
plot.scatter(df[:50]['sepal length'], df[:50]['sepal width'], label='0')
plot.scatter(df[50:100]['sepal length'], df[50:100]['sepal width'], label='1')
# 横坐标名称
plot.xlabel('sepal length')
# 纵坐标名称
plot.ylabel('sepal width')
plot.legend()
plot.show()结果如图
2. sklearn中提供了现成的感知机方法,我们可以直接调用
import sklearn
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from sklearn.datasets import load_iris
from sklearn.linear_model import Perceptron
iris = load_iris()
df = pd.DataFrame(iris.data, columns=iris.feature_names)
df['label'] = iris.target
# df.columns = [
# 'sepal length', 'sepal width', 'petal length', 'petal width', 'label'
# ]
data = np.array(df.iloc[:100, [0, 1, -1]])
X, y = data[:, :-1], data[:, -1]
y = np.array([1 if i == 1 else -1 for i in y])
clf = Perceptron(fit_intercept=True, # true表示估计截距
max_iter=1000, # 训练数据的最大次数
shuffle=True, # 每次训练之后是否重新训练
tol=None) # 如果不设置none那么迭代将在误差小于1e-3结束
clf.fit(X, y)
# 输出粘合之后的w
print(clf.coef_)
# 输出拟合之后的截距b
print(clf.intercept_)
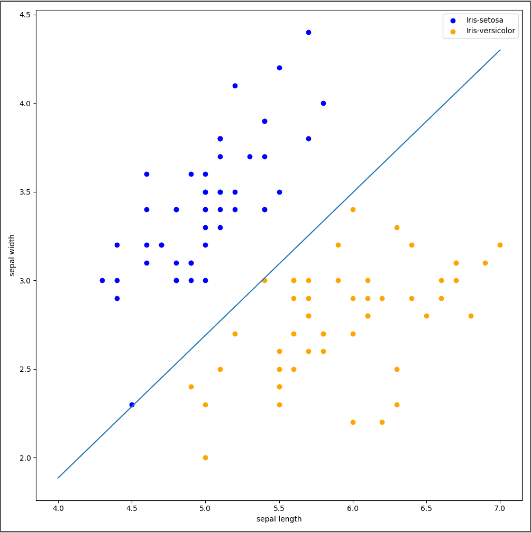
# 画布大小
plt.figure(figsize=(10, 10))
# 中文标题
# plt.rcParams['font.sans-serif'] = ['SimHei']
# plt.rcParams['axes.unicode_minus'] = False
# plt.title('鸢尾花线性数据示例')
plt.scatter(data[:50, 0], data[:50, 1], c='b', label='Iris-setosa',)
plt.scatter(data[50:100, 0], data[50:100, 1], c='orange', label='Iris-versicolor')
# 画感知机的线
x_ponits = np.arange(4, 8)
y_ = -(clf.coef_[0][0]*x_ponits + clf.intercept_)/clf.coef_[0][1]
plt.plot(x_ponits, y_)
# 其他部分
plt.legend() # 显示图例
plt.grid(False) # 不显示网格
plt.xlabel('sepal length')
plt.ylabel('sepal width')
plt.legend()
plt.show()结果如图
看完上述内容,你们对python中怎么模拟感知机算法有进一步的了解吗?如果还想了解更多知识或者相关内容,请关注亿速云行业资讯频道,感谢大家的支持。
亿速云「云服务器」,即开即用、新一代英特尔至强铂金CPU、三副本存储NVMe SSD云盘,价格低至29元/月。点击查看>>
免责声明:本站发布的内容(图片、视频和文字)以原创、转载和分享为主,文章观点不代表本网站立场,如果涉及侵权请联系站长邮箱:is@yisu.com进行举报,并提供相关证据,一经查实,将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容。
原文链接:https://my.oschina.net/LevideGrowthHistory/blog/4710101