这篇文章主要讲解了“如何编写代码实现LRU算法”,文中的讲解内容简单清晰,易于学习与理解,下面请大家跟着小编的思路慢慢深入,一起来研究和学习“如何编写代码实现LRU算法”吧!
运用你所掌握的数据结构,设计和实现一个 LRU (最近最少使用) 缓存机制 。
实现 LRUCache 类:LRUCache(int capacity) 以正整数作为容量 capacity 初始化 LRU 缓存
int get(int key) 如果关键字 key 存在于缓存中,则返回关键字的值,否则返回 -1 。
void put(int key, int value) 如果关键字已经存在,则变更其数据值;如果关键字不存在,则插入该组「关键字-值」。当缓存容量达到上限时,它应该在写入新数据之前删除最久未使用的数据值,从而为新的数据值留出空间。
要求:在 O(1) 时间复杂度内完成这两种操作。
1 所谓缓存,必须要有读+写两个操作,按照命中率的思路考虑,写操作+读操作时间复杂度都需要为O(1)
2 特性要求分析
2.1 必须有顺序之分,以区分最近使用的和很久没用到的数据排序。
2.2 写和读操作 一次搞定。
2.3 如果容量(坑位)满了要删除最不长用的数据,每次新访问还要把新的数据插入到队头(按照业务你自己设定左右那一边是队头)
查找快,插入快,删除快,且还需要先后排序-------->什么样的数据结构满足这个问题?
你是否可以在O(1)时间复杂度内完成这两种操作?
如果一次就可以找到,你觉得什么数据结构最合适??参考LinkedHashMap
package com.lau.lrualgorithm.way;
import java.util.LinkedHashMap;
import java.util.Map;
/**
* 复用现有api中的HashMap
*/
public class ReuseLinkedHashMap<K, V> extends LinkedHashMap<K, V> {
//允许缓存个数上限
private int cacheSize;
//重载构造器
public ReuseLinkedHashMap(int cacheSize) {
super(cacheSize, 0.75f, true);
this.cacheSize = cacheSize;
}
@Override
protected boolean removeEldestEntry(Map.Entry<K, V> eldest) {
return super.size() > cacheSize;
}
public V put(K key, V value){
// if(super.size() == this.cachesize){
// super.removeEldestEntry();
// }
return super.put(key, value);
}
public V get(Object key){
return super.get(key);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
ReuseLinkedHashMap map = new ReuseLinkedHashMap(3);
map.put(1, 1);
map.put(2, 2);
map.put(3, 3);
System.out.println(map.keySet());
map.put(4, 1);
System.out.println(map.keySet());
map.put(3, 1);
System.out.println(map.keySet());
map.put(3, 1);
System.out.println(map.keySet());
map.put(3, 1);
System.out.println(map.keySet());
map.put(5, 1);
System.out.println(map.keySet());
}
}
/**
* true
* [1, 2, 3]
* [2, 3, 4]
* [2, 4, 3]
* [2, 4, 3]
* [2, 4, 3]
* [4, 3, 5]
* */
/**false
[1, 2, 3]
[2, 3, 4]
[2, 3, 4]
[2, 3, 4]
[2, 3, 4]
[3, 4, 5]
*/关键点:
1、复写removeEldestEntry()方法
2、accessOrder – the ordering mode - true for access-order, false for insertion-order
3、最新节点存储顺序:从右至左
package com.lau.lrualgorithm.way;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
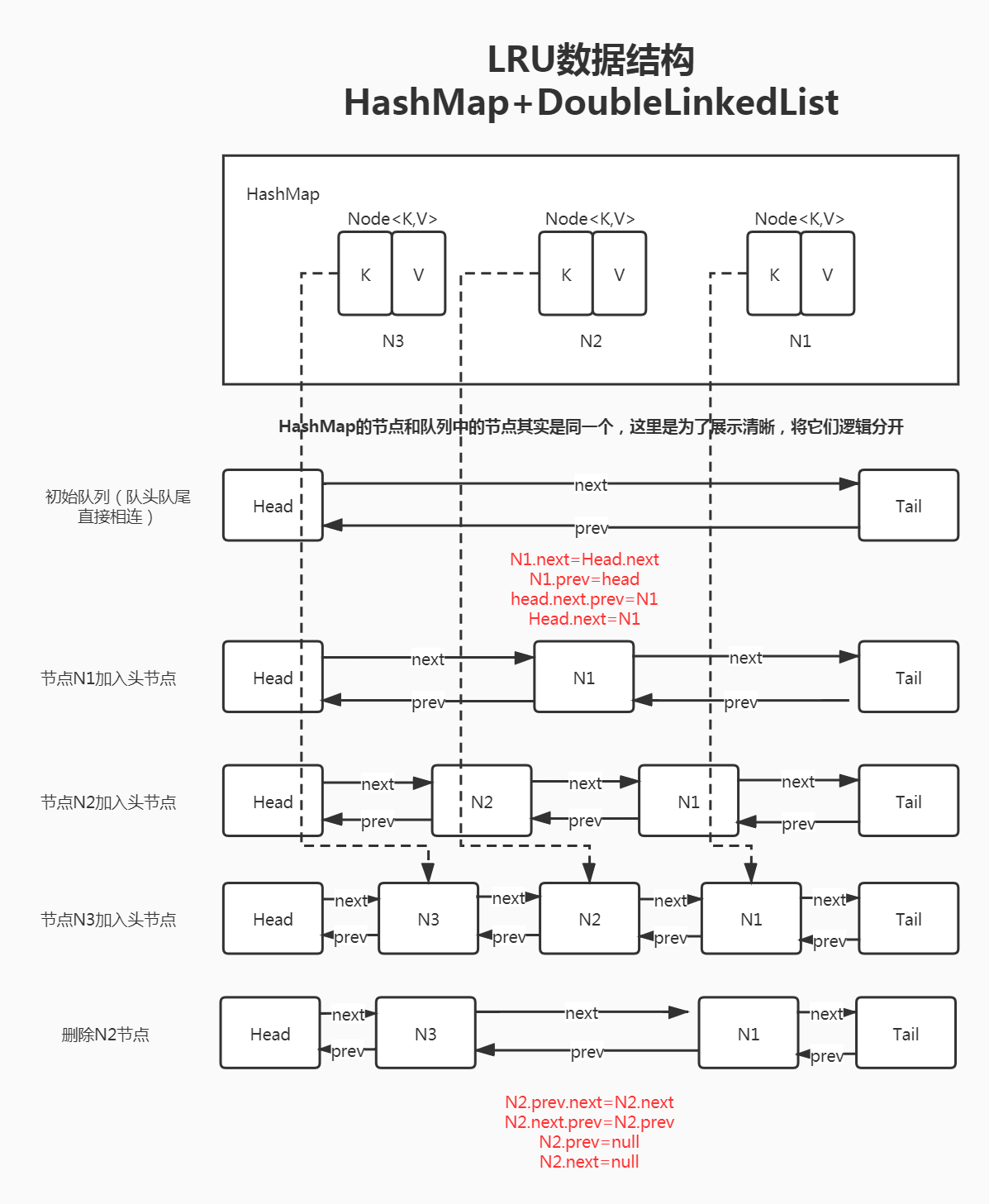
//map负责查找,构建一个虚拟的双向链表,它里面安装的就是一个个Node节点,作为数据载体。
public class LruCacheDemo {
//1.构造一个node节点作为数据载体
class Node<K, V> {
K key;
V value;
Node<K, V> prev;
Node<K, V> next;
public Node() {
this.prev = this.next = null;
}
public Node(K key, V value) {
this.key = key;
this.value = value;
this.prev = this.next = null;
}
}
//2 构建一个虚拟的双向链表,里面安放的就是我们的Node
class DoubleLinkedList<K, V> {
Node<K, V> head;
Node<K, V> tail;
public DoubleLinkedList() {
head = new Node<>();
tail = new Node<>();
head.next = tail;
tail.prev = head;
}
//3. 添加到头
public void addHead(Node<K, V> node) {
node.next = head.next;
node.prev = head;
head.next.prev = node;
head.next = node;
}
//4.删除节点
public void removeNode(Node<K, V> node) {
node.next.prev = node.prev;
node.prev.next = node.next;
node.prev = null;
node.next = null;
}
//5.获得最后一个节点
public Node getLast() {
return tail.prev;
}
}
private int cacheSize;
Map<Integer, Node<Integer, Integer>> map;
DoubleLinkedList<Integer, Integer> doubleLinkedList;
public LruCacheDemo(int cacheSize) {
this.cacheSize = cacheSize;//坑位
map = new HashMap<>();//查找
doubleLinkedList = new DoubleLinkedList<>();
}
public int get(int key) {
if (!map.containsKey(key)) {
return -1;
}
Node<Integer, Integer> node = map.get(key);
doubleLinkedList.removeNode(node);
doubleLinkedList.addHead(node);
return node.value;
}
public void put(int key, int value) {
if (map.containsKey(key)) { //update
Node<Integer, Integer> node = map.get(key);
node.value = value;
// map.put(key, node);
doubleLinkedList.removeNode(node);
doubleLinkedList.addHead(node);
} else {
if (map.size() == cacheSize) //坑位满了
{
Node<Integer, Integer> lastNode = doubleLinkedList.getLast();
map.remove(lastNode.key);
doubleLinkedList.removeNode(lastNode);
}
//新增一个
Node<Integer, Integer> newNode = new Node<>(key, value);
map.put(key, newNode);
doubleLinkedList.addHead(newNode);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
LruCacheDemo lruCacheDemo = new LruCacheDemo(3);
lruCacheDemo.put(1, 1);
lruCacheDemo.put(2, 2);
lruCacheDemo.put(3, 3);
//不能直接打印map,因为此map是无序的!!!
// System.out.println(lruCacheDemo.map.keySet());
printKeys(lruCacheDemo);
lruCacheDemo.put(4, 1);
// System.out.println(lruCacheDemo.map.keySet());
printKeys(lruCacheDemo);
lruCacheDemo.put(3, 1);
// System.out.println(lruCacheDemo.map.keySet());
printKeys(lruCacheDemo);
lruCacheDemo.put(3, 1);
// System.out.println(lruCacheDemo.map.keySet());
printKeys(lruCacheDemo);
lruCacheDemo.put(3, 1);
// System.out.println(lruCacheDemo.map.keySet());
printKeys(lruCacheDemo);
lruCacheDemo.put(5, 1);
// System.out.println(lruCacheDemo.map.keySet());
printKeys(lruCacheDemo);
}
private static void printKeys(LruCacheDemo lruCacheDemo){
Node<Integer, Integer> node = lruCacheDemo.doubleLinkedList.head.next;
while( node != null && node.key != null){
System.out.print(node.key + " ");
node = node.next;
}
System.out.println();
}
}
/**
* true
* [1, 2, 3]
* [2, 3, 4]
* [2, 4, 3]
* [2, 4, 3]
* [2, 4, 3]
* [4, 3, 5]
* */
/**false
[1, 2, 3]
[2, 3, 4]
[2, 3, 4]
[2, 3, 4]
[2, 3, 4]
[3, 4, 5]
*/注:
最新节点存储顺序:从左至右
感谢各位的阅读,以上就是“如何编写代码实现LRU算法”的内容了,经过本文的学习后,相信大家对如何编写代码实现LRU算法这一问题有了更深刻的体会,具体使用情况还需要大家实践验证。这里是亿速云,小编将为大家推送更多相关知识点的文章,欢迎关注!
亿速云「云服务器」,即开即用、新一代英特尔至强铂金CPU、三副本存储NVMe SSD云盘,价格低至29元/月。点击查看>>
免责声明:本站发布的内容(图片、视频和文字)以原创、转载和分享为主,文章观点不代表本网站立场,如果涉及侵权请联系站长邮箱:is@yisu.com进行举报,并提供相关证据,一经查实,将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容。
原文链接:https://my.oschina.net/Howard2016/blog/5015474