这篇文章给大家介绍Python 图形绘制详细代码怎么写,内容非常详细,感兴趣的小伙伴们可以参考借鉴,希望对大家能有所帮助。
下面介绍条形图的画法。
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# x-coordinates of left sides of bars
left = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
# heights of bars
height = [10, 24, 36, 40, 5]
# labels for bars
tick_label = ['one', 'two', 'three', 'four', 'five']
# plotting a bar chart
plt.bar(left, height, tick_label = tick_label,
width = 0.8, color = ['red', 'green'])
# naming the x-axis
plt.xlabel('x - axis')
# naming the y-axis
plt.ylabel('y - axis')
# plot title
plt.title('My bar chart!')
# function to show the plot
plt.show()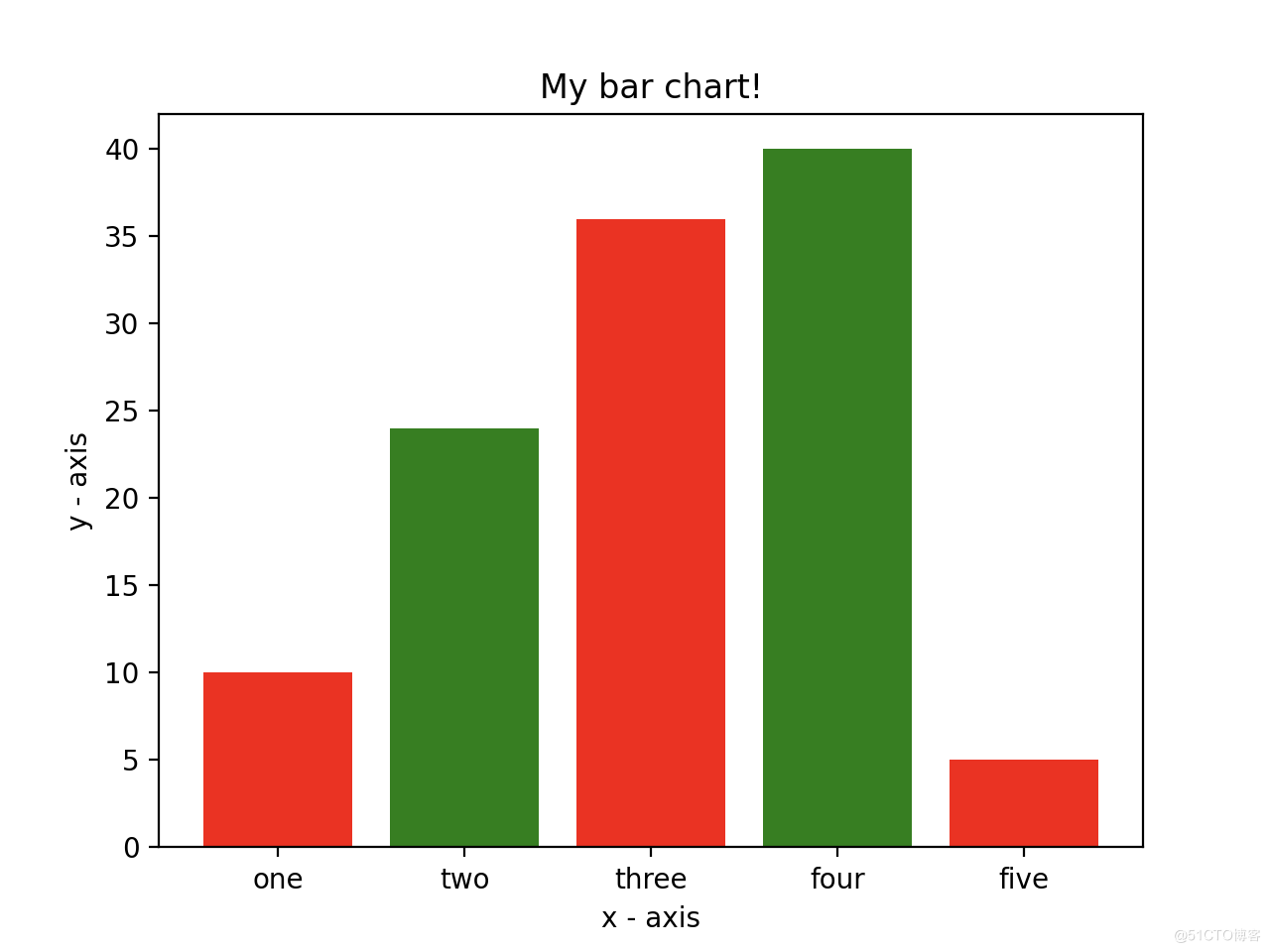
1)使用 plt.bar() 函数来绘制条形图。
2)x轴与height两个参数必须有。
3)可以通过定义 tick_labels 为 x 轴坐标指定另外的名称。
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# frequencies
ages = [2,5,70,40,30,45,50,45,43,40,44,
60,7,13,57,18,90,77,32,21,20,40]
# setting the ranges and no. of intervals
range = (0, 100)
bins = 10
# plotting a histogram
plt.hist(ages, bins, range, color = 'green',
histtype = 'bar', rwidth = 0.8)
# x-axis label
plt.xlabel('age')
# frequency label
plt.ylabel('No. of people')
# plot title
plt.title('My histogram')
# function to show the plot
plt.show()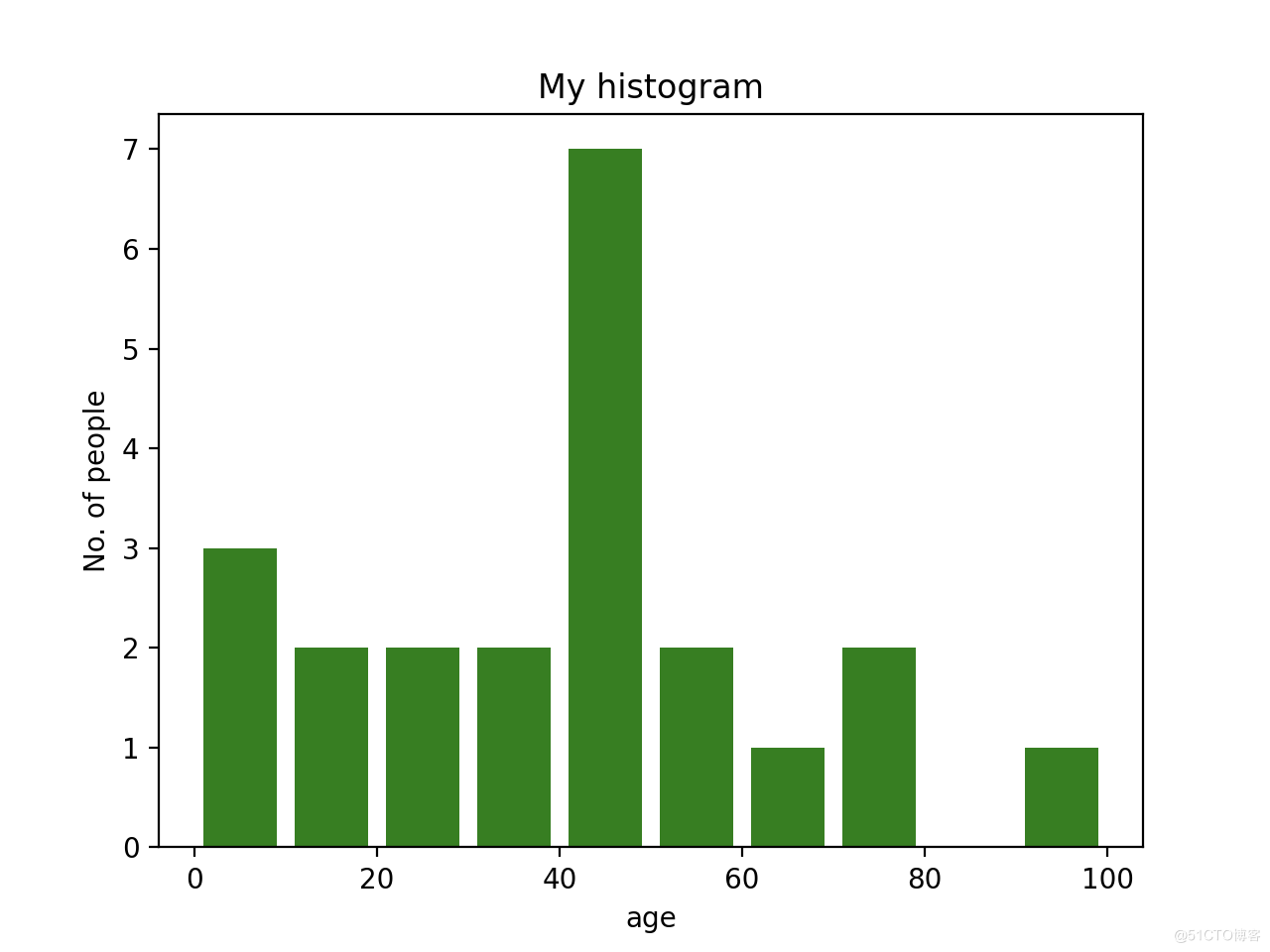
1)使用 plt.hist() 函数绘制直方图。
2)age列表作为频率传入函数。
3)可以通过定义包含最小值和最大值的元组来设置范围。
4)下一步是对值的范围进行“装箱”——即将整个值范围划分为一系列区间——然后计算落入每个区间的值的数量。 这里我们定义了 bins = 10。所以,总共有 100/10 = 10 个区间。
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# x-axis values
x = [1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10]
# y-axis values
y = [2,4,5,7,6,8,9,11,12,12]
# plotting points as a scatter plot
plt.scatter(x, y, label= "stars", color= "green",
marker= "*", s=30)
# x-axis label
plt.xlabel('x - axis')
# frequency label
plt.ylabel('y - axis')
# plot title
plt.title('My scatter plot!')
# showing legend
plt.legend()
# function to show the plot
plt.show()
1)使用 plt.scatter() 函数绘制散点图。
2)作为一条线,我们在这里也定义了 x 和相应的 y 轴值。
3)标记参数用于设置用作标记的字符。 它的大小可以使用 s 参数定义。
关于Python 图形绘制详细代码怎么写就分享到这里了,希望以上内容可以对大家有一定的帮助,可以学到更多知识。如果觉得文章不错,可以把它分享出去让更多的人看到。
免责声明:本站发布的内容(图片、视频和文字)以原创、转载和分享为主,文章观点不代表本网站立场,如果涉及侵权请联系站长邮箱:is@yisu.com进行举报,并提供相关证据,一经查实,将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容。