这篇文章主要介绍“springboot1.X和2.X中怎么解决Bean名字相同时覆盖”,在日常操作中,相信很多人在springboot1.X和2.X中怎么解决Bean名字相同时覆盖问题上存在疑惑,小编查阅了各式资料,整理出简单好用的操作方法,希望对大家解答”springboot1.X和2.X中怎么解决Bean名字相同时覆盖”的疑惑有所帮助!接下来,请跟着小编一起来学习吧!
在2版本之前的版本,项目中有两个相同名字的bean是可以启动成功的,但是会有覆盖问题
但是在2.X版本的时候会报错:
could not be registered. A bean with that name has already been defined in class path resource
这时候解决办法可以在配置文件中添加:
spring.main.allow-bean-definition-overriding=true
/** 是否允许使用相同名称重新注册不同的bean实现. 默认是允许*/
private boolean allowBeanDefinitionOverriding = true;
/**
* Set whether it should be allowed to override bean definitions by registering
* a different definition with the same name, automatically replacing the former.
* If not, an exception will be thrown. This also applies to overriding aliases.
* <p>Default is "true".【这里明确说明了默认是true】
* @see #registerBeanDefinition
*/
public boolean isAllowBeanDefinitionOverriding() {
return this.allowBeanDefinitionOverriding;
}
@Override
public void registerBeanDefinition(String beanName, BeanDefinition beanDefinition)
throws BeanDefinitionStoreException {
Assert.hasText(beanName, "Bean name must not be empty");
Assert.notNull(beanDefinition, "BeanDefinition must not be null");
if (beanDefinition instanceof AbstractBeanDefinition) {
try {
((AbstractBeanDefinition) beanDefinition).validate();
}
catch (BeanDefinitionValidationException ex) {
throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException(beanDefinition.getResourceDescription(), beanName,
"Validation of bean definition failed", ex);
}
}
//bean加载到spring的工程中后,会存储在beanDefinitionMap中,key是bean的名称。
BeanDefinition existingDefinition = this.beanDefinitionMap.get(beanName);
if (existingDefinition != null) {//不为空,说明相同名称的bean已经存在了
if (!isAllowBeanDefinitionOverriding()) {//如果不允许相同名称的bean存在,则直接抛出异常
throw new BeanDefinitionOverrideException(beanName, beanDefinition, existingDefinition);
}
else if (existingDefinition.getRole() < beanDefinition.getRole()) {
// e.g. was ROLE_APPLICATION, now overriding with ROLE_SUPPORT or ROLE_INFRASTRUCTURE
if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
logger.info("Overriding user-defined bean definition for bean '" + beanName +
"' with a framework-generated bean definition: replacing [" +
existingDefinition + "] with [" + beanDefinition + "]");
}
}
else if (!beanDefinition.equals(existingDefinition)) {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Overriding bean definition for bean '" + beanName +
"' with a different definition: replacing [" + existingDefinition +
"] with [" + beanDefinition + "]");
}
}
else {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Overriding bean definition for bean '" + beanName +
"' with an equivalent definition: replacing [" + existingDefinition +
"] with [" + beanDefinition + "]");
}
}
//可见,上面allowBeanDefinitionOverriding =true时,只是记录了一些日志,然后后来发现的这个bean,会覆盖之前老的bean。
this.beanDefinitionMap.put(beanName, beanDefinition);
}
else {
if (hasBeanCreationStarted()) {
// Cannot modify startup-time collection elements anymore (for stable iteration)
synchronized (this.beanDefinitionMap) {
this.beanDefinitionMap.put(beanName, beanDefinition);
List<String> updatedDefinitions = new ArrayList<>(this.beanDefinitionNames.size() + 1);
updatedDefinitions.addAll(this.beanDefinitionNames);
updatedDefinitions.add(beanName);
this.beanDefinitionNames = updatedDefinitions;
if (this.manualSingletonNames.contains(beanName)) {
Set<String> updatedSingletons = new LinkedHashSet<>(this.manualSingletonNames);
updatedSingletons.remove(beanName);
this.manualSingletonNames = updatedSingletons;
}
}
}
else {
// Still in startup registration phase
this.beanDefinitionMap.put(beanName, beanDefinition);
this.beanDefinitionNames.add(beanName);
this.manualSingletonNames.remove(beanName);
}
this.frozenBeanDefinitionNames = null;
}
if (existingDefinition != null || containsSingleton(beanName)) {
resetBeanDefinition(beanName);
}
}上面贴出来的是spring的代码,而springboot2.X对这个参数又进行了二次封装,springboot中的allowBeanDefinitionOverriding是没有初始化默认值的,我们知道,java中的boolean类型不初始化时是false。
springboot中源代码:
在SpringApplication类中
public class SpringApplication {
...
//boolean没初始化,所以默认为false
private boolean allowBeanDefinitionOverriding;
...
private void prepareContext(ConfigurableApplicationContext context, ConfigurableEnvironment environment, SpringApplicationRunListeners listeners, ApplicationArguments applicationArguments, Banner printedBanner) {
context.setEnvironment(environment);
this.postProcessApplicationContext(context);
this.applyInitializers(context);
listeners.contextPrepared(context);
if (this.logStartupInfo) {
this.logStartupInfo(context.getParent() == null);
this.logStartupProfileInfo(context);
}
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = context.getBeanFactory();
beanFactory.registerSingleton("springApplicationArguments", applicationArguments);
if (printedBanner != null) {
beanFactory.registerSingleton("springBootBanner", printedBanner);
}
//将false值传过去
if (beanFactory instanceof DefaultListableBeanFactory) {
((DefaultListableBeanFactory)beanFactory).setAllowBeanDefinitionOverriding(this.allowBeanDefinitionOverriding);
}
if (this.lazyInitialization) {
context.addBeanFactoryPostProcessor(new LazyInitializationBeanFactoryPostProcessor());
}
Set<Object> sources = this.getAllSources();
Assert.notEmpty(sources, "Sources must not be empty");
this.load(context, sources.toArray(new Object[0]));
listeners.contextLoaded(context);
}而在1.5.8版本中,SpringApplication中,没有allowBeanDefinitionOverriding属性,因此在prepareContext方法中也就没有对allowBeanDefinitionOverriding进行赋值为false,所以在springboot1.5.8版本中默认就是支持名称相同的bean的覆盖。
什么情况下要覆写原有的Spring Bean ? 例如引入的第三方jar包中的某个类有些问题,然有没有源码提供或者嫌编译源码太费事,这个时间可以考虑覆写原有的类。
方式简单粗暴,可以直接覆盖掉jar包中的类,spring项目会优先加载自定义的类。
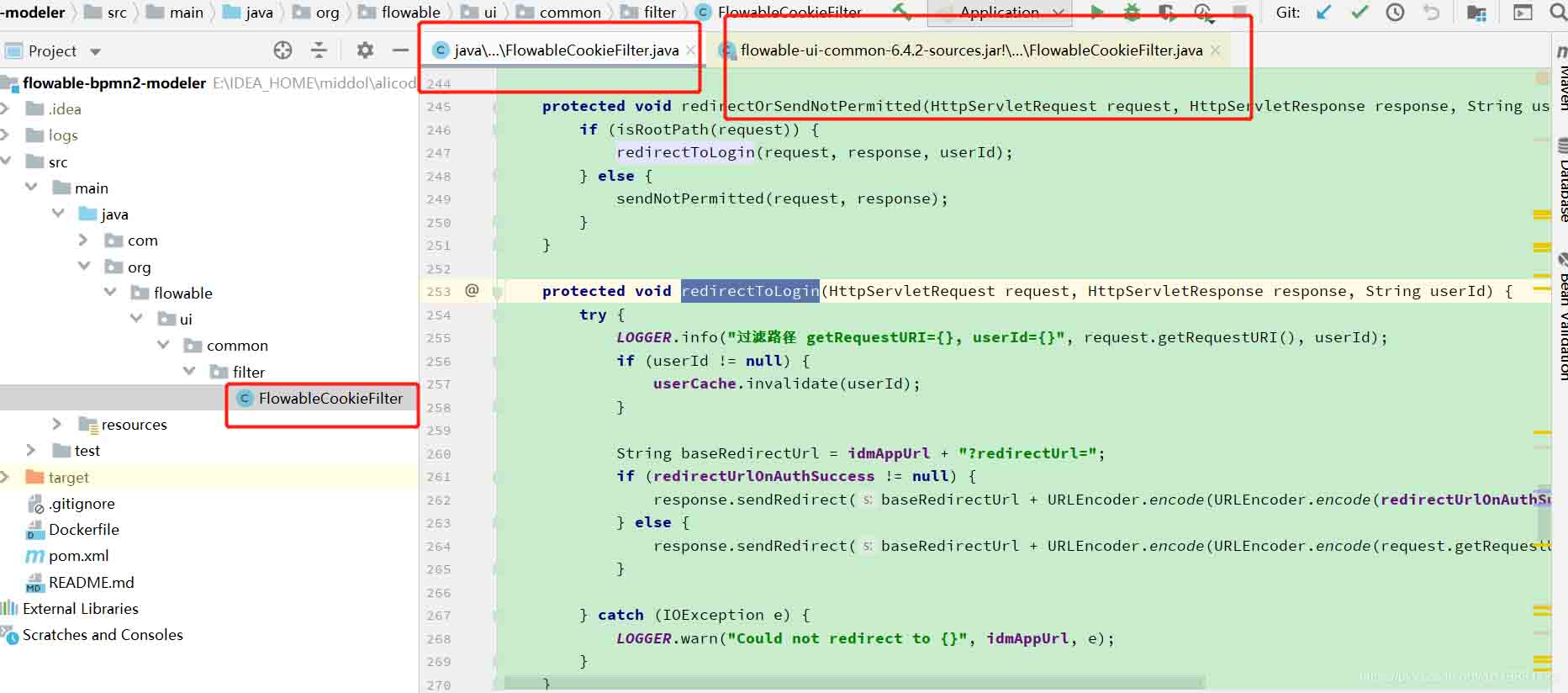
下面是覆盖 flowable框架中的一个类 FlowableCookieFilter,主要是想修改它里面的redirectToLogin方法的业务逻辑。包路径为 org.flowable.ui.common.filter, 直接工程里面新建一样路径一样类名FlowableCookieFilter即可。
方法2 采用@Primary注解
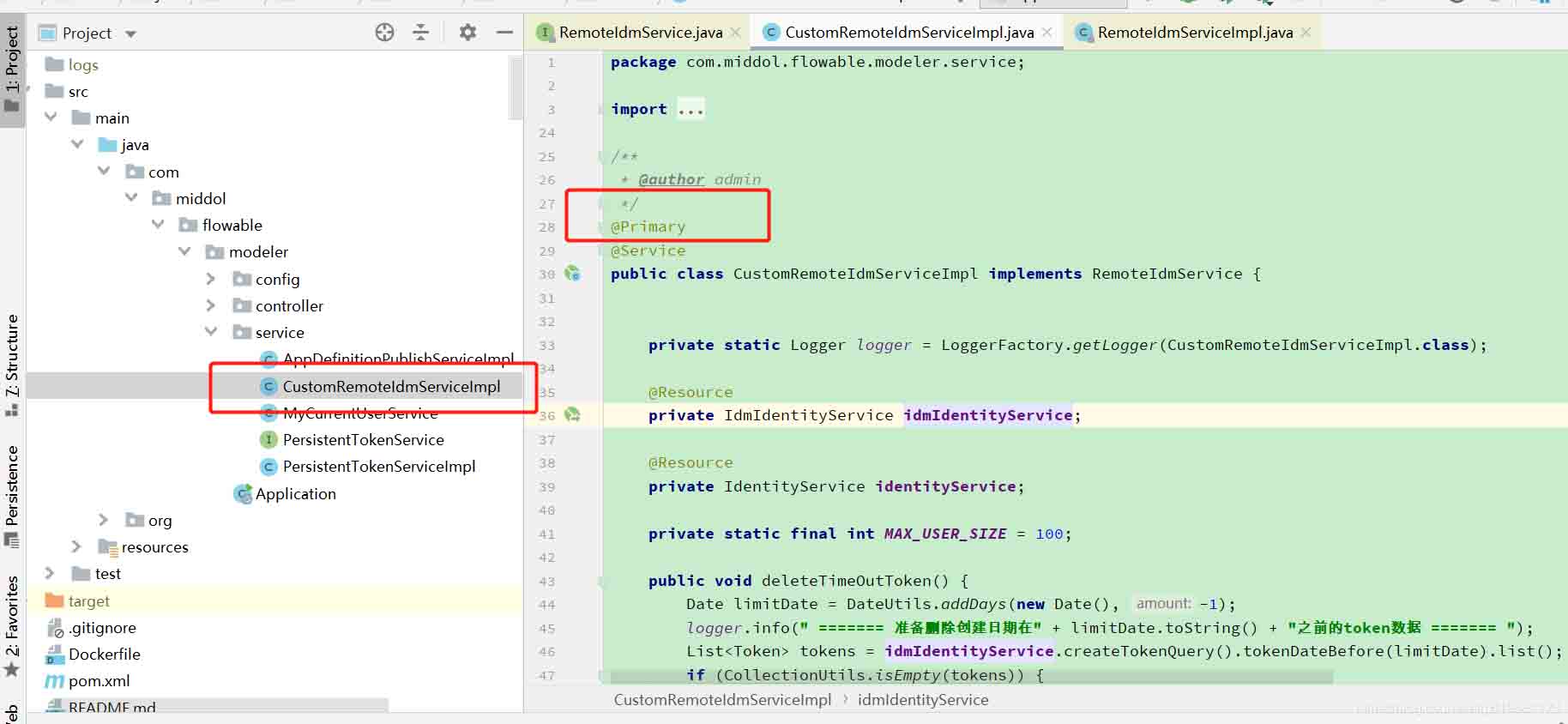
该方法适用于接口实现类,自己创建一个原jar包接口的实现类,然后类上加上@Primary注解,spring则默认加载该类实例化出的Bean。
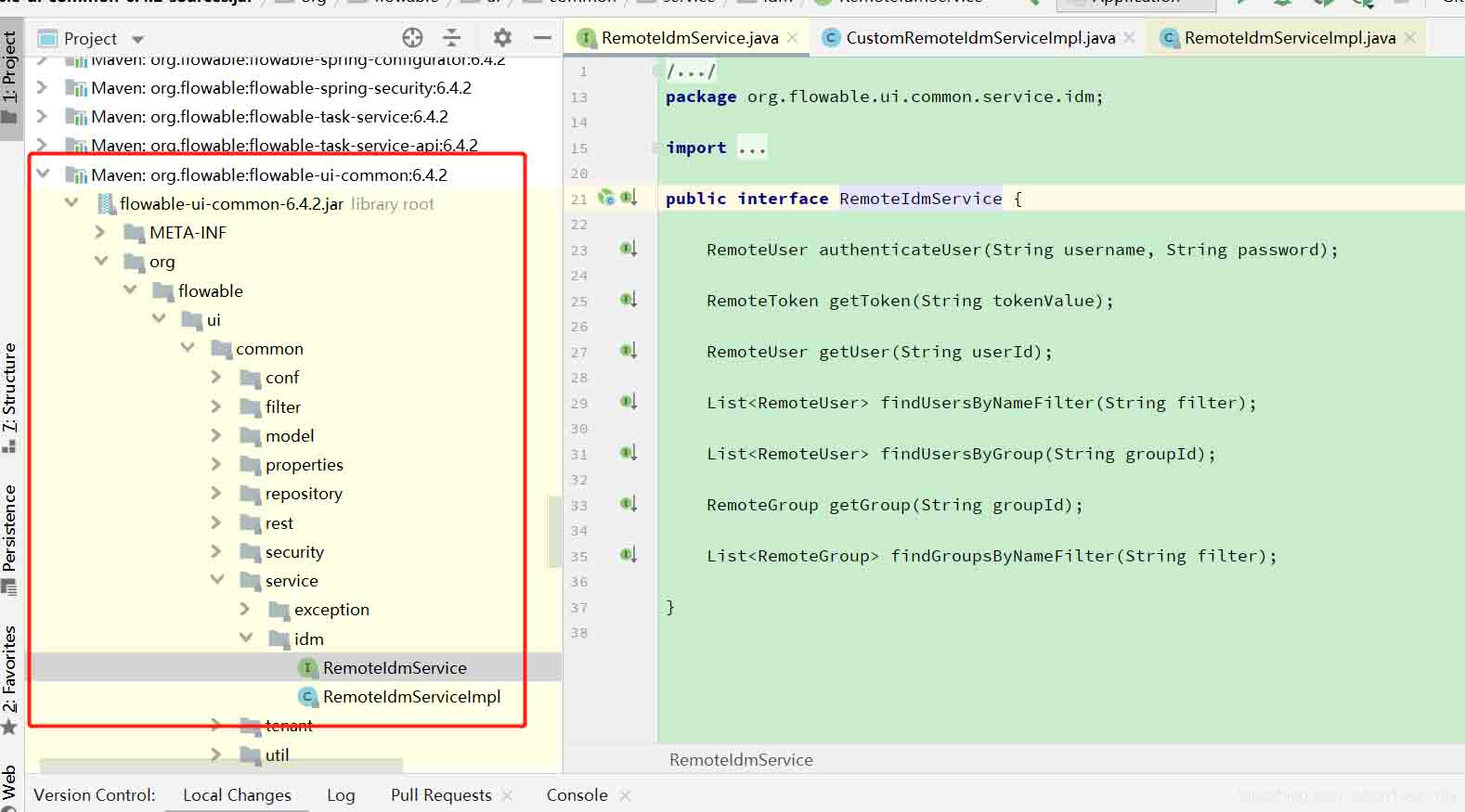
下面的例子: 一个接口 RemoteIdmService,原先jar包中只有一个实现类 RemoteIdmServiceImpl,现在自己工程里面创建一个 CustomRemoteIdmServiceImpl 继承RemoteIdmService接口,然后发现所有调用RemoteIdmService接口里面的方法实际调用走的是CustomRemoteIdmServiceImpl 里面的方法。
使用 @ComponentScan 里面的 excludeFilters 功能排除调用要替换的类,然后自己写个类继承替换的类即可。
下面的例子是替换掉 jar包中的PersistentTokenServiceImpl类
@SpringBootApplication
@ComponentScan(excludeFilters = {@ComponentScan.Filter(type =
FilterType.ASSIGNABLE_TYPE, classes = {PersistentTokenServiceImpl.class})})
public class Application {
public static void main(String[] args) {
new SpringApplication(Test.class).run(args);
}
}@Service
public class MyPersistentTokenServiceImpl extends PersistentTokenServiceImpl{
@Override
public Token saveAndFlush(Token token) {
// 覆写该方法的业务逻辑
tokenCache.put(token.getId(), token);
idmIdentityService.saveToken(token);
return token;
}
@Override
public void delete(Token token) {
// 覆写该方法的业务逻辑
tokenCache.invalidate(token.getId());
idmIdentityService.deleteToken(token.getId());
}
@Override
public Token getPersistentToken(String tokenId) {
// 覆写该方法的业务逻辑
return getPersistentToken(tokenId, false);
}
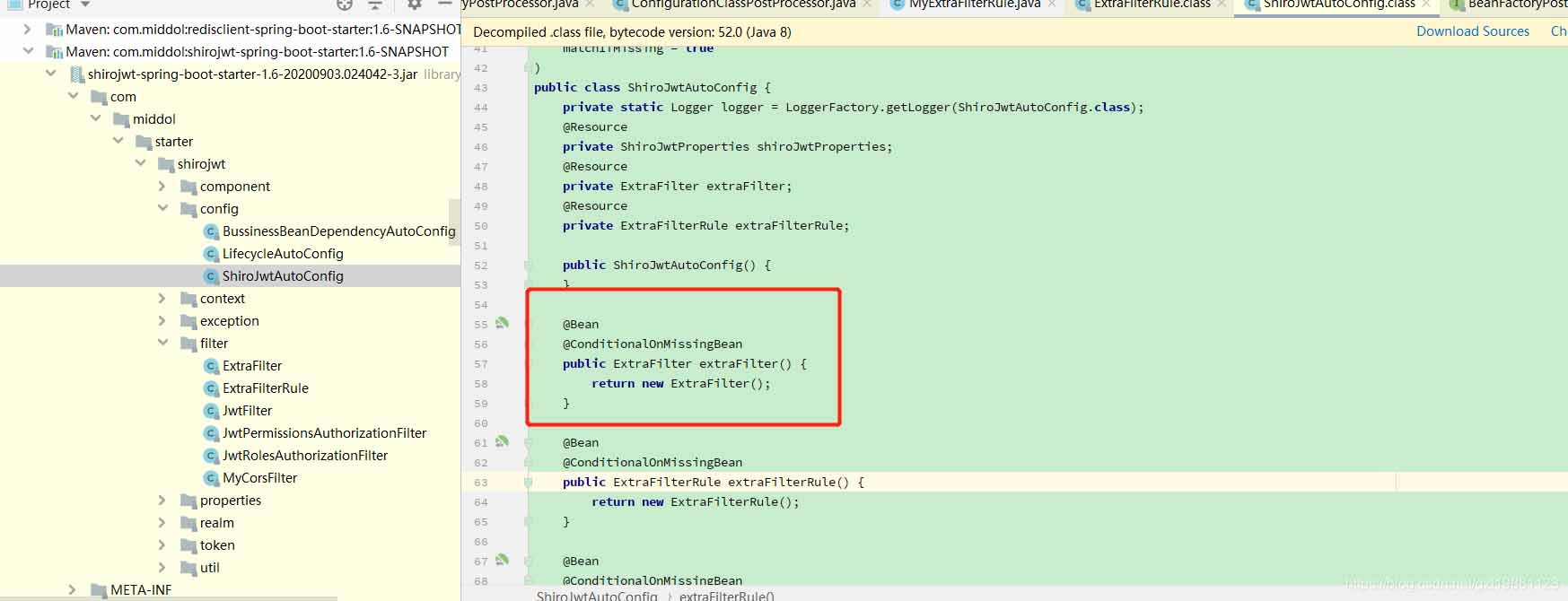
}该场景针对,框架jar包中有@ConditionalOnMissingBean注解,这种注解是说明如果你也创建了一个一样的Bean则框架就不自己再次创建这个bean了,这样你可以覆写自己的bean。原jar包中的配置类:
直接继承要覆盖的类,自己重写里面方法,使用@Component注入到spring中去
关于 BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor 、 BeanFactoryPostProcessor可以参考这篇文章:
BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor 说白了就是可以在初始化Bean之前修改Bean的属性,甚至替换原先准备要实例化的bean。
实战演示:
假设jar包中有一个类 MyTestService,正常情况下它会被spring自动扫描到注入IOC容器中去。
package com.middol.mytest.config.beantest.register.jar;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import javax.annotation.PostConstruct;
import javax.annotation.PreDestroy;
/**
* @author guzt
*/
@Service("myTestService")
public class MyTestService {
private String name1;
private String name2;
private String name3;
public MyTestService() {
this.name1 = "";
this.name2 = "";
this.name3 = "";
}
public MyTestService(String name1, String name2, String name3) {
this.name1 = name1;
this.name2 = name2;
this.name3 = name3;
}
@PostConstruct
public void init() {
System.out.println("MyTestService init");
}
@PreDestroy
public void destory() {
System.out.println("MyTestService destroy");
}
public void show() {
System.out.println("------------------------");
System.out.println("我是jar中通过注解@Service主动加入Spring的IOC里面的");
System.out.println("------------------------");
}
public String getName1() {
return name1;
}
public void setName1(String name1) {
this.name1 = name1;
}
public String getName2() {
return name2;
}
public void setName2(String name2) {
this.name2 = name2;
}
public String getName3() {
return name3;
}
public void setName3(String name3) {
this.name3 = name3;
}
}自己工程中继承该类,并且覆写里面的show中的方法
package com.middol.mytest.config.beantest.register;
import com.middol.mytest.config.beantest.register.jar.MyTestService;
/**
* @author guzt
*/
public class MyTestServiceIpml extends MyTestService {
public MyTestServiceIpml() {
}
public MyTestServiceIpml(String name1, String name2, String name3) {
super(name1, name2, name3);
}
@Override
public void show() {
System.out.println("------------------------");
System.out.println("我是被BeanDefinitionRegistry手动注册到Spring的IOC里面的");
System.out.println("------------------------");
}
}然后 实现 BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor 接口,修改原来bean定义,主要查看postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry方法的实现,先清空原bean定义,注册我们自己的bean定义来达到替换的目的。
package com.middol.mytest.config.beantest.register;
import org.slf4j.Logger;
import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory;
import org.springframework.beans.BeansException;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.config.ConfigurableListableBeanFactory;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.support.BeanDefinitionBuilder;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.support.BeanDefinitionRegistry;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.support.BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import java.util.Map;
/**
* @author amdin
*/
@Component
public class MyBeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor implements BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor {
private Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(this.getClass());
@Override
public void postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry(BeanDefinitionRegistry beanDefinitionRegistry) throws BeansException {
logger.info("bean 定义查看和修改...");
String beanName = "myTestService";
// 先移除原来的bean定义
beanDefinitionRegistry.removeBeanDefinition(beanName);
// 注册我们自己的bean定义
BeanDefinitionBuilder beanDefinitionBuilder = BeanDefinitionBuilder.rootBeanDefinition(MyTestServiceIpml.class);
// 如果有构造函数参数, 有几个构造函数的参数就设置几个 没有就不用设置
beanDefinitionBuilder.addConstructorArgValue("构造参数1");
beanDefinitionBuilder.addConstructorArgValue("构造参数2");
beanDefinitionBuilder.addConstructorArgValue("构造参数3");
// 设置 init方法 没有就不用设置
beanDefinitionBuilder.setInitMethodName("init");
// 设置 destory方法 没有就不用设置
beanDefinitionBuilder.setDestroyMethodName("destory");
// 将Bean 的定义注册到Spring环境
beanDefinitionRegistry.registerBeanDefinition("myTestService", beanDefinitionBuilder.getBeanDefinition());
}
@Override
public void postProcessBeanFactory(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory configurableListableBeanFactory) throws BeansException {
// bean的名字为key, bean的实例为value
Map<String, Object> beanMap = configurableListableBeanFactory.getBeansWithAnnotation(RestController.class);
logger.info("所有 RestController 的bean {}", beanMap);
}
}写一个 业务类BusinessTestService测试一下,期望结果:所有用到 MyTestService的地方实际调用的变成了MyTestServiceIpml里面的方法。
package com.middol.mytest.config.beantest.register;
import com.middol.mytest.config.beantest.register.jar.MyTestService;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import javax.annotation.PostConstruct;
import javax.annotation.Resource;
/**
* @author guzt
*/
@Service
public class BusinessTestService {
@Resource
private MyTestService myTestService;
@PostConstruct
public void init() {
System.out.println(myTestService.getName1());
System.out.println(myTestService.getName2());
System.out.println(myTestService.getName3());
// 看看到底是哪一个Bean
myTestService.show();
}
}控制台打印如下:

可以发现,和我们期望的结果的一样:所有用到 MyTestService的地方实际调用的变成了MyTestServiceIpml里面的方法 !
到此,关于“springboot1.X和2.X中怎么解决Bean名字相同时覆盖”的学习就结束了,希望能够解决大家的疑惑。理论与实践的搭配能更好的帮助大家学习,快去试试吧!若想继续学习更多相关知识,请继续关注亿速云网站,小编会继续努力为大家带来更多实用的文章!
免责声明:本站发布的内容(图片、视频和文字)以原创、转载和分享为主,文章观点不代表本网站立场,如果涉及侵权请联系站长邮箱:is@yisu.com进行举报,并提供相关证据,一经查实,将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容。