这篇文章主要介绍“python中的Flask Web表单如何使用”,在日常操作中,相信很多人在python中的Flask Web表单如何使用问题上存在疑惑,小编查阅了各式资料,整理出简单好用的操作方法,希望对大家解答”python中的Flask Web表单如何使用”的疑惑有所帮助!接下来,请跟着小编一起来学习吧!
在创建模板login.html页面中直接写form表单。
login.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<form action="" method="post">
<input type="text" name="username" placeholder="Username">
<input type="password" name="password" placeholder="Password">
<input type="submit" value="提交">
</form>
{% if method == 'GET' %}
请求方式:{{method}}
{% elif method == 'POST' %}
请求方式:{{method}}
用户名:{{ username }}
密码:{{ password }}
{% endif %}
</body>
</html>接下来,在视图函数中获取表单数据
login.py
from flask import Flask, render_template, request
app = Flask(__name__)
# index 视图函数
@app.route('/login', methods=['GET', 'POST'])
def login():
context = dict()
if request.method == 'POST':
username = request.form['username']
password = request.form['password']
print(username, password)
context = {
'username': username,
'password': password,
}
context.update({'method': request.method})
else:
context.update({'method': request.method})
return render_template('login.html', **context)
@app.route('/')
def index():
return 'hello'
if __name__ == '__main__':
app.run(debug=True)
当我们点击提交之后,则会显示:

上面的实现方式是直接采用表单的提交方式。但是有个弊端,假如参数很多的情况下,后台也需要一一进行验证,每次都是先接收参数,再对参数进行校验的话,工作量就会非常的庞大,而且还会出现csrf攻击,这时我们就可以采用Flask-WTF来创建表单,从而避免上述弊端。
Flask-WTF的主要作用是对用户的请求数据进行验证。我们可以使用pip命令安装该依赖,
pip install flask-wtf
在flask web程序中,因为类FlaskForm由Flask-WTF拓展定义,所以可以从flask.wtf中导入FlaskForm。而字段和函数可以直接从WTForms包中导入,WTForms包中可以支持如下所示的HTML标准字段。
| 字段 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| StringField | 表示文本字段 |
| TextAreaField | 表示多行文本字段 |
| PasswordField | 表示密码文本字段 |
| HiddenField | 表示隐藏文本字段 |
| DateField | 表示日期的文本字段 |
| DateTimeFiled | 表示时间的文本字段 |
| IntegerFiled | 表示整数类型的文本字段 |
| DecimalField | 表示Decimal类型的文本字段 |
| FloatFiled | 表示Float类型的文本字段 |
| RadioFiled | 表示单选框字段 |
| SelectFiled | 表示下拉列表字段 |
WTForm也包含验证器,它对表单字段进行验证,非常方便。
| 字段 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| DataRequire | 检查输入的字段是否为空 |
| 检查字段是否符合邮件格式的约定 | |
| IPAddress | 在输入字段中验证IP地址 |
| Length | 验证输入字段中的字符串长度是否符合给定长度 |
| NumberRange | 验证给定范围内输入字段中的文字 |
| URL | 验证是否为合法的URL |
编写两个视图函数,以及一个form表单类,用于注册以及跳转index页面。
login.py
from flask import Flask, render_template, redirect, url_for, session
from flask_wtf import FlaskForm
from wtforms import StringField, PasswordField, SubmitField
from wtforms.validators import DataRequired, EqualTo
app = Flask(__name__)
app.config["SECRET_KEY"] = "xhosd6f982yfhowefy29f"
class RegisterForm(FlaskForm):
username = StringField(label="用户名", validators=[DataRequired('用户名不能为空')])
password = PasswordField(label="密码", validators=[DataRequired('密码不能为空')])
password_comfirm = PasswordField(label="确认密码", validators=[DataRequired('密码不能为空'), EqualTo('password', '两次密码不一致')])
submit = SubmitField(label='提交')
@app.route('/register', methods=['GET', 'POST'])
def register():
form = RegisterForm()
if form.validate_on_submit():
uname = form.username.data
pwd = form.password.data
pwd_com = form.password_comfirm.data
print(uname, pwd, pwd_com)
session['username'] = uname
return redirect(url_for('index'))
return render_template('register.html', form=form)
@app.route('/index')
def index():
username = session.get('username', '')
return 'hello %s' % username
if __name__ == '__main__':
app.run(debug=True)接下来编写一个html模板文件,用于用户注册使用。
register.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<form action="" method="post">
{{form.csrf_token}}
{{form.username.label}}
<p>{{ form.username }}</p>
{% for msg in form.username.errors %}
<p>{{ msg }}</p>
{% endfor %}
{{form.password.label}}
<p>{{ form.password }}</p>
{% for msg in form.password.errors %}
<p>{{ msg }}</p>
{% endfor %}
{{form.password_comfirm.label}}
<p>{{ form.password_comfirm }}</p>
{% for msg in form.password.errors %}
<p>{{ msg }}</p>
{% endfor %}
{{ form.submit }}
</form>
</body>
</html>在Flask框架中,方法flash()功能是实现消息闪现提示效果。Flask官方对闪现的解释是对用户的请求做出无刷新的响应。类似于Ajax的刷新效果。
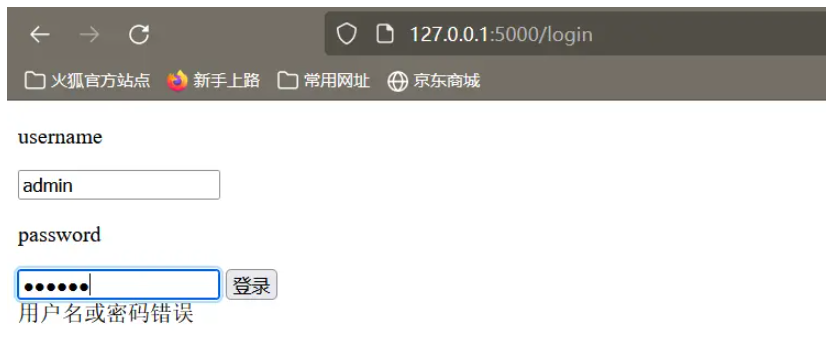
举一个简单的例子,当用户通过表单发送完请求之后,假如用户名或者是密码输入错误,那么服务器就会返回错误的提示信息,并在表单页面上显示。
具体代码,如下所示:
login.py
from flask import Flask, flash, redirect, render_template, request, url_for
app = Flask(__name__)
app.secret_key = 'random string'
@app.route('/')
def index():
return render_template('index.html')
@app.route('/login', methods=['GET', 'POST'])
def login():
error = None
if request.method == 'POST':
if request.form['username'] != 'admin' or request.form['password'] != 'admin':
flash("用户名或密码错误")
else:
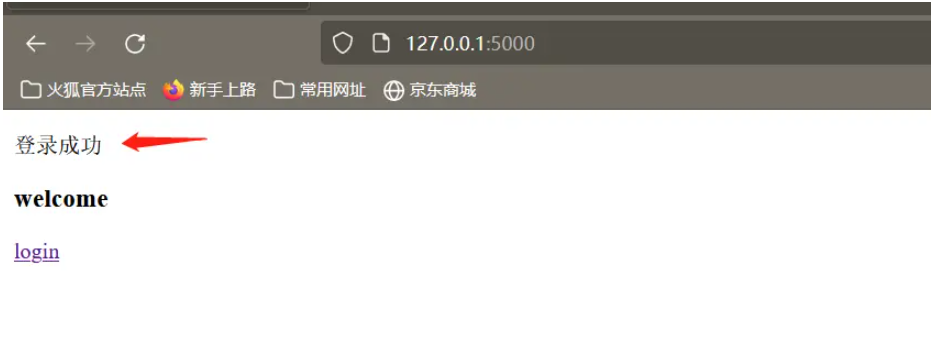
flash('登录成功')
return redirect(url_for('index'))
return render_template('login.html')
if __name__ == '__main__':
app.run(debug=True)login.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>登录</title>
</head>
<body>
<form action="" method="post">
<p>username</p>
<input type="text" name="username">
<p>password</p>
<input type="password" name="password">
<input type="submit" value="登录">
</form>
{% for message in get_flashed_messages() %}
{% if message %}
{{message}}
{% endif %}
{% endfor %}
</body>
</html>index.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
{% with messages = get_flashed_messages() %}
{% if messages %}
{% for message in messages %}
<p>{{ message }}</p>
{% endfor %}
{% endif %}
{% endwith %}
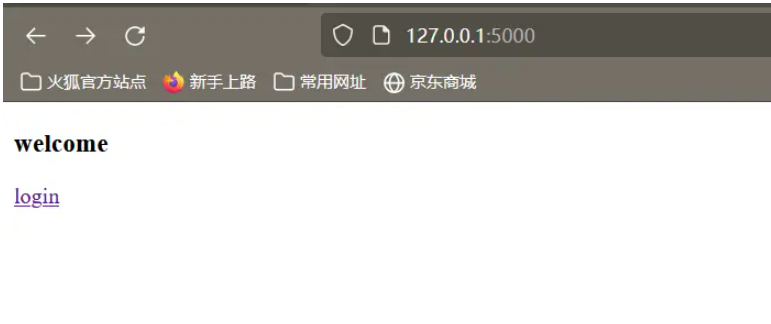
<h4>welcome</h4>
<a href="{{url_for('login')}}" rel="external nofollow" >login</a>
</body>
</html>上面的代码实现了URL的跳转,我们首先会进入首页,首页中包含了进入登录页面的链接。
在Flas Web程序中要实现文件的上传非常简单,与传递post和get非常的类似。基本流程如下:
(1)将在客户端上传的文件保存到flask.request.files对象。
(2)使用flask.request.files对象获取上传上来的文件名和文件对象
(3)调用文件对象中的方法save()将文件保存到指定的目录中。
简易的文件上传程序如下所示:
upload.py
from flask import Flask, flash, render_template, request
app = Flask(__name__)
@app.route('/upload', methods=['GET', 'POST'])
def upload():
if request.method == 'GET':
return render_template('upload.html')
else:
file = request.files['file']
if file:
file.save(file.name + '.png')
return '上传成功'
@app.route('/')
def index():
return render_template('index.html')
if __name__ == '__main__':
app.run(debug=True)index.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
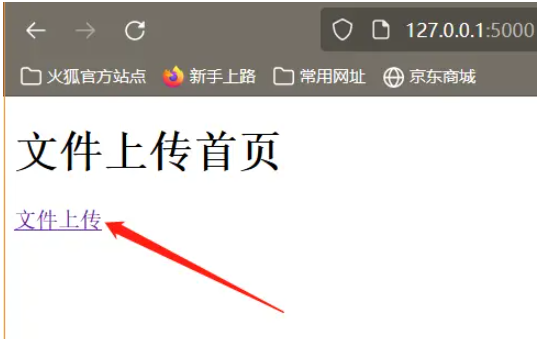
<h2>文件上传首页</h2>
<a href="{{url_for('upload')}}" rel="external nofollow" >文件上传</a>
</body>
</html>upload.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>文件上传</title>
</head>
<body>
<form action="" method="post" enctype="multipart/form-data">
<input type="file" name="file">
<input type="submit" value="点击我上传">
</form>
</body>
</html>本程序需要点击跳转之后才能进入文件上传页面,这样写的目的只是因为我比较懒,不想再浏览器中输入一大串的url。
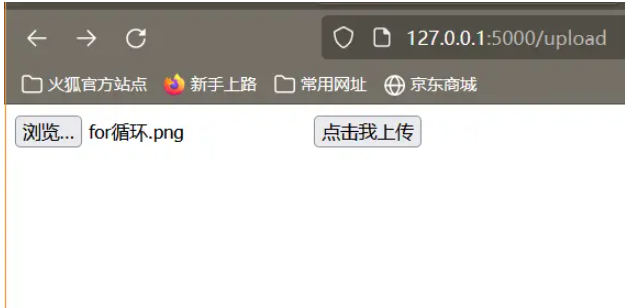
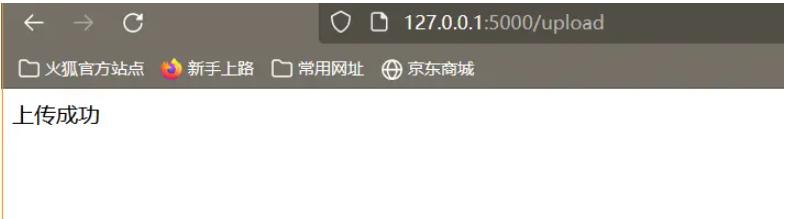
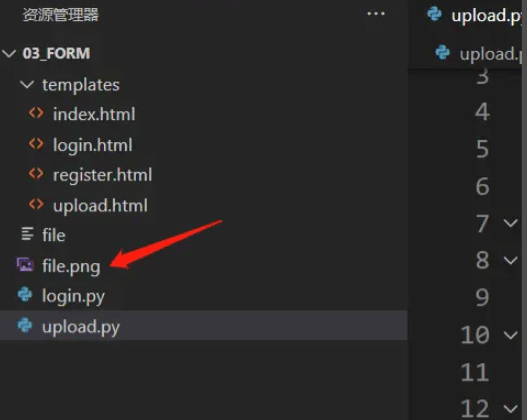
目前上述程序仅仅可以上传图片!
在Flask中上传文件的步骤非常简单,首先需要一个HTML表单,将enctype属性设置为"multipart/form-data"即可。URL处理程序会从request.file[]对象中提取文件,并将它保存到所需要的位置上。
每个上传的文件首先会保存到服务器上的临时位置,然后将其保存到最终的实际位置。建议使用secure_filename函数获取。
index.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<form action="/uploader" method="post" enctype="multipart/form-data">
<input type="file" name="file">
<input type="submit" value="提交">
</form>
</body>
</html>upload.py
from flask import Flask, render_template, request
from werkzeug.utils import secure_filename
import os
app = Flask(__name__)
app.config['UPLOAD_FLODER']= 'upload/' # 设置文件保存的路径
@app.route('/')
def upload_file():
return render_template('upload.html')
@app.route('/uploader', methods=['GET', 'POST'])
def uploader():
if request.method == 'POST':
f = request.files['file']
print(request.files)
f.save(os.path.join(app.config['UPLOAD_FLODER'], secure_filename(f.filename)))
return '上传成功'
else:
render_template('upload.html')
if __name__ == '__main__':
app.run(debug=True)到此,关于“python中的Flask Web表单如何使用”的学习就结束了,希望能够解决大家的疑惑。理论与实践的搭配能更好的帮助大家学习,快去试试吧!若想继续学习更多相关知识,请继续关注亿速云网站,小编会继续努力为大家带来更多实用的文章!
免责声明:本站发布的内容(图片、视频和文字)以原创、转载和分享为主,文章观点不代表本网站立场,如果涉及侵权请联系站长邮箱:is@yisu.com进行举报,并提供相关证据,一经查实,将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容。