本文小编为大家详细介绍“Netty4之怎么实现HTTP请求、响应”,内容详细,步骤清晰,细节处理妥当,希望这篇“Netty4之怎么实现HTTP请求、响应”文章能帮助大家解决疑惑,下面跟着小编的思路慢慢深入,一起来学习新知识吧。
请求(FullHttpRequest)
/**
* Combine the {@link HttpRequest} and {@link FullHttpMessage}, so the request is a <i>complete</i> HTTP
* request.
*/
public interface FullHttpRequest extends HttpRequest, FullHttpMessage {可以看到,它结合了HttpRequest、FullHttpMessag,作为一个完整的HTTP请求体。
默认实现为DefaultFullHttpRequest
响应(FullHttpResponse)
/**
* Combination of a {@link HttpResponse} and {@link FullHttpMessage}.
* So it represent a <i>complete</i> http response.
*/
public interface FullHttpResponse extends HttpResponse, FullHttpMessage {同样,它结合了HttpResponse、FullHttpMessage
默认实现为DefaultFullHttpResponse
*
作为服务端而言:
主要工作就是接收客户端请求,将客户端的请求内容解码;发送响应给客户端,并将发送内容编码
所以,服务端需要两个编解码器
* HttpRequestDecoder(将请求内容解码)
* HttpResponseEncoder(将响应内容编码)
作为客户端而言:
主要工作就是发送请求给服务端,并将发送内容编码;接收服务端响应,并将接收内容解码;
所以,客户端需要两个编解码器
* HttpResponseDecoder(将响应内容解码)
* HttpRequestEncoder(将请求内容编码)
创建Handler,命名为HttpHandler,具体内容如下:
import com.alibaba.fastjson.JSONObject;
import io.netty.buffer.ByteBuf;
import io.netty.buffer.Unpooled;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelFutureListener;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelHandlerContext;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter;
import io.netty.handler.codec.http.DefaultFullHttpResponse;
import io.netty.handler.codec.http.FullHttpRequest;
import io.netty.handler.codec.http.FullHttpResponse;
import io.netty.handler.codec.http.HttpHeaderNames;
import io.netty.handler.codec.http.HttpHeaders;
import io.netty.handler.codec.http.HttpMethod;
import io.netty.handler.codec.http.HttpResponseStatus;
import io.netty.handler.codec.http.HttpVersion;
import io.netty.util.CharsetUtil;
import lombok.Data;
/**
* 处理HTTP请求
* @author Administrator
*
*/
public class HttpHandler extends ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter {
@Override
public void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) throws Exception {
if(msg instanceof FullHttpRequest){
FullHttpRequest req = (FullHttpRequest)msg;
try {
// 1.获取URI
String uri = req.uri();
// 2.获取请求体
ByteBuf buf = req.content();
String content = buf.toString(CharsetUtil.UTF_8);
// 3.获取请求方法
HttpMethod method = req.method();
// 4.获取请求头
HttpHeaders headers = req.headers();
// 5.根据method,确定不同的逻辑
if(method.equals(HttpMethod.GET)){
// TODO
}
if(method.equals(HttpMethod.POST)){
// 接收用户输入,并将输入返回给用户
Content c = new Content();
c.setUri(uri);
c.setContent(content);
response(ctx, c);
}
if(method.equals(HttpMethod.PUT)){
// TODO
}
if(method.equals(HttpMethod.DELETE)){
// TODO
}
} finally {
req.release();
}
}
}
private void response(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Content c) {
// 1.设置响应
FullHttpResponse resp = new DefaultFullHttpResponse(HttpVersion.HTTP_1_1,
HttpResponseStatus.OK,
Unpooled.copiedBuffer(JSONObject.toJSONString(c), CharsetUtil.UTF_8));
resp.headers().set(HttpHeaderNames.CONTENT_TYPE, "text/html; charset=UTF-8");
// 2.发送
// 注意必须在使用完之后,close channel
ctx.writeAndFlush(resp).addListener(ChannelFutureListener.CLOSE);
}
}
@Data
class Content{
String uri;
String content;
}注意:
在处理过程中,把msg转换为FullHttpRequest,可以获取关于请求的所有内容;
在发送响应时必须要监听CLOSE
*
启动Server类使用客户端发送请求
在这里,笔者不单独编写Netty客户端代码,直接使用PostMan来充当客户端发送请求,具体如下:
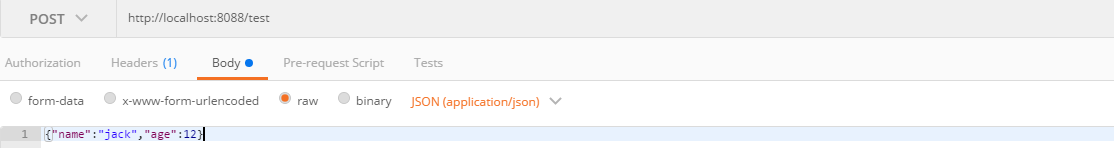
发送一个post请求,并填写body,点击send,可以看到响应如下所示:
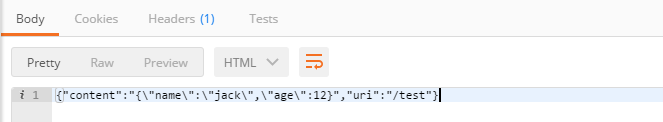
读到这里,这篇“Netty4之怎么实现HTTP请求、响应”文章已经介绍完毕,想要掌握这篇文章的知识点还需要大家自己动手实践使用过才能领会,如果想了解更多相关内容的文章,欢迎关注亿速云行业资讯频道。
亿速云「云服务器」,即开即用、新一代英特尔至强铂金CPU、三副本存储NVMe SSD云盘,价格低至29元/月。点击查看>>
免责声明:本站发布的内容(图片、视频和文字)以原创、转载和分享为主,文章观点不代表本网站立场,如果涉及侵权请联系站长邮箱:is@yisu.com进行举报,并提供相关证据,一经查实,将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容。
原文链接:https://kldwzz.blog.csdn.net/article/details/84236481