本篇内容介绍了“Spring Security怎么实现基于角色的访问控制框架”的有关知识,在实际案例的操作过程中,不少人都会遇到这样的困境,接下来就让小编带领大家学习一下如何处理这些情况吧!希望大家仔细阅读,能够学有所成!
Spring Security是一个功能强大且高度可定制的身份验证和访问控制框架。Spring Security是一个专注于为Java应用程序提供身份验证和授权的框架。与所有Spring项目一样,Spring安全性的真正威力在于它可以很容易地扩展以满足定制需求。
一般Web应用的需要进行认证和授权。
用户认证(Authentication):验证当前访问系统的是不是本系统的用户,并且要确认具体是哪个用户。
用户授权(Authorization):经过认证后判断当前用户是否有权限进行某个操作。在一个系统中,不同用户所具有的权限是不同的。
Spring Security 是 Spring家族中的一个安全管理框架。相比与另外一个安全框架Shiro,它提供了更丰富的功能,社区资源也比Shiro丰富。相对于Shiro,在SSH/SSM中整合Spring Security都是比较麻烦的操作,但有了Spring boot之后,Spring Boot 对于 Spring Security 提供了 自动化配置方案,可以零配置使用 Spring Security。因此,一般来说常见的安全管理技术栈组合是:
SSM+Shiro
Spring Boot /Spring Clound +Spring Security
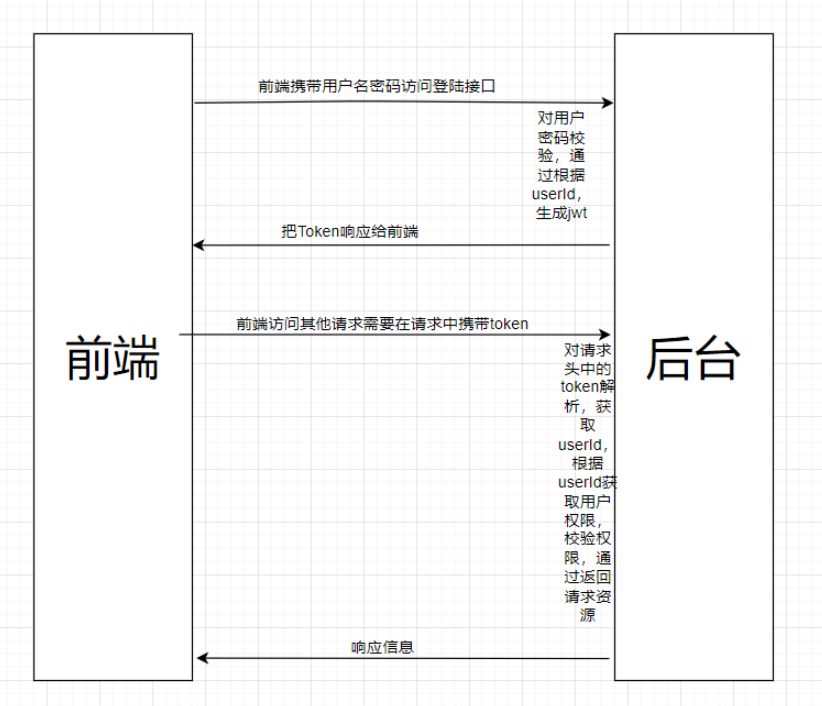
在SpringBoot项目中使用SpringSecurity只需要引入依赖即可。
<!-- spring security 安全认证 --> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-security</artifactId> </dependency>
在application.properties中添加属性:
server.port=8080 #spring.security.user.name=root #spring.security.user.password=123456 #mysql数据库连接 spring.datasource.driver-class-name=com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver spring.datasource.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/security?serverTimezone=GMT%2B8 spring.datasource.username=root spring.datasource.password=123456
但是在application.properties中添加属性意味着登录系统的用户名的密码都是固定的,不推荐。可以使用配置类,在配置类中设置,配置类的优先级更高。
@EnableGlobalMethodSecurity(prePostEnabled = true, securedEnabled = true)
public class SecurityConfig extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter
{
/**
* 自定义用户认证逻辑
*/
@Autowired
private UserDetailsService userDetailsService;
/**
* 认证失败处理类
*/
@Autowired
private AuthenticationEntryPointImpl unauthorizedHandler;
/**
* 退出处理类
*/
@Autowired
private LogoutSuccessHandlerImpl logoutSuccessHandler;
/**
* token认证过滤器
*/
@Autowired
private JwtAuthenticationTokenFilter authenticationTokenFilter;
/**
* 解决 无法直接注入 AuthenticationManager
*
* @return
* @throws Exception
*/
@Bean
@Override
public AuthenticationManager authenticationManagerBean() throws Exception
{
return super.authenticationManagerBean();
}
/**
* anyRequest | 匹配所有请求路径
* access | SpringEl表达式结果为true时可以访问
* anonymous | 匿名可以访问
* denyAll | 用户不能访问
* fullyAuthenticated | 用户完全认证可以访问(非remember-me下自动登录)
* hasAnyAuthority | 如果有参数,参数表示权限,则其中任何一个权限可以访问
* hasAnyRole | 如果有参数,参数表示角色,则其中任何一个角色可以访问
* hasAuthority | 如果有参数,参数表示权限,则其权限可以访问
* hasIpAddress | 如果有参数,参数表示IP地址,如果用户IP和参数匹配,则可以访问
* hasRole | 如果有参数,参数表示角色,则其角色可以访问
* permitAll | 用户可以任意访问
* rememberMe | 允许通过remember-me登录的用户访问
* authenticated | 用户登录后可访问
*/
@Override
protected void configure(HttpSecurity httpSecurity) throws Exception
{
httpSecurity
// CRSF禁用,因为不使用session
.csrf().disable()
// 认证失败处理类
.exceptionHandling().authenticationEntryPoint(unauthorizedHandler).and()
// 基于token,所以不需要session
.sessionManagement().sessionCreationPolicy(SessionCreationPolicy.STATELESS).and()
// 过滤请求
.authorizeRequests()
// 对于登录login 允许匿名访问
.antMatchers("/login").anonymous()
.antMatchers(
HttpMethod.GET,
"/*.html",
"/**/*.html",
"/**/*.css",
"/file/**",
"/**/*.js"
).permitAll()
// 除上面外的所有请求全部需要鉴权认证
.anyRequest().authenticated()
.and()
.headers().frameOptions().disable();
httpSecurity.logout().logoutUrl("/logout").logoutSuccessHandler(logoutSuccessHandler);
// 添加JWT filter
httpSecurity.addFilterBefore(authenticationTokenFilter, UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter.class);
}
/**
* 强散列哈希加密实现
*/
@Bean
public BCryptPasswordEncoder bCryptPasswordEncoder()
{
return new BCryptPasswordEncoder();
}
/**
* 身份认证接口
*/
@Override
protected void configure(AuthenticationManagerBuilder auth) throws Exception
{
auth.userDetailsService(userDetailsService).passwordEncoder(bCryptPasswordEncoder());
}
}@EnableGlobalMethodSecurity :当我们想要开启spring方法级安全时,只需要在任何 @Configuration实例上使用 @EnableGlobalMethodSecurity 注解就能达到此目的。
prePostEnabled = true 会解锁 @PreAuthorize 和 @PostAuthorize 两个注解。从名字就可以看出@PreAuthorize 注解会在方法执行前进行验证,而 @PostAuthorize 注解会在方法执行后进行验证。
/**
* 自定义权限实现,ss取自SpringSecurity首字母
*/
@Service("ss")
public class PermissionService
{
/** 所有权限标识 */
private static final String ALL_PERMISSION = "*:*:*";
/** 管理员角色权限标识 */
private static final String SUPER_ADMIN = "admin";
private static final String ROLE_DELIMETER = ",";
private static final String PERMISSION_DELIMETER = ",";
@Autowired
private TokenService tokenService;
/**
* 验证用户是否具备某权限
*
* @param permission 权限字符串
* @return 用户是否具备某权限
*/
public boolean hasPermi(String permission)
{
if (StringUtils.isEmpty(permission))
{
return false;
}
LoginUser loginUser = tokenService.getLoginUser(ServletUtils.getRequest());
if (StringUtils.isNull(loginUser) || CollectionUtils.isEmpty(loginUser.getPermissions()))
{
return false;
}
return hasPermissions(loginUser.getPermissions(), permission);
}
/**
* 验证用户是否不具备某权限,与 hasPermi逻辑相反
*
* @param permission 权限字符串
* @return 用户是否不具备某权限
*/
public boolean lacksPermi(String permission)
{
return hasPermi(permission) != true;
}
/**
* 验证用户是否具有以下任意一个权限
*
* @param permissions 以 PERMISSION_NAMES_DELIMETER 为分隔符的权限列表
* @return 用户是否具有以下任意一个权限
*/
public boolean hasAnyPermi(String permissions)
{
if (StringUtils.isEmpty(permissions))
{
return false;
}
LoginUser loginUser = tokenService.getLoginUser(ServletUtils.getRequest());
if (StringUtils.isNull(loginUser) || CollectionUtils.isEmpty(loginUser.getPermissions()))
{
return false;
}
Set<String> authorities = loginUser.getPermissions();
for (String permission : permissions.split(PERMISSION_DELIMETER))
{
if (permission != null && hasPermissions(authorities, permission))
{
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
/**
* 判断用户是否拥有某个角色
*
* @param role 角色字符串
* @return 用户是否具备某角色
*/
public boolean hasRole(String role)
{
if (StringUtils.isEmpty(role))
{
return false;
}
LoginUser loginUser = tokenService.getLoginUser(ServletUtils.getRequest());
if (StringUtils.isNull(loginUser) || CollectionUtils.isEmpty(loginUser.getUser().getRoles()))
{
return false;
}
for (SysRole sysRole : loginUser.getUser().getRoles())
{
String roleKey = sysRole.getRoleKey();
if (SUPER_ADMIN.contains(roleKey) || roleKey.contains(StringUtils.trim(role)))
{
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
/**
* 验证用户是否不具备某角色,与 isRole逻辑相反。
*
* @param role 角色名称
* @return 用户是否不具备某角色
*/
public boolean lacksRole(String role)
{
return hasRole(role) != true;
}
/**
* 验证用户是否具有以下任意一个角色
*
* @param roles 以 ROLE_NAMES_DELIMETER 为分隔符的角色列表
* @return 用户是否具有以下任意一个角色
*/
public boolean hasAnyRoles(String roles)
{
if (StringUtils.isEmpty(roles))
{
return false;
}
LoginUser loginUser = tokenService.getLoginUser(ServletUtils.getRequest());
if (StringUtils.isNull(loginUser) || CollectionUtils.isEmpty(loginUser.getUser().getRoles()))
{
return false;
}
for (String role : roles.split(ROLE_DELIMETER))
{
if (hasRole(role))
{
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
/**
* 判断是否包含权限
*
* @param permissions 权限列表
* @param permission 权限字符串
* @return 用户是否具备某权限
*/
private boolean hasPermissions(Set<String> permissions, String permission)
{
return permissions.contains(ALL_PERMISSION) || permissions.contains(StringUtils.trim(permission));
}
} /**
* 获取用户列表
*/
@PreAuthorize("@ss.hasPermi('system:user:list')")
@GetMapping("/list")
public TableDataInfo list(SysUser user)
{
startPage();
List<SysUser> list = userService.selectUserList(user);
return getDataTable(list);
}antMatchers():可传入多个String参数,用于匹配多个请求API。结合permitAll(),可同时对多个请求设置忽略认证。
and():用于表示上一项配置已经结束,下一项配置将开始。
创建一个Service文件用于Security查询用户信息:
@Service
public class UserDetailsServiceImpl implements UserDetailsService
{
private static final Logger log = LoggerFactory.getLogger(UserDetailsServiceImpl.class);
@Autowired
private ISysUserService userService;
@Autowired
private SysPermissionService permissionService;
@Override
public UserDetails loadUserByUsername(String username) throws UsernameNotFoundException
{
// 根据账户号查询用户信息
SysUser user = userService.selectUserByUserName(username);
if (StringUtils.isNull(user))
{
log.info("登录用户:{} 不存在.", username);
throw new UsernameNotFoundException("登录用户:" + username + " 不存在");
}
else if (UserStatus.DELETED.getCode().equals(user.getDelFlag()))
{
log.info("登录用户:{} 已被删除.", username);
throw new BaseException("对不起,您的账号:" + username + " 已被删除");
}
else if (UserStatus.DISABLE.getCode().equals(user.getStatus()))
{
log.info("登录用户:{} 已被停用.", username);
throw new BaseException("对不起,您的账号:" + username + " 已停用");
}
return createLoginUser(user);
}
public UserDetails createLoginUser(SysUser user)
{
// 获取用户权限
return new LoginUser(user, permissionService.getMenuPermission(user));
}
}当用户请求时,Security便会拦截请求,取出其中的username字段,从Service中查询该账户,并将信息填充到一个userDetails对象中返回。这样Security便拿到了填充后的userDetails对象,也就是获取到了包括权限在内的用户信息。
WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter.configure(HttpSecurity http)
Security的授权方式有两种:
WEB授权(基于请求URL),在configure(HttpSecurity httpSecurity)中设置。
方法授权(在方法上使用注解授权)
@Override
httpSecurity.authorizeRequests() // 对请求进行授权
.antMatchers("/test1").hasAuthority("p1") // 设置/test1接口需要p1权限
.antMatchers("/test2").hasAnyRole("admin", "manager") // 设置/test2接口需要admin或manager角色
.and()
.headers().frameOptions().disable();其中:
hasAuthority(“p1”)表示需要p1权限
hasAnyAuthority(“p1”, “p2”)表示p1或p2权限皆可
同理:
hasRole(“p1”)表示需要p1角色
hasAnyRole(“p1”, “p2”)表示p1或p2角色皆可
/**
* 获取用户列表
*/
@PreAuthorize("@ss.hasPermi('system:user:list')")
@GetMapping("/list")
public TableDataInfo list(SysUser user)
{
startPage();
List<SysUser> list = userService.selectUserList(user);
return getDataTable(list);
}校验是按照配置的顺序从上往下进行。若某个条件已匹配过,则后续同条件的匹配将不再被执行。也就是说,若多条规则是相互矛盾的,则只有第一条规则生效。典型地:
// 只有具有权限a的用户才能访问/get/resource
httpSecurity.authorizeRequests()
.antMatchers("/get/resource").hasAuthority("a")
.anyRequest().permitAll();
// 所有用户都能访问/get/resource
httpSecurity.authorizeRequests()
.anyRequest().permitAll()
.antMatchers("/get/resource").hasAuthority("a");但若是包含关系,则需要将细粒度的规则放在前面:
// /get/resource需要权限a,除此之外所有的/get/**都可以随意访问
httpSecurity.authorizeRequests()
.antMatchers("/get/resource").hasAuthority("a")
.antMatchers("/get/**").permitAll();httpSecurity.logoutUrl()和httpSecurity.addLogoutHandler()是冲突的,通常只用其中之一。对于使用token且服务端不进行存储的情况,不需要请求服务端进行登出,直接由前端将token丢弃即可。
httpSecurity.logout().logoutUrl(“/logout”).logoutSuccessHandler(logoutSuccessHandler);
/**
* 自定义退出处理类 返回成功
*/
@Configuration
public class LogoutSuccessHandlerImpl implements LogoutSuccessHandler
{
@Autowired
private TokenService tokenService;
/**
* 退出处理
*
* @return
*/
@Override
public void onLogoutSuccess(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Authentication authentication)
throws IOException, ServletException
{
LoginUser loginUser = tokenService.getLoginUser(request);
if (StringUtils.isNotNull(loginUser))
{
String userName = loginUser.getUsername();
// 删除用户缓存记录
tokenService.delLoginUser(loginUser.getToken());
}
ServletUtils.renderString(response, JSON.toJSONString(AjaxResult.error(HttpStatus.SUCCESS, "退出成功")));
}
}httpSecurity.cors() .and() .csrf().disable();
cors()允许跨域资源访问。
csrf().disable()禁用跨域安全验证。
/**
* 认证失败处理类 返回未授权
*/
@Component
public class AuthenticationEntryPointImpl implements AuthenticationEntryPoint, Serializable
{
private static final long serialVersionUID = -8970718410437077606L;
@Override
public void commence(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, AuthenticationException e)
throws IOException
{
int code = HttpStatus.UNAUTHORIZED;
String msg = StringUtils.format("请求访问:{},认证失败,无法访问系统资源", request.getRequestURI());
ServletUtils.renderString(response, JSON.toJSONString(AjaxResult.error(code, msg)));
}
}“Spring Security怎么实现基于角色的访问控制框架”的内容就介绍到这里了,感谢大家的阅读。如果想了解更多行业相关的知识可以关注亿速云网站,小编将为大家输出更多高质量的实用文章!
免责声明:本站发布的内容(图片、视频和文字)以原创、转载和分享为主,文章观点不代表本网站立场,如果涉及侵权请联系站长邮箱:is@yisu.com进行举报,并提供相关证据,一经查实,将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容。