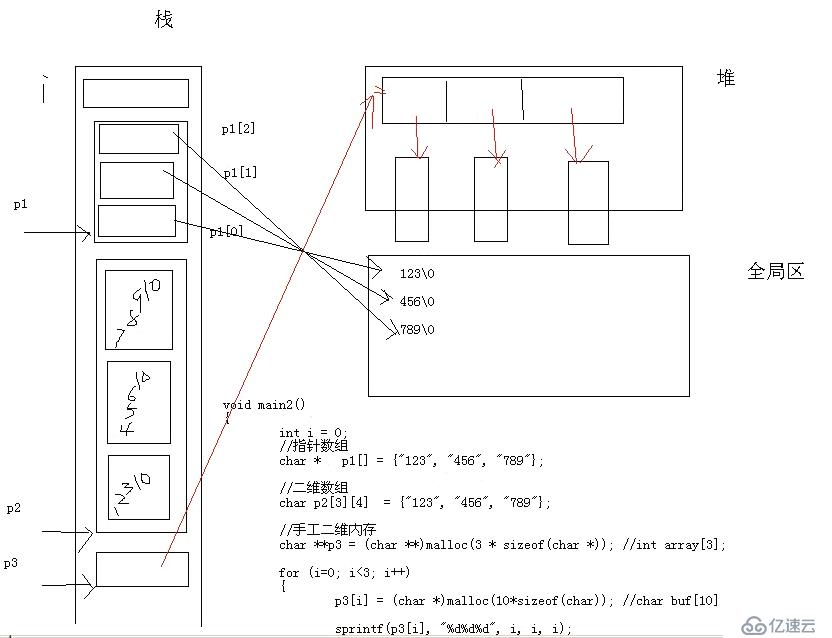
二维指针三种内存模型图:
统计字符串两头,非空字符的长度
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
int main()
{
//统计字符串两头,非空字符的长度
char *p = " abc ";
int i = 0;
int j = strlen(p) - 1;
int count = 0;
while (isspace(p[i]) && p[i] != '\0')
{
i++;
}
while (isspace(p[j]) && p[j] != '\0')
{
j--;
}
count = j + 1 - i;
printf("%d \n",count);
printf("Hello World!\n");
system("pause");
}
/*
编译运行:
3
Hello World!
请按任意键继续. . .
*///函数封装,统计字符串两头,非空字符的长度
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
//函数封装,统计字符串两头,非空字符的长度
int getstrlen(char *str,int *count)
{
if (str == NULL || count == NULL)
{
return -1;
}
char *p =str;
int i = 0;
int j = strlen(p) - 1;
while (isspace(p[i]) && p[i] != '\0')
{
i++;
}
while (isspace(p[j]) && p[j] != '\0')
{
j--;
}
*count = j + 1 - i;
}
int main()
{
int count = 0;
char *s = " hello ";
getstrlen(s,&count);
printf("%d \n", count);
system("pause");
}
/*
编译运行:
5
请按任意键继续. . .
*/【两头堵模型】
昨天的第一题作业--函数封装,去除一个字符串的首尾空格
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
//函数封装,去除一个字符串的首尾空格
int trimSpace(char *str,char *newstr)
{
if (str == NULL || newstr == NULL)
{
return -1;
}
char *p =str;
int i = 0;
int j = strlen(p) - 1;
while (isspace(p[i]) && p[i] != '\0')
{
i++;
}
while (isspace(p[j]) && p[j] != '\0')
{
j--;
}
int count = j + 1 - i;
strncpy(newstr, str+i,count);
newstr[count] = '\0';
return 0;
}
int main()
{
char newstr[100] ;
char *str = " hello ";
trimSpace(str,newstr);
printf("%s", newstr);
return 0;
}
/*
编译运行:
C:\Users\chunli>gcc main.c & a
hello
C:\Users\chunli>
*/再次优化,不需要另外使用新的数组
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
//函数封装,去除一个字符串的首尾空格
int trimSpace(char *str)
{
if (str == NULL )
{
return -1;
}
char *p =str;
int i = 0;
int j = strlen(p) - 1;
while (isspace(p[i]) && p[i] != '\0')
{
i++;
}
while (isspace(p[j]) && p[j] != '\0')
{
j--;
}
int count = j + 1 - i;
strncpy(str, str+i,count);//必须是地址
str[count] = '\0';
return 0;
}
int main()
{
char str[100] = " hello ";
trimSpace(str);//不能使用常量区的内存
printf("%s<--end", str);
return 0;
}
/*
编译运行:
C:\Users\chunli>gcc -o myfun main.c & myfun
hello<--end
C:\Users\chunli>
*/字符串翻转模型:
1,两头堵模型,字符串翻转:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
int main()
{
int ret = 0;
char s[100] = "hello world!";
char *p1 = s;
char *p2 = s+strlen(s)-1;
while(p1 < p2 )
{
*p1 = *p1 ^ *p2;
*p2 = *p1 ^ *p2;
*p1 = *p1 ^ *p2;
p1++;
p2--;
}
printf("%s<--end",s);
return ret;
}
/*
编译运行:
C:\Users\chunli>gcc -o myfun main.c & myfun
!dlrow olleh<--end
C:\Users\chunli>
*/2, 两头堵模型,字符串翻转,函数封装
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
int inverse(char *s)
{
if(s == NULL)
{
return -1;
}
char *p1 = s;
char *p2 = s+strlen(s)-1;
while(p1 < p2 )
{
*p1 = *p1 ^ *p2;
*p2 = *p1 ^ *p2;
*p1 = *p1 ^ *p2;
p1++;
p2--;
}
}
int main()
{
int ret = 0;
char s[100] = "hello world!";
inverse(s);
printf("%s<--end",s);
return ret;
}
/*
编译运行:
C:\Users\chunli>gcc -o myfun main.c & myfun
!dlrow olleh<--end
C:\Users\chunli>
*/3, 字符串翻转,递归---全局变量
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
char g_buf[1024]={0};
int inverse(char *s)
{
static char buf[200];
int i = 0;
if(s == NULL) return -1;
if(*s == '\0') return 0;
inverse(s+1);
strncat(g_buf,s,1);
}
int main()
{
int ret = 0;
char s[100] = "hello world!";
inverse(s);
printf("%s \n",g_buf);
return ret;
}
/*
编译运行:
C:\Users\chunli>gcc -o myfun main.c & myfun
!dlrow olleh
*/4, 字符串翻转,递归---非全局变量
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
int inverse(char *s,char *to)
{
static char buf[200];
int i = 0;
if(s == NULL || to == NULL) return -1;
if(*s == '\0') return 0;
inverse(s+1,to);
strncat(to,s,1);
}
int main()
{
char g_buf[1024]={0};
int ret = 0;
char s[100] = "hello world!";
inverse(s,g_buf);
printf("%s \n",g_buf);
return ret;
}
/*
编译运行:
C:\Users\chunli>gcc -o myfun main.c & myfun
!dlrow olleh
*/函数的集成:
昨天的第三题作业:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
int trimSpace(char *str,char *newstr)
{
if (str == NULL || newstr == NULL)
{
return -1;
}
char *p =str;
int i = 0;
int j = strlen(p) - 1;
while (isspace(p[i]) && p[i] != '\0')
{
i++;
}
while (isspace(p[j]) && p[j] != '\0')
{
j--;
}
int count = j + 1 - i;
strncpy(newstr, str+i,count);
newstr[count] = '\0';
return 0;
}
int get_Valude_By_Key(char *Key_And_Value,char *Key,char *Value)
{
if(Key_And_Value == NULL ||Key == NULL || Value == NULL )
{
printf("ERROR FUN get_Valude_By_Key:"
"Key_And_Value == NULL ||Key == NULL || Value == NULL");
return -1;
}
int ret = 0;
char *p = Key_And_Value;
p = strstr(p,Key);
if(p == NULL)
{
printf("FUN get_Valude_By_Key: strstr(p,Key) == NULL \n");
return -1;
}
p = p + strlen(Key);
p = strstr(p,"=");
if(p == NULL)
{
printf("FUN get_Valude_By_Key: strstr(p,\"=\") == NULL \n");
return -1;
}
p = p+ strlen("=");
ret = trimSpace(p,Value);
if(ret!=0)
{
printf("FUN get_Valude_By_Key: trimSpace(p,Value) != 0 \n");
return -2;
}
return 0;
}
int main()
{
int ret = 0;
char *Key_value = " id=666 = value=hahaha ";
char *key = "id=666";
char value[100]={0};
ret = get_Valude_By_Key(Key_value,key,value);
printf("[%s]\n",value);
return ret;
}
/*
编译运行:
C:\Users\chunli>gcc main.c & a
[value=hahaha]
*/C Const 指针 与变量:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
void fun1(const char *p)//指针所指向的内存空间不能修改
{
printf("%s",p); //指针所指向的内存空间可以读取
p = (char *)0x99;//指针的本身的值可以修改
// p[1] = 1;//指针所指向的内存空间不能修改
// *(p+1) = 1;//指针所指向的内存空间不能修改
}
void fun2(char *const p)//指针的本身的值不可以修改
{
// p = (char *)0x99;//指针的本身的值不可以修改
p[1] = 'A';//指针所指向的内存空间可以修改
*(p+1) = 'A';//指针所指向的内存空间可以修改
printf("%s",p);//指针所指向的内存空间可以读取
}
void fun3(const char *const p)//只能读这个指针
{
// p = (char *)0x99;//指针的本身的值不可以修改
// p[1] = 'A';//指针所指向的内存空间不可以修改
// *(p+1) = 'A';//指针所指向的内存空间不可以修改
printf("%s",p);//指针所指向的内存空间可以读取
}
int main()
{
char p[] = "Hello World!\n";//定义一个普通指针
fun1(p);
fun2(p);
fun3(p);
const int a = 10;
int const b = 11;
// a= 11; 编译不通过
// int *p2 = &a; //编译这个不通过
// int *p3 = &b; //编译这个不通过
return 0;
}
/*
编译运行:
C:\Users\chunli>gcc main.c & a
Hello World!
HAllo World!
HAllo World!
*/指针做输出模型,被调函数分配内存
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
int fun1(char **myp1,int *mylen1,char **myp2,int *mylen2)
{
char *tmp1 = NULL;
tmp1 = (char *)malloc(100);
if(tmp1 == NULL)
{
printf("ERROR in tmp = (char *)malloc(100); \n");
return -1;
}
strcpy(tmp1,"Hello ");
*mylen1 = strlen(tmp1);
*myp1 = tmp1;
char *tmp2 = NULL;
tmp2 = (char *)malloc(100);
if(tmp2 == NULL)
{
printf("ERROR in tmp2 = (char *)malloc(100); \n");
return -2;
}
strcpy(tmp2,"World !");
*mylen2 = strlen(tmp2);
*myp2 = tmp2;
return 0;
}
int my_free(char **p)
{
if(p == NULL)
{
printf("ERROR in my_free p == NULL \n");
return -1;
}
//方法1
/*
*p 是一级指针的地址
**p ,*(*p)就是取二级指针所指向的值
free(*p);//释放完指针变量所指向的内存空间
*p = NULL;//把实参改成NULL
*/
//方法2
char *tmp = NULL;
tmp = *p;
free(tmp);
tmp = NULL;
}
int main()
{
int ret = 0;
char *p1 = NULL;
char *p2 = NULL;
int len1 = 0;
int len2 = 0;
ret = fun1(&p1,&len1,&p2,&len2);
if(ret != 0)
{
printf("ERROR in fun1 :%d \n",ret);
return ret;
}
printf("[1]%s,%d\n",p1,len1);
printf("[2]%s,%d\n",p2,len2);
my_free(&p1);//p1所指向的内存释放了,但是p1没有改成NULL,有野指针现象
my_free(&p2);
return 0;
}
/*
编译运行:
C:\Users\chunli>gcc main.c & a
[1]Hello ,6
[2]World !,7
*///二级指针三种模型
// 第一种输入,内存模型
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
//二级指针三种模型
// 第一种输入,内存模型
//遍历二级指针
void print_arr(char **array,int num)
{
int i = 0 ;
for(i = 0;i<num;i++)
{
printf("%s\n",*(array + i ));
}
}
// 排序
void sort_arr(char **array,int num)
{
int i = 0;
int j = 0;
for(i = 0;i<num;i++)
{
for(j=i+1;j<num;j++)
{
if(strcmp(array[i],array[j]) < 0)
{
char *tmp = array[i]; // 交换指针
array[i] = array[j];
array[j] =tmp;
}
}
}
}
int main()
{
int i = 0;
int j = 0;
int num = 0;
char *array[] = {"aaaa","abaaa","ac"};//数组的每一个元素都是一个普通指针
num = sizeof(array)/sizeof(array[0]);
print_arr(array,num);
sort_arr(array,num);
printf("------------------------\n");
print_arr(array,num);
return 0;
}
/*
编译运行:
C:\Users\chunli>gcc main.c & a
aaaa
abaaa
ac
------------------------
ac
abaaa
aaaa
*///二级指针三种模型
//第2种内存模型,注意本次指针的步长是30个char
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
//二级指针三种模型
//第2种内存模型,注意本次指针的步长是30个char
int main()
{
char myBuf[30];
char array[10][30] = {"aa","ab","ac"};
int i = 0;
int j = 0;
int num =4;
for(i = 0;i<num;i++)
{
printf("%s\n",array[i]);
}
for(i= 0;i<num;i++)
{
for(j=i+1;j<num;j++)
{
if(strcmp(array[i],array[j]) < 0)
{
char tmp[30];
strcpy(tmp,array[i]); // 内存块交换
strcpy(array[i],array[j]);
strcpy(array[j],tmp);
}
}
}
for(i = 0;i<num;i++)
{
printf("%s\n",array[i]);
}
return 0;
}
/*
编译运行:
C:\Users\chunli>gcc main.c & a
aaaa
abaaa
ac
------------------------
ac
abaaa
aaaa
*/二级指针三种模型--第3种内存模型
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
//二级指针三种模型
//第3种内存模型,
int main()
{
char **p = NULL;
int num = 5;
int i = 0;
int j = 0;
//在堆中申请一片空间,能装num个char 类型的指针
p = malloc(sizeof(char *) * num);
//在这num个指针,每个都指向不同的内存块
for(i = 0;i<num;i++)
{
p[i] = malloc(sizeof(char) * 100);
sprintf(p[i],"%d,%d,%d",i,i+10,i*i);
}
//遍历
printf("-----------------------\n");
for(i = 0;i<num;i++)
{
printf("%s \n",p[i]);
}
//指针交换
for(i = 0;i<num;i++)
{
for(j=i+1;j<num;j++)
{
if(strcmp(p[i],p[j])<0)
{
char * tmp = p[i];
p[i] = p[j];
p[j] = tmp;
}
}
}
//遍历
printf("-----------------------\n");
for(i = 0;i<num;i++)
{
printf("%s \n",p[i]);
}
//内存数据交换
for(i = 0;i<num;i++)
{
for(j=i+1;j<num;j++)
{
if(strcmp(p[i],p[j])> 0)
{
char tmp[100] ;
strcpy(tmp,p[i]);
strcpy(p[i],p[j]);
strcpy(p[j],tmp);
}
}
}
//遍历
printf("-----------------------\n");
for(i = 0;i<num;i++)
{
printf("%s \n",p[i]);
}
for(i = 0;i<num;i++)
{
if(p[i] != NULL)
{
free(p[i]);
p[i] = NULL;
}
}
return 0;
}
/*
编译运行:
C:\Users\chunli>gcc main.c & a
-----------------------
0,10,0
1,11,1
2,12,4
3,13,9
4,14,16
-----------------------
4,14,16
3,13,9
2,12,4
1,11,1
0,10,0
-----------------------
0,10,0
1,11,1
2,12,4
3,13,9
*///二级指针三种模型
//二维指针输入 输出
//第3种内存模型,堆中开辟,我们自己定义的数组,不需要编译在栈中为我们那样开辟
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
//二级指针三种模型
//二维指针输入 输出
//第3种内存模型,堆中开辟,我们自己定义的数组,不需要编译在栈中为我们那样开辟
char **getmem(num)
{
int i =0;
char **p = NULL;
//在堆中申请一片空间,能装num个char* 类型的指针
p = (char **)malloc(sizeof(char *) * num);
if(p == NULL)
{
return NULL;
}
//在这num个指针,每个都指向不同的内存块
for(i = 0;i<num;i++)
{
p[i] = malloc(sizeof(char) * 100);
sprintf(p[i],"%d,%d,%d",i,i+10,i*i);
}
return p;
}
void print_arr(char **p,int num)
{
int i = 0;
for(i = 0;i<num;i++)
{
printf("%s \n",p[i]);
}
}
void sort_arr1(char **p,int num)
{
int i = 0;
int j = 0;
//指针交换
for(i = 0;i<num;i++)
{
for(j=i+1;j<num;j++)
{
if(strcmp(p[i],p[j])<0)
{
char * tmp = p[i];
p[i] = p[j];
p[j] = tmp;
}
}
}
}
void sort_arr2(char **p,int num)
{
int i = 0;
int j = 0;
//内存数据交换
for(i = 0;i<num;i++)
{
for(j=i+1;j<num;j++)
{
if(strcmp(p[i],p[j])> 0)
{
char tmp[100] ;
strcpy(tmp,p[i]);
strcpy(p[i],p[j]);
strcpy(p[j],tmp);
}
}
}
}
void free_arr(char **p,int num)
{
int i =0;
for(i = 0;i<num;i++)
{
if(p[i] != NULL)
{
free(p[i]);
p[i] = NULL;
}
}
}
int main()
{
char **p = NULL;
int num = 5;
int i = 0;
int j = 0;
p = getmem(num);
printf("--------\n");
print_arr(p,num);
sort_arr1(p,num);
printf("--------\n");
print_arr(p,num);
sort_arr2(p,num);
printf("--------\n");
print_arr(p,num);
free_arr(p,num);
if(p != NULL)
{
free(p);
p = NULL;
}
return 0;
}
/*
编译运行:
C:\Users\chunli>gcc main.c & a
--------
0,10,0
1,11,1
2,12,4
3,13,9
4,14,16
--------
4,14,16
3,13,9
2,12,4
1,11,1
0,10,0
--------
0,10,0
1,11,1
2,12,4
3,13,9
4,14,16
*///玩转多级指针
//玩转多级指针
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
//玩转多级指针
int getmem(char ***p,int num)
{
int i =0;
if(p == NULL)//里面应该是实参的取地址
{
return -1;
}
char **tmp = (char **)malloc(sizeof(char *) * num);
if(tmp == NULL)
{
return -1;
}
for(i = 0;i<num;i++)
{
tmp[i] = malloc(sizeof(char) * 100);
sprintf(tmp[i],"%d -> %d -> %d",i,i+10,i*i);
}
*p = tmp;
}
int freemem(char ***p,int num)
{
if(p == NULL )
{
return -1;
}
char **tmp = NULL;
tmp = *p;
int i;
for(i = 0;i<num;i++)
{
if(tmp[i] != NULL)
{
free(tmp[i]);
tmp[i] = NULL;
}
}
free(tmp);
*p = NULL;
}
int print_arr(char ***p,int num)
{
if(p == NULL)
{
printf("2 Hello \n");
return -1;
}
int i;
for(i =0;i<num;i++)
{
printf("%s \n",*(*(p)+i));
}
}
int main()
{
char **p = NULL;
int num = 5;
getmem(&p,num);
print_arr(&p,num);
freemem(&p,num);
return 0;
}
/*
编译运行:
C:\Users\chunli>gcc main.c & a
0 -> 10 -> 0
1 -> 11 -> 1
2 -> 12 -> 4
3 -> 13 -> 9
4 -> 14 -> 16
*/作业题:


免责声明:本站发布的内容(图片、视频和文字)以原创、转载和分享为主,文章观点不代表本网站立场,如果涉及侵权请联系站长邮箱:is@yisu.com进行举报,并提供相关证据,一经查实,将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容。